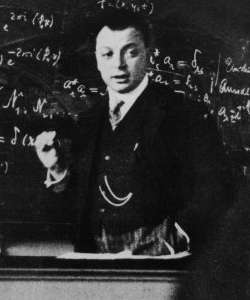|
Spin Magnetic Quantum Number
In physics and chemistry, the spin quantum number is a quantum number (designated ) that describes the intrinsic angular momentum (or spin angular momentum, or simply ''spin'') of an electron or other particle. It has the same value for all particles of the same type, such as = for all electrons. It is an integer for all bosons, such as photons, and a half-odd-integer for all fermions, such as electrons and protons. The component of the spin along a specified axis is given by the spin magnetic quantum number, conventionally written . The value of is the component of spin angular momentum, in units of the reduced Planck constant , parallel to a given direction (conventionally labelled the –axis). It can take values ranging from + to − in integer increments. For an electron, can be either or . Nomenclature The phrase ''spin quantum number'' refers to quantized spin angular momentum. The symbol is used for the spin quantum number, and is described as the spin ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azimuthal Quantum Number
In quantum mechanics, the azimuthal quantum number is a quantum number for an atomic orbital that determines its orbital angular momentum and describes aspects of the angular shape of the orbital. The azimuthal quantum number is the second of a set of quantum numbers that describe the unique quantum state of an electron (the others being the principal quantum number , the magnetic quantum number , and the spin quantum number ). For a given value of the principal quantum number (''electron shell''), the possible values of are the integers from 0 to . For instance, the shell has only orbitals with \ell=0, and the shell has only orbitals with \ell=0, and \ell=1. For a given value of the azimuthal quantum number , the possible values of the magnetic quantum number are the integers from to , including 0. In addition, the spin quantum number can take two distinct values. The set of orbitals associated with a particular value of are sometimes collectively called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli ( ; ; 25 April 1900 – 15 December 1958) was an Austrian theoretical physicist and a pioneer of quantum mechanics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics "for the discovery of the Exclusion Principle, also called the Pauli exclusion principle, Pauli Principle". The discovery involved Spin (physics), spin theory, which is the basis of a theory of the Matter#Structure, structure of matter. To preserve the conservation of energy in beta decay, he posited the existence of a small neutral particle, dubbed the neutrino by Enrico Fermi. The neutrino was detected in 1956. Early life Pauli was born in Vienna to a chemist, (''né'' Wolf Pascheles, 1869–1955), and his wife, Bertha Camilla Schütz; his sister was Hertha Pauli, a writer and actress. Pauli's middle name was given in honor of his Godparent, godfather, physicist Ernst Mach. Pauli's paternal grandparents were from prominent Jewish families of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomalous Zeeman Effect
The Zeeman effect () is the splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of a static magnetic field. It is caused by the interaction of the magnetic field with the magnetic moment of the atomic electron associated with its orbital motion and spin; this interaction shifts some orbital energies more than others, resulting in the split spectrum. The effect is named after the Dutch physicist Pieter Zeeman, who discovered it in 1896 and received a Nobel Prize in Physics for this discovery. It is analogous to the Stark effect, the splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of an electric field. Also, similar to the Stark effect, transitions between different components have, in general, different intensities, with some being entirely forbidden (in the dipole approximation), as governed by the selection rules. Since the distance between the Zeeman sub-levels is a function of magnetic field strength, this effect can be used to measure m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Magazine
The ''Philosophical Magazine'' is one of the oldest scientific journals published in English. It was established by Alexander Tilloch in 1798;John Burnett"Tilloch, Alexander (1759–1825)" Dictionary of National Biography#Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, Sept 2004; online edn, May 2006, accessed 17 Feb 2010 in 1822 Richard Taylor (editor), Richard Taylor became joint editor and it has been published continuously by Taylor & Francis ever since. Early history The name of the journal dates from a period when "natural philosophy" embraced all aspects of science. The very first paper published in the journal carried the title "Account of Mr Cartwright's Patent Steam Engine". Other articles in the first volume include "Methods of discovering whether Wine has been adulterated with any Metals prejudicial to Health" and "Description of the Apparatus used by Lavoisier to produce Water from its component Parts, Oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Stoner
Edmund Clifton Stoner Royal Society, FRS (2 October 1899 – 27 December 1968) was a British theoretical physicist. He is principally known for his work on the origin and nature of itinerant ferromagnetism (the type of ferromagnetic behaviour associated with pure transition metals like cobalt, nickel, and iron), including the collective electron theory of ferromagnetism and the Stoner criterion for ferromagnetism. Stoner made significant contributions to the electron configurations in the periodic table. Biography Stoner was born in Esher, Surrey, the son of cricketer Arthur Stoner, Arthur Hallett Stoner. He won a scholarship to Bolton School (1911–1918) and then attended Emmanuel College, Cambridge, graduating with a degree in natural sciences in 1921. After graduation, he worked at the Cavendish Laboratory on the absorption of X-rays by matter and electron energy levels; his 1924 paper on this subject prefigured the Pauli exclusion principle. Stoner was appointed a Lecturer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |