|
SLAC
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, originally named the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, is a federally funded research and development center in Menlo Park, California, United States. Founded in 1962, the laboratory is now sponsored by the United States Department of Energy and administrated by Stanford University. It is the site of the Stanford Linear Accelerator, a 3.2 kilometer (2-mile) linear accelerator constructed in 1966 that could accelerate electrons to energies of 50 GeV. Today SLAC research centers on a broad program in atomic and solid-state physics, chemistry, biology, and medicine using X-rays from synchrotron radiation and a free-electron laser as well as experimental and theoretical research in elementary particle physics, accelerator physics, astroparticle physics, and cosmology. The laboratory is under the programmatic direction of the United States Department of Energy Office of Science. History Founded in 1962 as the Stanford Linear Accelera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
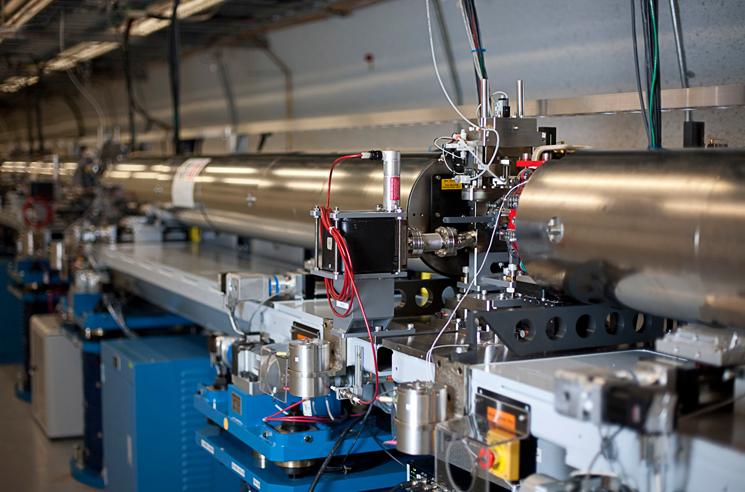
Linear Particle Accelerator
A linear particle accelerator (often shortened to linac) is a type of particle accelerator that accelerates charged subatomic particles or ions to a high speed by subjecting them to a series of Oscillation, oscillating electric potentials along a Line (geometry), linear beamline. The principles for such machines were proposed by Gustav Ising in 1924, while the first machine that worked was constructed by Rolf Widerøe in 1928 at the RWTH Aachen University. Linacs have many applications: they generate X-rays and high energy electrons for medicinal purposes in radiation therapy, serve as particle injectors for higher-energy accelerators, and are used directly to achieve the highest kinetic energy for light particles (electrons and positrons) for particle physics. The design of a linac depends on the type of particle that is being accelerated: electrons, protons or ions. Linacs range in size from a cathode-ray tube (which is a type of linac) to the linac at the SLAC National Accele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Accelerator
A linear particle accelerator (often shortened to linac) is a type of particle accelerator that accelerates charged subatomic particles or ions to a high speed by subjecting them to a series of oscillating electric potentials along a linear beamline. The principles for such machines were proposed by Gustav Ising in 1924, while the first machine that worked was constructed by Rolf Widerøe in 1928 at the RWTH Aachen University. Linacs have many applications: they generate X-rays and high energy electrons for medicinal purposes in radiation therapy, serve as particle injectors for higher-energy accelerators, and are used directly to achieve the highest kinetic energy for light particles (electrons and positrons) for particle physics. The design of a linac depends on the type of particle that is being accelerated: electrons, protons or ions. Linacs range in size from a cathode-ray tube (which is a type of linac) to the linac at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burton Richter
Burton Richter (March 22, 1931 – July 18, 2018) was an American physicist. He led the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC) team which co-discovered the J/ψ meson in 1974, alongside the Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) team led by Samuel Ting for which they won Nobel Prize for Physics in 1976. This discovery was part of the November Revolution of particle physics. He was the SLAC director from 1984 to 1999. Life and work A native of New York City, Richter was born into a Jewish family in Brooklyn, and was raised in the Queens neighborhood of Far Rockaway. His parents were Fanny (Pollack) and Abraham Richter, a textile worker. He graduated from Far Rockaway High School, a school that also produced fellow laureates Baruch Samuel Blumberg and Richard Feynman. He attended Mercersburg Academy in Pennsylvania, then continued on to study at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, where he received his bachelor's degree in 1952 and his PhD in 1956. He then joined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth List of governors of California, governor of and then-incumbent List of United States senators from California, United States senator representing California) and his wife, Jane Stanford, Jane, in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., Leland Jr. The university admitted its first students in 1891, opening as a Mixed-sex education, coeducational and non-denominational institution. It struggled financially after Leland died in 1893 and again after much of the campus was damaged by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Following World War II, university Provost (education), provost Frederick Terman inspired an entrepreneurship, entrepreneurial culture to build a self-sufficient local industry (later Silicon Valley). In 1951, Stanfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-electron Laser
A free-electron laser (FEL) is a fourth generation light source producing extremely brilliant and short pulses of radiation. An FEL functions much as a laser but employs relativistic electrons as a active laser medium, gain medium instead of using Laser, stimulated emission from atomic or molecular excitations. In an FEL, a ''bunch'' of electrons passes through a magnetic structure called an undulator or Wiggler (synchrotron), wiggler to generate radiation, which re-interacts with the electrons to make them emit coherently, exponentially increasing its intensity. As electron kinetic energy and undulator parameters can be adapted as desired, free-electron lasers are tunable laser, tunable and can be built for a wider frequency range than any other type of laser, currently ranging in wavelength from microwaves, through terahertz radiation and infrared, to the visible spectrum, ultraviolet, and X-ray. The first free-electron laser was developed by John Madey in 1971 at Stanford Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high-energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The field also studies combinations of elementary particles up to the scale of protons and neutrons, while the study of combinations of protons and neutrons is called nuclear physics. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three Generation (particle physics), generations of fermions, although ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of Up quark, up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quark, Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up quark, up and down quark, down quarks. Electrons are extremely lightweight particles that orbit the positively charged atomic nucleus, nucleus of atoms. Their negative charge is balanced by the positive charge of protons in the nucleus, giving atoms their overall electric charge#Charge neutrality, neutral charge. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, each consisting of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a number of orbiting electrons equal to the number of protons. The configuration and energy levels of these orbiting electrons determine the chemical properties of an atom. Electrons are bound to the nucleus to different degrees. The outermost or valence electron, valence electrons are the least tightly bound and are responsible for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elementary Particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a subatomic particle that is not composed of other particles. The Standard Model presently recognizes seventeen distinct particles—twelve fermions and five bosons. As a consequence of flavor and color combinations and antimatter, the fermions and bosons are known to have 48 and 13 variations, respectively. Among the 61 elementary particles embraced by the Standard Model number: electrons and other leptons, quarks, and the fundamental bosons. Subatomic particles such as protons or neutrons, which contain two or more elementary particles, are known as composite particles. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, themselves once thought to be indivisible elementary particles. The name ''atom'' comes from the Ancient Greek word ''ἄτομος'' ( atomos) which means ''indivisible'' or ''uncuttable''. Despite the theories about atoms that had existed for thousands of years, the factual existence of ato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federally Funded Research And Development Centers
Federally funded research and development centers (FFRDCs) are public-private partnerships that conduct research and development for the United States Government. Under Federal Acquisition Regulationbr>§ 35.017 FFRDCs are operated by universities and corporations to fulfill certain long-term needs of the government that "...cannot be met as effectively by existing in-house or contractor resources." While similar in many ways to University Affiliated Research Centers, FFRDCs are prohibited from competing for work. There are currently 42 FFRDCs, each sponsored by one or more U.S. government departments or agencies. History During World War II scientists, engineers, mathematicians, and other specialists became part of the massive United States war effort—leading to evolutions in radar, aircraft, computing and, most famously, the development of nuclear weapons through the Manhattan Project. The end of armed conflict did not end the need for organized research and development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sand Hill Road
Sand Hill Road (SHR) or Sand Hill is an arterial road in western Silicon Valley, California, running through Palo Alto, Menlo Park, and Woodside, notable for its concentration of venture capital firms. The road has become a metonym for that industry; nearly every top Silicon Valley company has been the beneficiary of early funding from firms on Sand Hill Road. Its significance as a symbol of private equity and venture capitalism in the United States has been compared to that of Wall Street and the stock market. Location Connecting El Camino Real and Interstate 280, the road provides easy access to Stanford University and the northwestern area of Silicon Valley. The road also runs southwest of Interstate 280 into a residential neighborhood of Woodside, California, but the private equity companies are concentrated to the east of the freeway on the main stretch of the road in Menlo Park. On its northeast end, it crosses into and runs briefly through Palo Alto before ending at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and energy production, the research and development of nuclear power, the military's nuclear weapons program, nuclear reactor production for the United States Navy, energy-related research, and energy conservation. The DOE was created in 1977 in the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis. It sponsors more physical science research than any other U.S. federal agency, the majority of which is conducted through its system of National Laboratories. The DOE also directs research in genomics, with the Human Genome Project originating from a DOE initiative. The department is headed by the secretary of energy, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the Cabinet. The current secretary of energy is Chris Wright, who has served in the position since February 2025. The department's headquarters are in sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |