|
Slavic Speakers Of Greek Macedonia
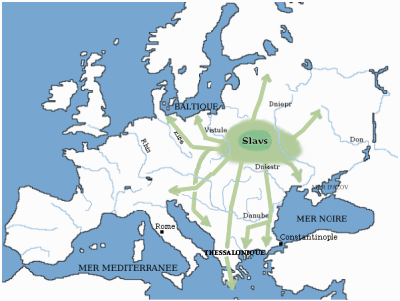
Slavic speakers are a minority population in the Geographic regions of Greece, northern Greek region of Macedonia, Greece, Macedonia, who are mostly concentrated in certain parts of the Peripheries of Greece, peripheries of West Macedonia, West and Central Macedonia, adjacent to the territory of the state of North Macedonia. Slavic dialects of Greece, Their dialects are called today "Slavic" in Greece, while generally they are considered Macedonian dialects, Macedonian. Some members have formed their own emigrant communities in neighbouring countries, as well as further abroad. History Middle Ages and Ottoman rule The Slavic peoples, Slavs took advantage of the desolation left by the nomadic tribes and in the 6th century settled the Balkan Peninsula. Aided by the Pannonian Avars, Avars and the Bulgars, the Slavic tribes started in the 6th century a gradual invasion into the Byzantine lands. They invaded Macedonia and reached as far south as Thessaly and the Peloponnese, settlin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florina (regional Unit)
Florina (, ''Perifereiakí Enótita Flórinas'') is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Western Macedonia, in the geographic regions of Greece, geographic region of Macedonia, Greece. Its capital is the town of Florina. The total population is around 45,000 (2021). Geography Florina borders the regional units of Pella (regional unit), Pella to the east, Kozani (regional unit), Kozani to the south and Kastoria (regional unit), Kastoriá to the southwest. At the Greek international borders, it is adjacent to Albania (Korçë County) to the west, North Macedonia (Bitola Municipality, Bitola and Resen Municipality, Resen municipalities) to the north and Lake Prespa to the northwest, where the two borders cross each other. Lake Vegoritida is situated in the east. Mountains in the regional unit include Verno (), Varnous () and Voras (). Administration As from 2011 the regional unit of Florina is subdivided into three municipal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
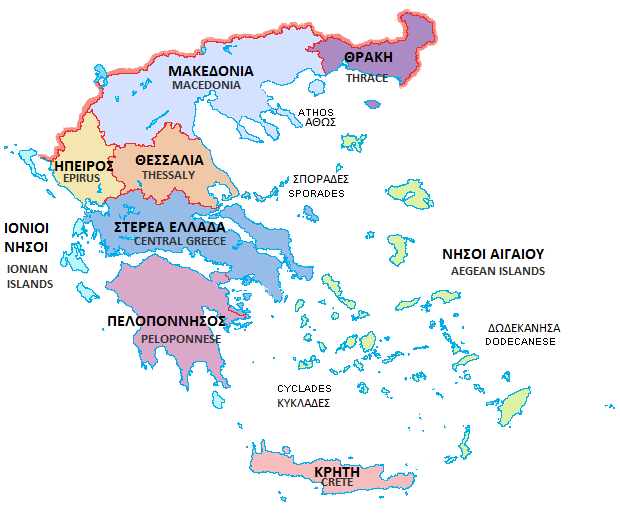
Geographic Regions Of Greece
The traditional geographic regions of Greece () are the country's main historical-geographic regions, and were also official administrative subdivisions of Greece, regional subdivisions of Greece until the 1987 administrative reform.Π.Δ. 51/87 "Καθορισμός των Περιφερειών της Χώρας για το σχεδιασμό κ.λ.π. της Περιφερειακής Ανάπτυξης" (''Determination of the Regions of the Country for the planning etc. of regional development, Government Gazette (Greece), ΦΕΚ A 26/06.03.1987 Despite their replacement as first-level administrative units by only partly identical regions of Greece, administrative regions (), the nine traditional geographic regions—six on the mainland and three island groups—are still widely referred to in unofficial contexts and in daily discourse. , the official administrative divisions of Greece consist of 13 regions ()—nine on the mainland and four island groups—which are furth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Emperors
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised sovereign authority are included, to the exclusion of junior co-emperors who never attained the status of sole or senior ruler, as well as of the List of Byzantine usurpers, various usurpers or rebels who claimed the imperial title. The following list starts with Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor, who rebuilt the city of Byzantium as an imperial capital, Constantinople, and who was regarded by the later emperors as the model ruler. Modern historians distinguish this later phase of the Roman Empire as Byzantine due to the imperial seat moving from Rome to Byzantium, the Empire's integration of Christianity, and the predominance of Greek instead of Latin. The Byzantine Empire was the direct legal continuation of the eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire (; was a medieval state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh of Bulgaria, Asparuh, moved south to the northeastern Balkans. There they secured Byzantine Empire, Byzantine recognition of their right to settle south of the Danube by Battle of Ongal, defeatingpossibly with the help of Seven Slavic tribes, local South Slavic tribesthe Byzantine army led by Constantine IV. During the 9th and 10th century, Bulgaria at the height of its power spread from the Danube Bend to the Black Sea and from the Dnieper River to the Adriatic Sea and became an important power in the region competing with the Byzantine Empire. As the state solidified its position in the Balkans, it entered into a centuries-long interaction, sometimes friendly and sometimes hostile, with the Byzantine Empire. Bulgaria emerged as Byzantium's chief antagonist to its north, resulting in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century, the peninsula was known as the Morea, a name still in colloquial use in its demotic form. The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth, where the Corinth Canal was constructed in 1893. However, it is also connected to the mainland by several bridges across the canal, including two submers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centuries. They became known as Eurasian nomads, nomadic equestrians in the Volga-Ural region, but some researchers trace Bulgar ethnic roots to Central Asia. During their westward migration across the Eurasian Steppe, the Bulgar tribes absorbed other tribal groups and cultural influences in a process of ethnogenesis, including Iranian peoples, Iranic, Finno-Ugric peoples, Finno-Ugric, and Huns, Hunnic tribes. The Bulgars spoke a Turkic languages, Turkic language, the Bulgar language of the Oghur languages, Oghuric branch. They preserved the military titles, organization, and customs of Eurasian steppes as well as pagan shamanism and belief in the sky deity Tengri, Tangra. The Bulgars became semi-sedentary during the 7th century in the Pontic- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus' people, Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine Empire, Byzantine sources, and the Apar () to the Göktürks. They established the Avar Khaganate, which spanned the Pannonian Basin and considerable areas of Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe from the late 6th to the early 9th century. The name Pannonian Avars (after the area in which they settled) is used to distinguish them from the Avars (Caucasus), Avars of the Caucasus, a separate people with whom the Pannonian Avars may or may not have had links. Although the name ''Avar'' first appeared in the mid-5th century, the Pannonian Avars entered the historical scene in the mid-6th century, on the Pontic–Caspian steppe as a people who wished to escape the rule of the Göktürks. They are probably best known for their invasions and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Peoples
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe, and North Asia, Northern Asia, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Early Slavs lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th century AD), and came to control large parts of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe between the sixth and seventh centuries. Beginning in the 7th century, they were gradually Christianization of the Slavs, Christianized. By the 12th century, they formed the core population of a number of medieval Christian states: East Slavs in the Kievan Rus', South Slavs in the First Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonian Dialects
The dialects of Macedonian comprise the Slavic dialects spoken in the Republic of North Macedonia as well as some varieties spoken in the wider geographic region of Macedonia. They are part of the dialect continuum of South Slavic languages that joins Macedonian with Bulgarian to the east and Torlakian to the north into the group of the Eastern South Slavic languages. The precise delimitation between these languages is fleeting and controversial. Classification Macedonian authors tend to treat all dialects spoken in the geographical region of Macedonia as Macedonian, including those spoken in the westernmost part of Bulgaria (so-called Pirin Macedonia), whereas Bulgarian authors treat all Macedonian dialects as part of the Bulgarian language. Prior to the codification of standard Macedonian in 1945, the dialects of Macedonia were for the most part classified as Bulgarian.Mazon, Andre. ''Contes Slaves de la Macédoine Sud-Occidentale: Etude linguistique; textes et traducti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the north. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical Macedonia (region), region of Macedonia. Skopje, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's population of over 1.83 million. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, a South Slavs, South Slavic people. Albanians in North Macedonia, Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks in North Macedonia, Turks, Romani people in North Macedonia, Roma, Serbs in North Macedonia, Serbs, Bosniaks in North Macedonia, Bosniaks, Aromanians in North Macedonia, Aromanians and a few other minorities. The region's history begins with the Paeonia (kingdom), kingdom of Paeonia. In the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Macedonia
Central Macedonia ( ; , ) is one of the thirteen Regions of Greece, administrative regions of Greece, consisting the central part of the Geographic regions of Greece, geographical and historical region of Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia. With a population of almost 1.8 million, it is the second most populous region in Greece after Attica (region), Attica. Geography The region of Central Macedonia is situated in Northern Greece, bordering the Administrative regions of Greece, regions of Western Macedonia (west), Thessaly (south), Eastern Macedonia and Thrace (east), and bounded to the north at the international borders of Greece by the Republic of North Macedonia and Bulgaria. The southern part is coastal and is bathed by the Thermaic Gulf, Thermaic, Toronean Gulf, Toroneos, Singitic Gulf, Singitic and Strymonian Gulf, Strymonic gulfs. The largest city and capital of the region is Thessaloniki. Serres is the second most populous city, followed by Katerini, Veria and Giannitsa. Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |