|
Spotfin Chub
Spotfin chub (''Erimonax monachus'') is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Leuciscidae, the shiners, daces and minnows. It is the only species in the monospecific genus ''Erimonax''. This fish is endemic to the Tennessee River watershed. Its other common names include turquoise shiner and chromium shiner. Appearance and anatomy Spotfin chub have an average length of . Geographic distribution The spotfin chub has a native range endemic to the Tennessee River drainage. This range includes five states: Alabama, Georgia, North Carolina, Virginia, and Tennessee. Current surveys show that spotfin chub has been extirpated from Alabama and Georgia.Yoichiro Kanno, Christina U. Schmidt, Steven B. Cook, Hayden T. Mattingly. 2012. Variation in microhabitat use of the threatened spotfin chub (''Erimonax monachus'') among stream sites and seasons. ''Ecology of Freshwater Fish'' 21: 363–374, The only remaining populations are confined to four tributaries along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Drinker Cope
Edward Drinker Cope (July 28, 1840 – April 12, 1897) was an American zoologist, paleontology, paleontologist, comparative anatomy, comparative anatomist, herpetology, herpetologist, and ichthyology, ichthyologist. Born to a wealthy Quaker family, he distinguished himself as a child prodigy interested in science, publishing his first scientific paper at the age of 19. Though his father tried to raise Cope as a gentleman farmer, he eventually acquiesced to his son's scientific aspirations. Cope had little formal scientific training, and he eschewed a teaching position for field work. He made regular trips to the Western United States, American West, prospecting in the 1870s and 1880s, often as a member of United States Geological Survey, U.S. Geological Survey teams. A personal feud between Cope and paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh led to a period of intense fossil-finding competition now known as the Bone Wars. Cope's financial fortunes soured after failed mining ventures i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasive Species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native species that become harmful to their native environment after human alterations to its food web. Since the 20th century, invasive species have become serious economic, social, and environmental threats worldwide. Invasion of long-established ecosystems by organisms is a natural phenomenon, but human-facilitated introductions have greatly increased the rate, scale, and geographic range of invasion. For millennia, humans have served as both accidental and deliberate dispersal agents, beginning with their earliest migrations, accelerating in the Age of Discovery, and accelerating again with the spread of international trade. Notable invasive plant species include the kudzu vine, giant hogweed (''Heracleum mantegazzianum''), Japanese knotw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
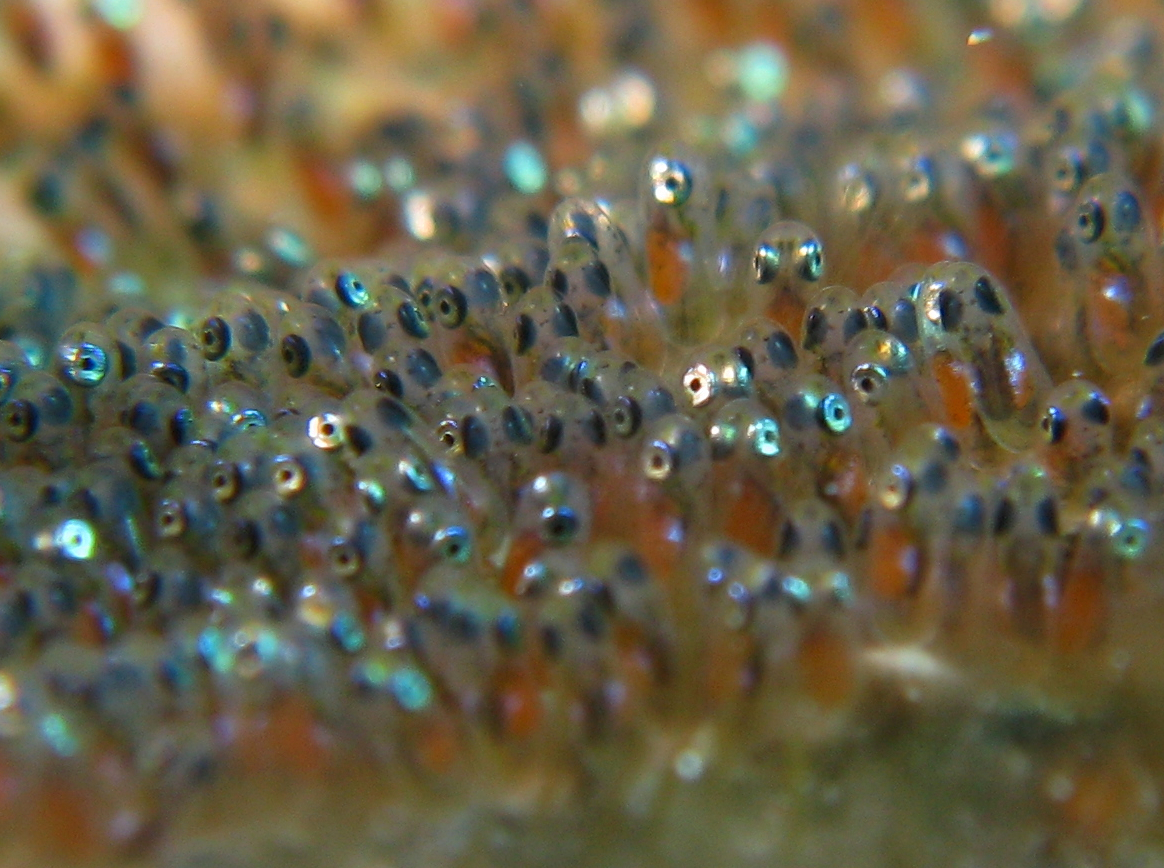
Spawn (biology)
Spawn is the eggs and sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of freely releasing eggs and sperm into a body of water (fresh or marine); the physical act is known as spawning. The vast majority of aquatic and amphibious animals reproduce through spawning. These include the following groups: * Bony fishes * Crustaceans (such as crabs, shrimps, etc.) *Mollusks (such as oysters, octopus, squid) *Echinoderms (such as sea urchins, sea stars, sea cucumbers, etc.) * Amphibians (such as frogs, toads, salamanders, newts) * Aquatic insects (such as dragonflies, mayflies, mosquitoes) *Coral, which are living colonies of tiny, aquatic organisms—not plants, as they are sometimes perceived to be. Corals, while appearing sedentary or botanical by nature, actually spawn by releasing clouds of sperm and egg cells into the water column, where the two mix. As a general rule, aquatic or semiaquatic reptiles, birds, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
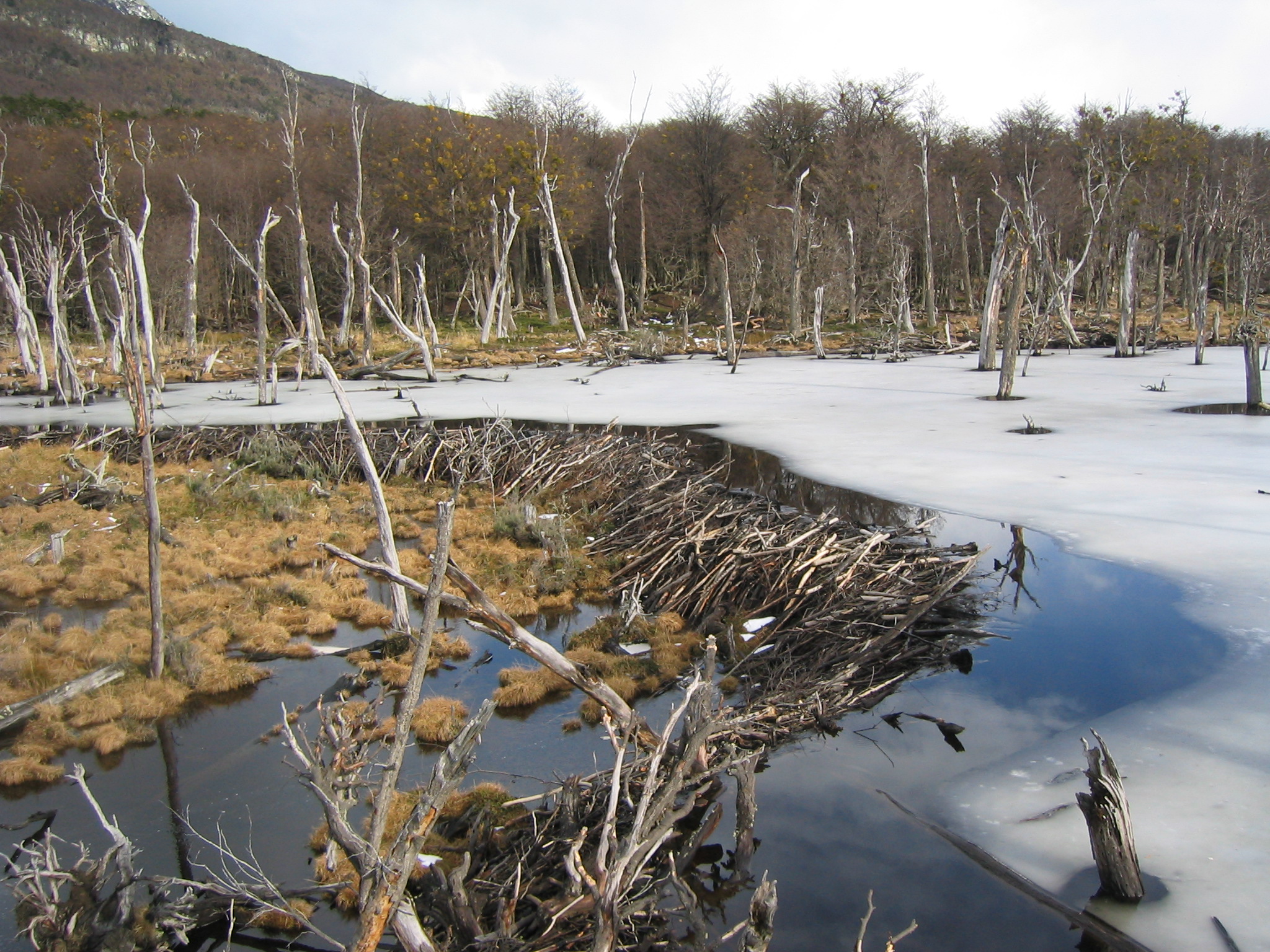
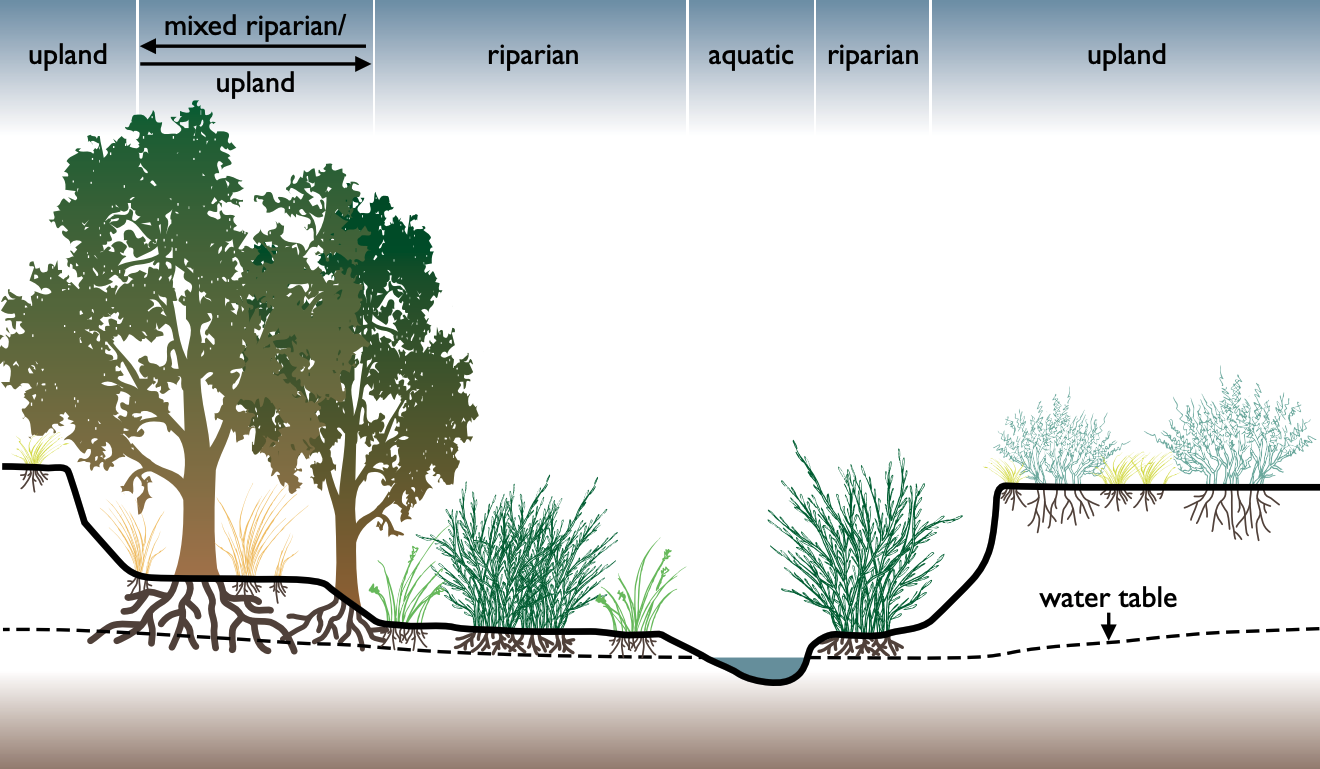
Riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin '' ripa'', meaning " river bank". Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on terrestrial and semiaquatic fauna as well as aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, and even non-vegetative areas. Riparian zones may be natural or engineered for soil stabilization or restoration. These zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warpaint Shiner
The warpaint shiner (''Coccotis coccogenis'') is a species of freshwater fish found in North America. It is common in the upper Tennessee River basin as well as in the Savannah River, the Santee River, and the New River in North Carolina. Adults have a mean length of and can reach a maximum length of . The maximum age reported for this species is 4 years. Warpaint shiners live in cool streams with gravel and rubble beds. They feed on aquatic insect larvae and on terrestrial insects they catch on the water surface. The warpaint shiner provides forage for sport fish such as small and large mouth bass. Importantly the warpaint shiner acts as host to the federally endangered freshwater mussels known as heelsplitters. Range and breeding Warpaint shiners were originally found only in the Tennessee River drainage. Due to human activity, the species has been introduced into the Upper Savannah, the Santee, and the New River drainages.Jenkins, R., N. Burkhead (1993) ''Freshwater Fishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxilus
''Luxilus'' is a genus of freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Leuciscidae, the shiners, daces and minnows. The species in this genus are found in North America. They are commonly known as highscale shiners. Species ''Luxilus'' contains the following valid species: * '' Luxilus albeolus'' ( D. S. Jordan, 1889) (white shiner) * '' Luxilus cardinalis'' ( Mayden, 1988) (cardinal shiner) * '' Luxilus cerasinus'' (Cope, 1868) (crescent shiner) * '' Luxilus chrysocephalus'' Rafinesque Constantine Samuel Rafinesque-Schmaltz (; 22 October 178318 September 1840) was a French early 19th-century polymath born near Constantinople in the Ottoman Empire and self-educated in France. He traveled as a young man in the United States, ult ..., 1820 (striped shiner) * '' Luxilus cornutus'' ( Mitchill, 1817) (common shiner) * '' Luxilus pilsbryi'' ( Fowler, 1904) (duskystripe shiner) * '' Luxilus zonatus'' ( Putnam, 1863) (bleeding shiner) References * Pogonichthyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitetail Shiners The whitetail shiner (''Cyprinella galactura'') is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish in the family Leuciscidae, the shiners, daces and minnows. It inhabits the Tennessee and Cumberland river drainages of Alabama, Mississippi, Georgia, North Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, and Kentucky, Atlantic slope headwaters (upper Savannah and Santee river systems, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia), the upper New River drainage in West Virginia and Virginia, and the Ozark Plateau and Ouachita Mountains portions of the White and St. Francis river systems in Missouri and Arkansas. References *http://www.bio.utk.edu/hulseylab/Fishlist.html External links *FishBase FishBase is a global species database of fish species (specifically finfish). It is the largest and most extensively accessed online database on adult finfish on the web. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprinella
''Cyprinella'' is a genus of freshwater ray-finned fish in the family Leuciscidae, the shiners, daces and minnows. They are known as the satinfin shiners. They are native to North America, and some are among the most common freshwater fish species on the eastern side of the continent.Broughton, R. E. and J. R. Gold. (2000)Phylogenetic relationships in the North American cyprinid genus ''Cyprinella'' (Actinopterygii: Cyprinidae) based on sequences of the mitochondrial ND2 and ND4L genes.''Copeia'' 2000(1) 1-10. Conversely, several ''Cyprinella'' species with small distributions are threatened and the Maravillas Creek subspecies of the red shiner (''Cyprinella lutrensis blairi'') is extinct. The largest species reach around in total length. Breeding males often develop bright coloration. Fish of the genus produce audible sounds during courtship and conflict.Phillips, C. T. and C. E. Johnston. (2008)Geographical divergence of acoustic signals in ''Cyprinella galactura'', the wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (biology)
In biology, a substrate is the surface on which an organism (such as a plant, fungus, or animal) lives. A substrate can include biotic or abiotic materials and animals. For example, encrusting algae that lives on a rock (its substrate) can be itself a substrate for an animal that lives on top of the algae. Inert substrates are used as growing support materials in the hydroponic cultivation of plants. In biology substrates are often activated by the nanoscopic process of substrate presentation. In agriculture and horticulture * Cellulose substrate * Expanded clay aggregate (LECA) * Rock wool * Potting soil * Soil In animal biotechnology Requirements for animal cell and tissue culture Requirements for animal cell and tissue culture are the same as described for plant cell, tissue and organ culture (In Vitro Culture Techniques: The Biotechnological Principles). Desirable requirements are (i) air conditioning of a room, (ii) hot room with temperature recorder, (iii) microsc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurythermal
A eurytherm is an organism, often an endotherm, that can function at a wide range of ambient temperatures. To be considered a eurytherm, all stages of an organism's life cycle must be considered, including juvenile and larval stages. These wide ranges of tolerable temperatures are directly derived from the tolerance of a given eurythermal organism's proteins. Extreme examples of eurytherms include Tardigrades (''Tardigrada''), the desert pupfish ( ''Cyprinodon macularis''), and green crabs (''Carcinus maenas''), however, nearly all mammals, including humans, are considered eurytherms. Eurythermy can be an evolutionary advantage: adaptations to cold temperatures, called cold-eurythemy, are seen as essential for the survival of species during ice ages. In addition, the ability to survive in a wide range of temperatures increases a species' ability to inhabit other areas, an advantage for natural selection. Eurythermy is an aspect of thermoregulation in organisms. It is in contras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
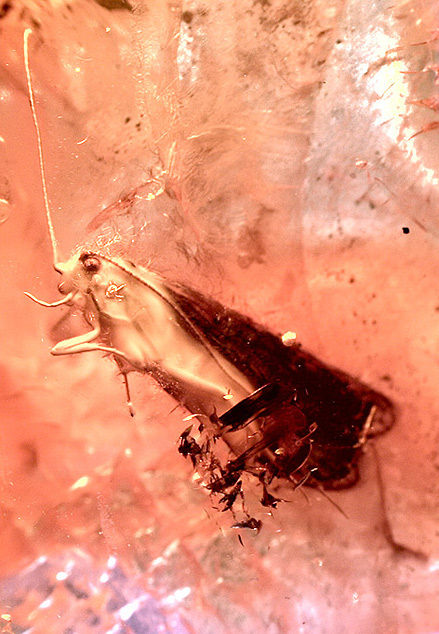
Caddisfly
The caddisflies (order Trichoptera) are a group of insects with aquatic larvae and terrestrial adults. There are approximately 14,500 described species, most of which can be divided into the suborders Integripalpia and Annulipalpia on the basis of the adult mouthparts. Integripalpian larvae construct a portable casing to protect themselves as they move around looking for food, while annulipalpian larvae make themselves a fixed retreat in which they remain, waiting for food to come to them. The affinities of the small third suborder Spicipalpia are unclear, and Molecular phylogenetics, molecular analysis suggests it may not be monophyletic. Also called sedge-flies or rail-flies, the adults are small moth-like insects with two pairs of hairy membranous insect wing, wings. They are closely related to the Lepidoptera (moths and butterflies) which have scales on their wings; the two orders together form the superorder Amphiesmenoptera. The aquatic larvae are found in a wide variety o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Fly
A black fly or blackfly (sometimes called a buffalo gnat, turkey gnat, or white socks) is any member of the family Simuliidae of the Culicomorpha infraorder. It is related to the Ceratopogonidae, Chironomidae, and Thaumaleidae. Over 2,200 species of black flies have been formally named, of which 15 are extinct. They are divided into two subfamilies: Parasimuliinae contains only one genus and four species; Simuliinae contains all the rest. Over 1,800 of the species belong to the genus '' Simulium''. Most black flies gain nourishment by feeding on the blood of mammals, including humans, although the males feed mainly on nectar. They are usually small, black or gray, with short legs and antennae. They are a common nuisance for humans, and many U.S. states have programs to suppress the black fly population. They spread several diseases, including river blindness in Africa (''Simulium damnosum'' and ''S. neavei'') and the Americas (''S. callidum'' and ''S. metallicum'' in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |