|
Solid-state Relays
Solid state contactor PCB mount solid-state DIL relay A solid state relay (SSR) is an electronic switching device that switches on or off when an external voltage (AC or DC) is applied across its control terminals. They serve the same function as an electromechanical relay, but solid-state electronics contain no moving parts and have a longer operational lifetime. Solid state relays were invented in 1971 by the Crydom Controls division of International Rectifier. SSRs consist of a sensor which responds to an appropriate input (control signal), an electronic switching device which switches power to the load circuitry, and a coupling mechanism to enable the control signal to activate this switch without mechanical parts. They may be designed to switch either AC or DC loads. Packaged SSRs use power semiconductor devices such as thyristors and transistors, to switch currents up to around a hundred amperes. SSRs have fast switching speeds compared with electromechanical relays, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSR Solid State Relay
SSR may refer to: Businesses, entertainment and products * Solid State Records, a Christian record label * Chevrolet SSR, a Chevrolet small truck * Disney's Saratoga Springs Resort & Spa * Small Screen Rendering, a technology part of Opera Mini * ''Sonic and the Secret Rings'', a 2007 platform video game * ''Stephen's Sausage Roll'', a 2016 puzzle video game * Sirius Satellite Radio, a satellite radio service operating in North America * Strategic Scientific Reserve, a fictional organization in Marvel Comics and precursor to the fictional organization S.H.I.E.L.D. * SSR Wheels, a Japanese wheel manufacturer Geographical locations * Soviet Socialist Republic, see Republics of the Soviet Union * Slovak Soviet Republic (1919), a very short-lived communist state in south and eastern Slovakia * Slovak Socialist Republic, the official name of Slovakia from 1969 to 1990 *Second Spanish Republic Railways * Sabah State Railway, a railway in Malaysia * Southern Shorthaul Railroad, an Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon-controlled Rectifier
A silicon controlled rectifier or semiconductor controlled rectifier (SCR) is a four-layer solid-state current-controlling device. The name "silicon controlled rectifier" is General Electric's trade name for a type of thyristor. The principle of four-layer p–n–p–n switching was developed by Moll, Tanenbaum, Goldey, and Holonyak of Bell Laboratories in 1956. The practical demonstration of silicon controlled switching and detailed theoretical behavior of a device in agreement with the experimental results was presented by Dr Ian M. Mackintosh of Bell Laboratories in January 1958. The SCR was developed by a team of power engineers led by Gordon Hall and commercialized by Frank W. "Bill" Gutzwiller in 1957. Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifiers and thyristors as synonymous while other sources define silicon-controlled rectifiers as a proper subset of the set of thyristors; the latter being devices with at least four layers of alternating n- and p-type mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
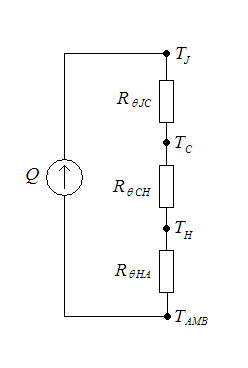
Thermal Resistance
In heat transfer, thermal engineering, and thermodynamics, thermal conductance and thermal resistance are fundamental concepts that describe the ability of materials or systems to conduct heat and the opposition they offer to the heat current. The ability to manipulate these properties allows engineers to control temperature gradient, prevent thermal shock, and maximize the efficiency of thermal systems. Furthermore, these principles find applications in a multitude of fields, including materials science, mechanical engineering, electronics, and energy management. Knowledge of these principles is crucial in various scientific, engineering, and everyday applications, from designing efficient temperature control, thermal insulation, and thermal management in industrial processes to optimizing the performance of electronic devices. Thermal conductance (''G'') measures the ability of a material or system to conduct heat. It provides insights into the ease with which heat can pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage Drop
In electronics, voltage drop is the decrease of electric potential along the path of a current flowing in a circuit. Voltage drops in the internal resistance of the source, across conductors, across contacts, and across connectors are undesirable because some of the energy supplied is dissipated. The voltage drop across the load is proportional to the power available to be converted in that load to some other useful form of energy. For example, an electric space heater may have a resistance of 10 ohms, and the wires that supply it may have a resistance of 0.2 ohms, about 2% of the total circuit resistance. This means that approximately 2% of the supplied voltage is lost in the wire itself. An excessive voltage drop may result in the unsatisfactory performance of the space heater and the overheating of the wires and connections. National and local electrical codes may set guidelines for the maximum voltage drop allowed in electrical wiring to ensure efficiency of dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Bounce
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of switch is an electromechanical device consisting of one or more sets of movable electrical contacts connected to external circuits. When a pair of contacts is touching current can pass between them, while when the contacts are separated no current can flow. Switches are made in many different configurations; they may have multiple sets of contacts controlled by the same knob or actuator, and the contacts may operate simultaneously, sequentially, or alternately. A switch may be operated manually, for example, a light switch or a keyboard button, or may function as a sensing element to sense the position of a machine part, liquid level, pressure, or temperature, such as a thermostat. Many specialized forms exist, such as the toggle switc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galvanic Isolation
Galvanic isolation is a principle of isolating functional sections of electrical systems to prevent current flow; no direct conduction path is permitted. Energy or information can still be exchanged between the sections by other means, such as capacitive, inductive, radiative, optical, acoustic, or mechanical coupling. Galvanic isolation is used where two or more electric circuits must communicate, but their grounds may be at different potentials. It is an effective method of breaking ground loops by preventing unwanted current from flowing between two units sharing a ground conductor. Galvanic isolation is also used for safety, preventing accidental electric shocks. Methods Transformer Transformers are probably the most common means of galvanic isolation. They are almost universally used in power supplies because they are a mature technology that can carry significant power. They are also used to isolate data signals in Ethernet over twisted pair. Transformers co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon-controlled Rectifier
A silicon controlled rectifier or semiconductor controlled rectifier (SCR) is a four-layer solid-state current-controlling device. The name "silicon controlled rectifier" is General Electric's trade name for a type of thyristor. The principle of four-layer p–n–p–n switching was developed by Moll, Tanenbaum, Goldey, and Holonyak of Bell Laboratories in 1956. The practical demonstration of silicon controlled switching and detailed theoretical behavior of a device in agreement with the experimental results was presented by Dr Ian M. Mackintosh of Bell Laboratories in January 1958. The SCR was developed by a team of power engineers led by Gordon Hall and commercialized by Frank W. "Bill" Gutzwiller in 1957. Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifiers and thyristors as synonymous while other sources define silicon-controlled rectifiers as a proper subset of the set of thyristors; the latter being devices with at least four layers of alternating n- and p-type mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and measurement applications, or for the generation of electrical power in solar cells. Photodiodes are used in a wide range of applications throughout the electromagnetic spectrum from visible light photocells to gamma ray spectrometers. Principle of operation A photodiode is a PIN diode, PIN structure or p–n junction. When a photon of sufficient energy strikes the diode, it creates an electron–electron hole, hole pair. This mechanism is also known as the inner photoelectric effect. If the absorption occurs in the junction's depletion region, or one diffusion length away from it, these carriers are swept from the junction by the built-in electric field of the depletion region. Thus holes move toward the anode, and electrons toward the cath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galvanic Isolation
Galvanic isolation is a principle of isolating functional sections of electrical systems to prevent current flow; no direct conduction path is permitted. Energy or information can still be exchanged between the sections by other means, such as capacitive, inductive, radiative, optical, acoustic, or mechanical coupling. Galvanic isolation is used where two or more electric circuits must communicate, but their grounds may be at different potentials. It is an effective method of breaking ground loops by preventing unwanted current from flowing between two units sharing a ground conductor. Galvanic isolation is also used for safety, preventing accidental electric shocks. Methods Transformer Transformers are probably the most common means of galvanic isolation. They are almost universally used in power supplies because they are a mature technology that can carry significant power. They are also used to isolate data signals in Ethernet over twisted pair. Transformers co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IGBT
An insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) is a three-terminal power semiconductor device primarily forming an electronic switch. It was developed to combine high efficiency with fast switching. It consists of four alternating layers (NPNP) that are controlled by a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) gate structure. Although the structure of the IGBT is topologically similar to a thyristor with a " MOS" gate ( MOS-gate thyristor), the thyristor action is completely suppressed, and only the transistor action is permitted in the entire device operation range. It is used in switching power supplies in high-power applications: variable-frequency drives (VFDs) for motor control in electric cars, trains, variable-speed refrigerators, and air conditioners, as well as lamp ballasts, arc-welding machines, photovoltaic and hybrid inverters, uninterruptible power supply systems (UPS), and induction stoves. Since it is designed to turn on and off rapidly, the IGBT can synthesize complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOSFET
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale. In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, MOS FET, or MOS transistor) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The term ''metal–insulator–semiconductor field-effect transistor'' (''MISFET'') is almost synonymous with ''MOSFET''. Another near-synonym is ''insulated-gate field-effect transistor'' (''IGFET''). The main advantage of a MOSFET is that it requires almost no input current to control the load current under steady-state or low-frequency conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Back EMF
Counter-electromotive force (counter EMF, CEMF, back EMF),Graf, "counterelectromotive force", Dictionary of Electronics is the electromotive force (EMF) manifesting as a voltage that opposes the change in current which induced it. CEMF is the EMF caused by electromagnetic induction. Details For example, the voltage appearing across an inductor or coil is due to a change in current which causes a change in the magnetic field within the coil, and therefore the self-induced voltage. The polarity of the voltage at every moment opposes that of the change in applied voltage, to keep the current constant. The term ''back electromotive force'' is also commonly used to refer to the voltage that occurs in electric motors where there is relative motion between the armature and the magnetic field produced by the motor's field coils or permanent magnet field, thus also acting as a generator while running as a motor. This effect is not due to the motor's inductance, which generates a volt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |