|
Software Package Metrics
Various software package metrics are used in modular programming. They have been mentioned by Robert Cecil Martin in his 2002 book ''Agile software development: principles, patterns, and practices''. The term software package here refers to a group of related classes in object-oriented programming. * Number of classes and interfaces: The number of concrete and abstract classes (and interfaces) in the package is an indicator of the extensibility of the package. * Afferent couplings (Ca): The number of classes in other packages that depend upon classes within the package is an indicator of the package's responsibility. Afferent couplings signal inward. * Efferent couplings (Ce): The number of classes in other packages that the classes in a package depend upon is an indicator of the package's dependence on externalities In economics, an externality is an indirect cost (external cost) or indirect benefit (external benefit) to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Modular Programming
Modular programming is a software design technique that emphasizes separating the functionality of a program into independent, interchangeable modules, such that each contains everything necessary to execute only one aspect or "concern" of the desired functionality. A module interface expresses the elements that are provided and required by the module. The elements defined in the interface are detectable by other modules. The implementation contains the working code that corresponds to the elements declared in the interface. Modular programming is closely related to structured programming and object-oriented programming, all having the same goal of facilitating construction of large software programs and systems by decomposition into smaller pieces, and all originating around the 1960s. While the historical usage of these terms has been inconsistent, "modular programming" now refers to the high-level decomposition of the code of an entire program into pieces: structured progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Robert Cecil Martin
Robert Cecil Martin (born 5 December 1952), colloquially called "Uncle Bob", is an American software engineer, instructor, and author. He is most recognized for promoting many software design principles and for being an author and signatory of the influential Agile Manifesto. Martin has authored many books and magazine articles. He was the editor-in-chief of '' C++ Report'' magazine and served as the first chairman of the Agile Alliance. Martin joined the software industry at age 17 and is self-taught. Professional work In 1991, Martin founded Object Mentor, now defunct, which provided instructor-led training on the extreme programming methodology. , he operated Uncle Bob Consulting, which provides consulting and training services. He serves as Master Craftsman / Mentor at ''Clean Coders,'' a company run by his son Micah Martin, and produces training videos. Software principles advocacy Martin is a proponent of software craftsmanship, agile software development, and test-dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
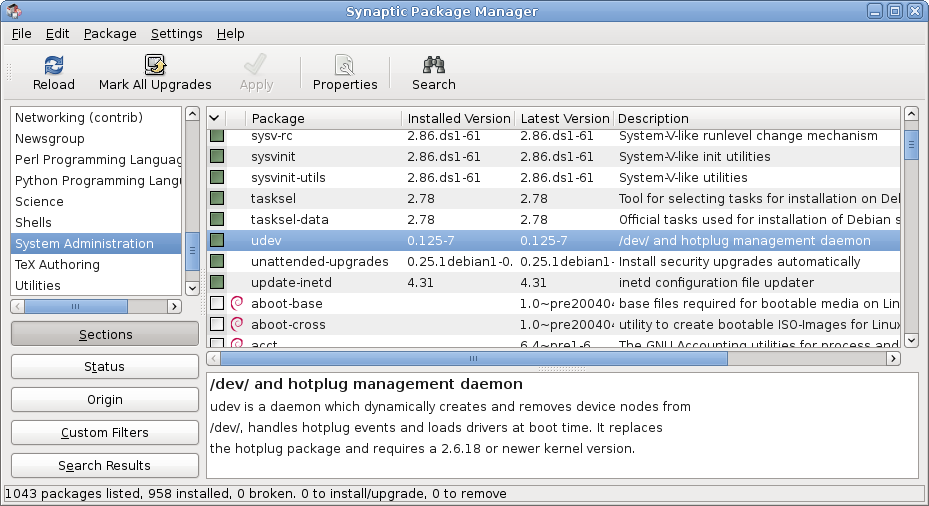
Package Manager
A package manager or package management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the need for manual installs and updates. This can be particularly useful for large e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Class (computer Science)
In object-oriented programming, a class defines the shared aspects of objects created from the class. The capabilities of a class differ between programming languages, but generally the shared aspects consist of state ( variables) and behavior ( methods) that are each either associated with a particular object or with all objects of that class. Object state can differ between each instance of the class whereas the class state is shared by all of them. The object methods include access to the object state (via an implicit or explicit parameter that references the object) whereas class methods do not. If the language supports inheritance, a class can be defined based on another class with all of its state and behavior plus additional state and behavior that further specializes the class. The specialized class is a ''sub-class'', and the class it is based on is its ''superclass''. Attributes Object lifecycle As an instance of a class, an object is constructed from a class via '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Object-oriented Programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of '' objects''. Objects can contain data (called fields, attributes or properties) and have actions they can perform (called procedures or methods and implemented in code). In OOP, computer programs are designed by making them out of objects that interact with one another. Many of the most widely used programming languages (such as C++, Java, and Python) support object-oriented programming to a greater or lesser degree, typically as part of multiple paradigms in combination with others such as imperative programming and declarative programming. Significant object-oriented languages include Ada, ActionScript, C++, Common Lisp, C#, Dart, Eiffel, Fortran 2003, Haxe, Java, JavaScript, Kotlin, Logo, MATLAB, Objective-C, Object Pascal, Perl, PHP, Python, R, Raku, Ruby, Scala, SIMSCRIPT, Simula, Smalltalk, Swift, Vala and Visual Basic.NET. History The idea of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coupling (computer Programming)
A coupling is a device used to connect two shafts together at their ends for the purpose of transmitting power. The primary purpose of couplings is to join two pieces of rotating equipment while permitting some degree of misalignment or end movement or both. In a more general context, a coupling can also be a mechanical device that serves to connect the ends of adjacent parts or objects. Couplings do not normally allow disconnection of shafts during operation, however there are torque-limiting couplings which can slip or disconnect when some torque limit is exceeded. Selection, installation and maintenance of couplings can lead to reduced maintenance time and maintenance cost. Uses Shaft couplings are used in machinery for several purposes. A primary function is to transfer power from one end to another end (ex: motor transfer power to pump through coupling). Other common uses: * To alter the vibration characteristics of rotating units * To connect the driving and the driven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Afferent Couplings
Various software package metrics are used in modular programming. They have been mentioned by Robert Cecil Martin in his 2002 book ''Agile software development: principles, patterns, and practices''. The term software package here refers to a group of related classes in object-oriented programming. * Number of classes and interfaces: The number of concrete and abstract classes (and interfaces) in the package is an indicator of the extensibility of the package. * Afferent couplings (Ca): The number of classes in other packages that depend upon classes within the package is an indicator of the package's responsibility. Afferent couplings signal inward. * Efferent couplings (Ce): The number of classes in other packages that the classes in a package depend upon is an indicator of the package's dependence on externalities. Efferent couplings signal outward. * Abstractness (A): The ratio of the number of abstract classes (and interfaces) in the analyzed package to the total number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Efferent Coupling
Efferent coupling is a coupling metric in software development. It measures the number of data types a class knows about. This includes inheritance, interface implementation, parameter types, variable types, and exceptions. This has also been referred to by Robert C. Martin as the Fan-out stability metric which in his book Clean Architecture he describes as Outgoing dependencies. This metric identifies the number of classes inside this component that depend on classes outside the component. This metric is often used to calculate instability of a component in software architecture Software architecture is the set of structures needed to reason about a software system and the discipline of creating such structures and systems. Each structure comprises software elements, relations among them, and properties of both elements a ... as ''I'' = Fan-out / (Fan-in + Fan-out). This metric has a range ,1 ''I'' = 0 is maximally stable while ''I'' = 1 is maximally unstable. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Externality
In economics, an externality is an Indirect costs, indirect cost (external cost) or indirect benefit (external benefit) to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced components that are involved in either consumer or producer consumption. Air pollution from motor vehicles is one example. The Air pollution#Health effects, cost of air pollution to society is not paid by either the producers or users of motorized transport. Water pollution from mills and factories are another example. All (water) consumers are made worse off by pollution but are not compensated by the market for this damage. The concept of externality was first developed by Alfred Marshall in the 1890s and achieved broader attention in the works of economist Arthur Cecil Pigou, Arthur Pigou in the 1920s. The prototypical example of a negative externality is environmental pollution. Pigou argued that a tax, equal to the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Efferent
Efferent may refer to: Anatomical structures Meaning 'conveying away from a center': *Efferent arterioles, conveying blood away from the Bowman's capsule in the kidney *Efferent nerve fiber, carries nerve impulses away from the central nervous system toward the peripheral effector organs *Efferent lymph vessel, lymph vessels that carry lymph from a lymph node *Efferent ducts The efferent ducts (also efferent ductules, ductuli efferentes, ductus efferentes, or vasa efferentia) connect the rete testis with the initial section of the epididymis.Hess 2018 There are two basic designs for efferent ductule structure: * a ..., connect the rete testis with the initial section of the epididymis Other uses * Efferent coupling, a metric in software development See also * Afferent (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dependency Inversion Principle
In object-oriented design, the dependency inversion principle is a specific methodology for Coupling (computer programming), loosely coupled software Modular programming, modules. When following this principle, the conventional dependency (computer science), dependency relationships established from high-level, policy-setting modules to low-level, dependency modules are reversed, thus rendering high-level modules independent of the low-level module implementation details. The principle states: By dictating that high-level and low-level objects must depend on the same abstraction, this design principle the way some people may think about object-oriented programming. The idea behind points A and B of this principle is that when designing the interaction between a high-level module and a low-level one, the interaction should be thought of as an abstract interaction between them. This has implications for the design of both the high-level and the low-level modules: the low-level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Software Metrics
In software engineering and Software development, development, a software metric is a standard of measure of a degree to which a software system or process possesses some property. Even if a metric is not a measurement (metrics are functions, while measurements are the numbers obtained by the application of metrics), often the two terms are used as synonyms. Since Quantitative research, quantitative measurements are essential in all sciences, there is a continuous effort by computer science practitioners and theoreticians to bring similar approaches to software development. The goal is obtaining objective, reproducible and quantifiable measurements, which may have numerous valuable applications in schedule and budget planning, cost estimation, quality assurance, testing, software debugging, software Program optimization, performance optimization, and optimal personnel task assignments. Common software measurements Common software measurements include: * ABC Software Metric * Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |