|
SPIRES
The Stanford Physics Information Retrieval System (SPIRES) is a database management system developed by Stanford University. It is used by universities, colleges and research institutions. The first website in North America was created to allow remote users access to its database. History SPIRES was originally developed at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC) in 1969, from a design based on a 1967 information study of physicists at SLAC. The system was designed as a physics database management system (DBMS) to deal with high-energy-physics preprints. Written in PL/I, SPIRES ran on an IBM System/360. In the early 1970s, an evaluation of this system resulted in the decision to implement a new system for use by faculty, staff and students at Stanford University. SPIRES was renamed the Stanford Public Information Retrieval System. The new development took place under a National Science Foundation grant headed by Edwin B. Parker, principal investigator. SPIRES joined force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INSPIRE-HEP
INSPIRE-HEP is an open access digital library for the field of high energy physics (HEP). It is the successor of the Stanford Physics Information Retrieval System (SPIRES) database, the main literature database for high energy physics since the 1970s. History SPIRES was (in addition to the CERN Document Server (CDS), arXiv and parts of Astrophysics Data System) one of the main Particle Information Resources. A survey conducted in 2007 found that SPIRES database users wanted the portal to provide more services than the, at that time, already 30-year-old system could provide. On the second annual Summit of Information Specialists in Particle Physics and Astrophysics in May 2008, the physics laboratories CERN, DESY, SLAC and Fermilab therefore announced that they would work together to create a new Scientific Information System for high energy physics called INSPIRE. It interacts with other HEP service providers like arXiv.org, Particle Data Group, NASA The National A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invenio
Invenio is a software framework for large-scale digital repositories that provides the tools for managing digital assets in an institutional repository and research data management systems. The software is typically used for open access repositories for scholarly and/or published digital content and as a digital library. It is free and open source software released under an MIT License. Invenio is initially developed by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) with both individual and organisational external contributors and is freely available for download. History Before 1 July 2006, the package was named CDSware, then renamed CDS Invenio, and now known simply as Invenio. Standards Invenio complies with standards such as the Open Archives Initiative metadata harvesting protocol ( OAI-PMH) and uses JSON/JSONSchema as its underlying bibliographic format. Support The service provider TIND Technologies, an official CERN spin-off based in Norway, offers Invenio vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PL360
PL360 (or PL/360) is a system programming language designed by Niklaus Wirth and written by Wirth, Joseph W. Wells Jr., and Edwin Satterthwaite Jr. for the IBM System/360 computer at Stanford University. A description of PL360 was published in early 1968, although the implementation was probably completed before Wirth left Stanford in 1967. Description PL/360 is a one-pass compiler with a syntax similar to ALGOL that provides facilities for specifying exact machine code (language) instructions and registers similar to assembly language, but also provides features commonly found in high-level programming languages, such as complex arithmetic expressions and control structures. Wirth used PL360 to create ALGOL W. Data types are: * Byte or character – 1 byte * Short integer – 2 bytes, interpreted as an integer in two's complement binary notation * Integer or logical – 4 bytes, interpreted as an integer in two's complement binary notation * Real – 4 bytes, interpreted as a base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michigan Terminal System
The Michigan Terminal System (MTS) is one of the first time-sharing computer operating systems.. Created in 1967 at the University of Michigan for use on IBM System/360, IBM S/360-67, S/370 and compatible mainframe computers, it was developed and used by a consortium of eight universities in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom over a period of 33 years (1967 to 1999).. Overview The University of Michigan Multiprogramming Supervisor (UMMPS) was initially developed by the staff of the academic computing center at the University of Michigan for operation of the System/360, IBM S/360-67, S/370 and compatible computers. The software may be described as a multiprogramming, multiprocessing, virtual memory, time-sharing supervisor that runs multiple resident, reentrant (subroutine), reentrant programs. Among these programs is the Michigan Terminal System (MTS) for command interpretation, execution control, file management, and accounting. End-users interact with the computin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford Physics Information Retrieval System Logo
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth List of governors of California, governor of and then-incumbent List of United States senators from California, United States senator representing California) and his wife, Jane Stanford, Jane, in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., Leland Jr. The university admitted its first students in 1891, opening as a Mixed-sex education, coeducational and non-denominational institution. It struggled financially after Leland died in 1893 and again after much of the campus was damaged by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Following World War II, university Provost (education), provost Frederick Terman inspired an entrepreneurship, entrepreneurial culture to build a self-sufficient local industry (later Silicon Valley). In 1951, Stanfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For High Energy Physics
An institute is an organizational body created for a certain purpose. They are often research organisations (research institutes) created to do research on specific topics, or can also be a professional body. In some countries, institutes can be part of a university or other institutions of higher education, either as a group of departments or an autonomous educational institution without a traditional university status such as a "university institute", or institute of technology. In some countries, such as South Korea and India, private schools are sometimes referred to as institutes; also, in Spain, secondary schools are referred to as institutes. Historically, in some countries, institutes were educational units imparting vocational training and often incorporating libraries, also known as mechanics' institutes. The word "institute" comes from the Latin word ''institutum'' ("facility" or "habit"), in turn derived from ''instituere'' ("build", "create", "raise" or "educat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ArXiv
arXiv (pronounced as "archive"—the X represents the Chi (letter), Greek letter chi ⟨χ⟩) is an open-access repository of electronic preprints and postprints (known as e-prints) approved for posting after moderation, but not Scholarly peer review, peer reviewed. It consists of scientific papers in the fields of mathematics, physics, astronomy, electrical engineering, computer science, quantitative biology, statistics, mathematical finance, and economics, which can be accessed online. In many fields of mathematics and physics, almost all scientific papers are self-archiving, self-archived on the arXiv repository before publication in a peer-reviewed journal. Some publishers also grant permission for authors to archive the peer-reviewed postprint. Begun on August 14, 1991, arXiv.org passed the half-million-article milestone on October 3, 2008, had hit a million by the end of 2014 and two million by the end of 2021. As of November 2024, the submission rate is about 24,000 arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
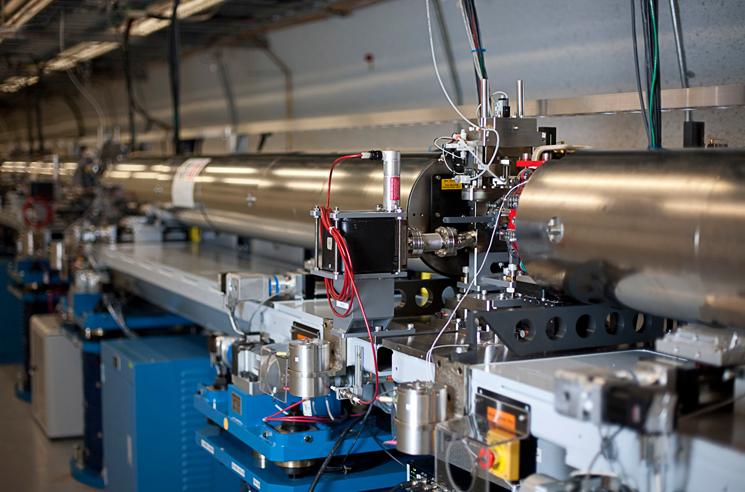
SLAC
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, originally named the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, is a federally funded research and development center in Menlo Park, California, United States. Founded in 1962, the laboratory is now sponsored by the United States Department of Energy and administrated by Stanford University. It is the site of the Stanford Linear Accelerator, a 3.2 kilometer (2-mile) linear accelerator constructed in 1966 that could accelerate electrons to energies of 50 GeV. Today SLAC research centers on a broad program in atomic and solid-state physics, chemistry, biology, and medicine using X-rays from synchrotron radiation and a free-electron laser as well as experimental and theoretical research in elementary particle physics, accelerator physics, astroparticle physics, and cosmology. The laboratory is under the programmatic direction of the United States Department of Energy Office of Science. History Founded in 1962 as the Stanford Linear Accelera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in Meyrin, western suburb of Geneva, on the France–Switzerland border. It comprises #Member states and budget, 24 member states. Israel, admitted in 2013, is the only full member geographically out of Europe. CERN is an official United Nations General Assembly observers#Intergovernmental organizations, United Nations General Assembly observer. The acronym CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory; in 2023, it had 2,666 scientific, technical, and administrative staff members, and hosted about 12,370 users from institutions in more than 80 countries. In 2016, CERN generated 49 Byte#Multiple-byte units, petabytes of data. CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research – consequently, numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Databases And Search Engines
This page contains a representative list of major databases and search engines useful in an academic setting for finding and accessing articles in academic journals, institutional repositories, archives, or other collections of scientific and other articles. As the distinction between a database and a search engine is unclear for these complex document retrieval systems, see: * the general list of search engines for all-purpose search engines that can be used for academic purposes * the article about bibliographic databases for information about databases giving bibliographic information about finding books and journal articles. Note that "free" or "subscription" can refer both to the availability of the database or of the journal articles included. This has been indicated as precisely as possible in the list: List See also * Academic publishing * Google Scholar * List of digital library projects * List of educational video websites * List of neuroscience databases * L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Energy Physics
Particle physics or high-energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The field also studies combinations of elementary particles up to the scale of protons and neutrons, while the study of combinations of protons and neutrons is called nuclear physics. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three generations of fermions, although ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that contain an odd number of quarks are called baryons and those that contain an even numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |