|
Social Judgment Theory
In social psychology, Social judgment theory (SJT) is a self-persuasion theory proposing that an individual's perception and evaluation of an idea is by comparing it with current attitudes. According to this theory, an individual weighs every new idea, comparing it with the individual's present point of view to determine where it should be placed on the attitude scale in an individual's mind. SJT is the subconscious sorting out of ideas that occurs at the instant of perception. The theory of Social Judgement attempts to explain why and how people have different reactions and responded toward the same information or issue. Social Judgment Theory can be used to improve the way people communicate with one another. The theory is also widely considered in persuasions. The Social Judgement Theory depends on the individual's position on a certain issue occurring. Depending on three elements Social Judgement Theory has, they are followed by their anchor, alternatives and ego-involvement. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Psychology
Social psychology is the methodical study of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others. Although studying many of the same substantive topics as its counterpart in the field of sociology, psychological social psychology places more emphasis on the individual, rather than society; the influence of social structure and culture on individual outcomes, such as personality, behavior, and one's position in social hierarchies. Social psychologists typically explain human behavior as a result of the relationship between mental states and social situations, studying the social conditions under which thoughts, feelings, and behaviors occur, and how these variables influence social interactions. History 19th century In the 19th century, social psychology began to emerge from the larger field of psychology. At the time, many psychologists were concerned with developing concrete explanations for the different aspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politics
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social status, status or resources. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. Politics may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and non-violent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but the word often also carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or in a limited way, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Impact Theory
Social Impact Theory was created by Bibb Latané in 1981 and consists of four basic rules which consider how individuals can be "sources or targets of social influence". Social impact is the result of social forces, including the strength of the source of impact, the immediacy of the event, and the number of sources exerting the impact. The more targets there are to impact, the less impact each target receives. Original research According to psychologist Bibb Latané, social impact is defined as any influence on individual feelings, thoughts, or behaviors that is created from the real, implied, or imagined presence or actions of others. The application of social impact varies from diffusion of responsibility to social loafing, stage fright, or persuasive communication. In 1981, Latané developed the social impact theory using three key variables: * Strength (S) is a net of all individual factors that make a person influential. It covers stable, trans-situational, intrapersonal f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
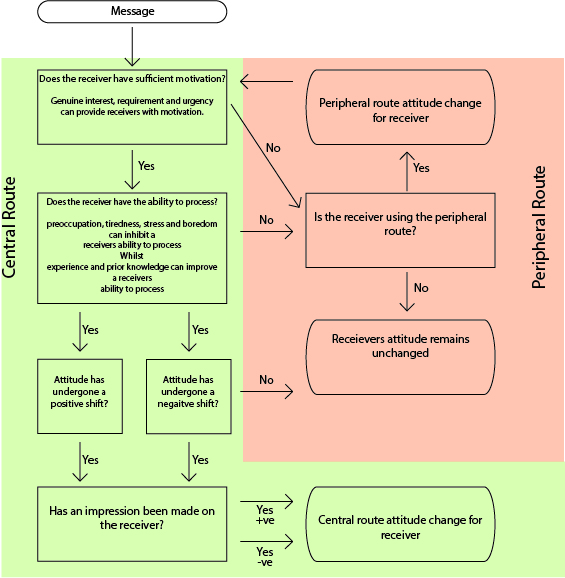
Elaboration Likelihood Model
The elaboration likelihood model (ELM) of persuasion is a dual process theory describing the change of attitudes. The ELM was developed by Richard E. Petty and John Cacioppo in 1980. The model aims to explain different ways of processing stimuli, why they are used, and their outcomes on attitude change. The ELM proposes two major routes to persuasion: the central route and the peripheral route. Origin Elaboration likelihood model is a general theory of attitude change. According to the theory's developers Richard E. Petty and John T. Cacioppo, the theory was created to provide a general "framework for organizing, categorizing, and understanding the basic processes underlying the effectiveness of persuasive communications". The study of Attitude (psychology), attitudes and persuasion began as the central focus of social psychology, featured in the work of psychologists Gordon Allport (1935) and Edward Alsworth Ross (1908). Allport described attitudes as "the most distinctive and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Soon after, it spread to other areas of Asia, and COVID-19 pandemic by country and territory, then worldwide in early 2020. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) on 30 January 2020, and assessed the outbreak as having become a pandemic on 11 March. COVID-19 symptoms range from asymptomatic to deadly, but most commonly include fever, sore throat, nocturnal cough, and fatigue. Transmission of COVID-19, Transmission of the virus is often airborne transmission, through airborne particles. Mutations have variants of SARS-CoV-2, produced many strains (variants) with varying degrees of infectivity and virulence. COVID-19 vaccines were developed rapidly and deplo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohio State University
The Ohio State University (Ohio State or OSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio, United States. A member of the University System of Ohio, it was founded in 1870. It is one of the List of largest United States university campuses by enrollment, largest universities by enrollment in the United States, with nearly 50,000 undergraduate students and nearly 15,000 graduate students. The university consists of sixteen colleges and offers over 400 degree programs at the undergraduate and Graduate school, graduate levels. It is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". the university has an List of colleges and universities in the United States by endowment, endowment of $7.9 billion. Its athletic teams compete in NCAA Division I as the Ohio State Buckeyes as a member of the Big Ten Conference for the majority of fielde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
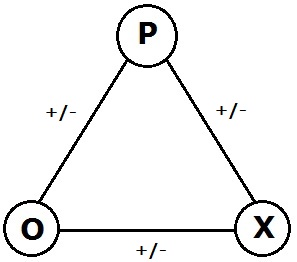
Balance Theory
In the psychology of motivation, balance theory is a theory of attitude change, proposed by Fritz Heider. It conceptualizes the cognitive consistency motive as a drive toward psychological balance. The consistency motive is the urge to maintain one's values and beliefs over time. Heider proposed that "sentiment" or liking relationships are balanced if the affect (psychology), affect valence (psychology), valence in a system multiplies out to a positive result. Research in 2020 provided neuroscientific evidence supporting Heider's balance theory. A study using neuroimaging techniques found distinct differences in brain activation when individuals were exposed to unbalanced versus balanced triads. These differences were observed in brain regions associated with processing cognitive dissonance, offering biological support for Heider's original psychological explanation of balance theory in social context. Structural balance theory in social network analysis is the extension proposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
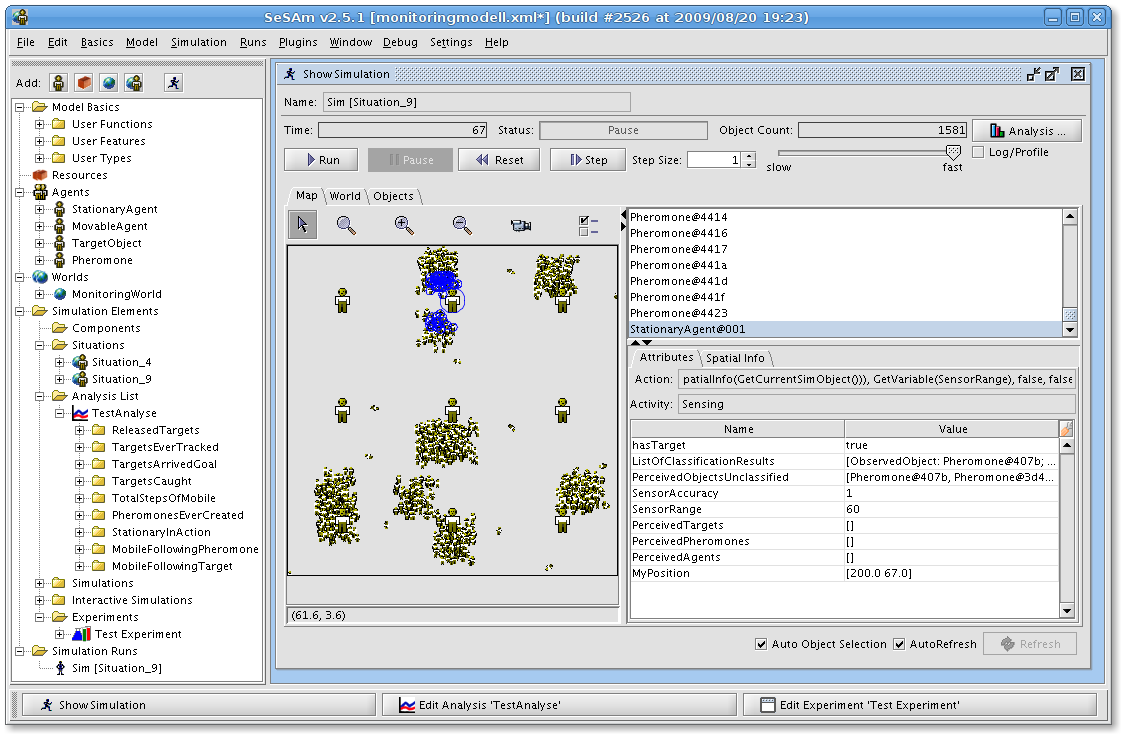
Agent-based Social Simulation
Agent-based social simulation (or ABSS) consists of social simulations that are based on agent-based modeling, and implemented using artificial agent technologies. Agent-based social simulation is a scientific discipline concerned with simulation of social phenomena, using computer-based multiagent models. In these simulations, persons or group of persons are represented by agents. MABSS is a combination of social science, multiagent simulation and computer simulation. ABSS models the different elements of the social systems using artificial agents, (varying on scale) and placing them in a computer simulated society to observe the behaviors of the agents. From this data it is possible to learn about the reactions of the artificial agents and translate them into the results of non-artificial agents and simulations. Three main fields in ABSS are agent-based computing, social science, and computer simulation. Agent-based computing is the design of the model and agents, while the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boomerang Effect (psychology)
In social psychology, the boomerang effect, also known as " reactance", refers to the unintended consequences of an attempt to persuade resulting in the adoption of an opposing position instead. It is sometimes also referred to as "the theory of psychological reactance", stating that attempts to restrict a person's freedom often produce an " anticonformity boomerang effect". In other words, the boomerang effect is a situation where people tend to pick the opposite of what something or someone is saying or doing because of how it is presented to them. Typically, the more aggressively a position is presented to someone, the more likely they are to adopt an opposing view. Conditions and explanations Early recognition Hovland, Janis and Kelly first recorded and named the boomerang effect in 1953, noting that it is more likely under certain conditions: * When weak arguments are paired with a negative source. * When weak or unclear persuasion leads the recipient to believe that the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrality
In graph theory and network analysis, indicators of centrality assign numbers or rankings to nodes within a graph corresponding to their network position. Applications include identifying the most influential person(s) in a social network, key infrastructure nodes in the Internet or urban networks, super-spreaders of disease, and brain networks. Centrality concepts were first developed in social network analysis, and many of the terms used to measure centrality reflect their sociological origin.Newman, M.E.J. 2010. ''Networks: An Introduction.'' Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. Definition and characterization of centrality indices Centrality indices are answers to the question "What characterizes an important vertex?" The answer is given in terms of a real-valued function on the vertices of a graph, where the values produced are expected to provide a ranking which identifies the most important nodes. The word "importance" has a wide number of meanings, leading to many d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
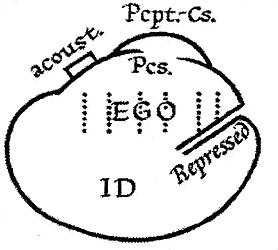
Ego (Freudian)
In psychoanalytic theory, the id, ego, and superego are three distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus, outlined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche. The three agents are theoretical constructs that Freud employed to describe the basic structure of mental life as it was encountered in psychoanalytic practice. Freud himself used the German terms ''das Es'', ''Ich'', and ''Über-Ich'', which literally translate as "the it", "I", and "over-I". The Latin terms id, ego and superego were chosen by his original translators and have remained in use. The structural model was introduced in Freud's essay '' Beyond the Pleasure Principle'' (1920) and further refined and formalised in later essays such as '' The Ego and the Id'' (1923). Freud developed the model in response to the perceived ambiguity of the terms "conscious" and "unconscious" in his earlier ''topographical'' model. Broadly speaking, the id is the organism's unconscious array of uncoordinated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assimilation (psychology)
Constructivism in education is a theory that suggests that learners do not passively acquire knowledge through direct instruction. Instead, they ''construct'' their understanding through experiences and social interaction, integrating new information with their existing knowledge. This theory originates from Swiss developmental psychologist Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development. Background Constructivism in education is rooted in epistemology, a theory of knowledge concerned with the logical categories of knowledge and its justification. It acknowledges that learners bring prior knowledge and experiences shaped by their social and cultural environment and that learning is a process of students "constructing" knowledge based on their experiences. While behaviorism focuses on understanding what students are doing, constructivism emphasizes the importance of understanding what students are thinking and how to enrich their thinking.Seifert, Kelvin & Sutton, Rosemary. Educ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |