|
Sequential Pattern Mining
Sequential pattern mining is a topic of data mining concerned with finding statistically relevant patterns between data examples where the values are delivered in a sequence. It is usually presumed that the values are discrete, and thus time series mining is closely related, but usually considered a different activity. Sequential pattern mining is a special case of structured data mining. There are several key traditional computational problems addressed within this field. These include building efficient databases and indexes for sequence information, extracting the frequently occurring patterns, comparing sequences for similarity, and recovering missing sequence members. In general, sequence mining problems can be classified as ''string mining'' which is typically based on string processing algorithms and ''itemset mining'' which is typically based on association rule learning. ''Local process models'' extend sequential pattern mining to more complex patterns that can incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Mining
Data mining is the process of extracting and finding patterns in massive data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. Data mining is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and statistics with an overall goal of extracting information (with intelligent methods) from a data set and transforming the information into a comprehensible structure for further use. Data mining is the analysis step of the " knowledge discovery in databases" process, or KDD. Aside from the raw analysis step, it also involves database and data management aspects, data pre-processing, model and inference considerations, interestingness metrics, complexity considerations, post-processing of discovered structures, visualization, and online updating. The term "data mining" is a misnomer because the goal is the extraction of patterns and knowledge from large amounts of data, not the extraction (''mining'') of data itself. It also is a buzzwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
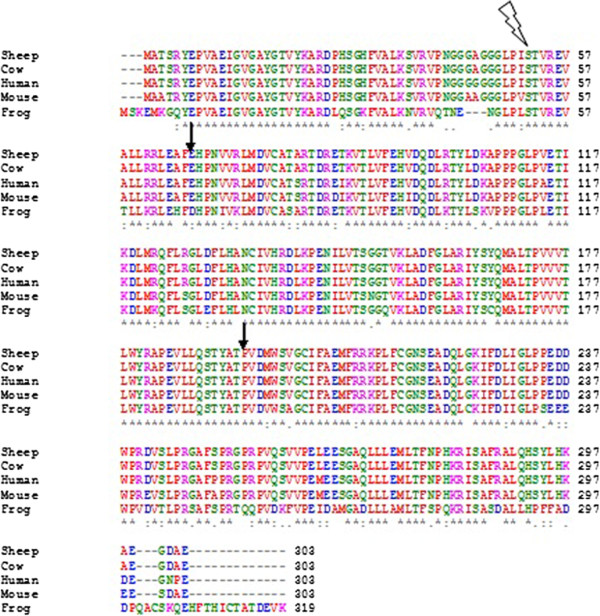
Insertion (genetics)
In genetics, an insertion (also called an insertion mutation) is the addition of one or more nucleotide base pairs into a DNA sequence. This can often happen in Microsatellite (genetics), microsatellite regions due to the DNA polymerase slipping. Insertions can be anywhere in size from one base pair incorrectly inserted into a DNA sequence to a section of one chromosome inserted into another. The mechanism of the smallest single base insertion mutations is believed to be through base-pair separation between the template and primer strands followed by non-neighbor base stacking, which can occur locally within the DNA polymerase active site. On a chromosome level, an ''insertion'' refers to the insertion of a larger sequence into a chromosome. This can happen due to unequal Chromosomal crossover, crossover during meiosis. N region addition is the addition of non-coded nucleotides during genetic recombination, recombination by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. P nucleotide ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Mining
Data mining is the process of extracting and finding patterns in massive data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. Data mining is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and statistics with an overall goal of extracting information (with intelligent methods) from a data set and transforming the information into a comprehensible structure for further use. Data mining is the analysis step of the " knowledge discovery in databases" process, or KDD. Aside from the raw analysis step, it also involves database and data management aspects, data pre-processing, model and inference considerations, interestingness metrics, complexity considerations, post-processing of discovered structures, visualization, and online updating. The term "data mining" is a misnomer because the goal is the extraction of patterns and knowledge from large amounts of data, not the extraction (''mining'') of data itself. It also is a buzzwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug tracking system, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, GitHub, Inc. has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. GitHub reported having over 100 million developers and more than 420 million Repository (version control), repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the world's largest source code host Over five billion developer contributions were made to more than 500 million open source projects in 2024. About Founding The development of the GitHub platform began on October 19, 2005. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSP Algorithm
GSP algorithm (''Generalized Sequential Pattern'' algorithm) is an algorithm used for sequence mining. The algorithms for solving sequence mining problems are mostly based on the '' apriori'' (level-wise) algorithm. One way to use the level-wise paradigm is to first discover all the frequent items in a level-wise fashion. It simply means counting the occurrences of all singleton elements in the database. Then, the transactions are filtered by removing the non-frequent items. At the end of this step, each transaction consists of only the frequent elements it originally contained. This modified database becomes an input to the GSP algorithm. This process requires one pass over the whole database. GSP algorithm makes multiple database passes. In the first pass, all single items (1-sequences) are counted. From the frequent items, a set of candidate 2-sequences are formed, and another pass is made to identify their frequency. The frequent 2-sequences are used to generate the candidate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buying Pattern
Consumer behaviour is the study of individuals, groups, or organisations and all activities associated with the Purchasing, purchase, Utility, use and disposal of goods and services. It encompasses how the consumer's emotions, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and Preference (economics), preferences affect Buyer decision process, buying behaviour, and how external cues—such as visual prompts, auditory signals, or tactile (haptic) feedback—can shape those responses. Consumer behaviour emerged in the 1940–1950s as a distinct sub-discipline of marketing, but has become an Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary social science that blends elements from psychology, sociology, Social Anthropology, social anthropology, anthropology, ethnography, ethnology, marketing, and economics (especially behavioural economics). The study of consumer behaviour formally investigates individual qualities such as demographics, personality lifestyles, and behavioural variables (like usage rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apriori Algorithm
AprioriRakesh Agrawal and Ramakrishnan SrikanFast algorithms for mining association rules Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases, VLDB, pages 487-499, Santiago, Chile, September 1994. is an algorithm for frequent item set mining and association rule learning over relational databases. It proceeds by identifying the frequent individual items in the database and extending them to larger and larger item sets as long as those item sets appear sufficiently often in the database. The frequent item sets determined by Apriori can be used to determine association rules which highlight general trends in the database: this has applications in domains such as market basket analysis. Overview The Apriori algorithm was proposed by Agrawal and Srikant in 1994. Apriori is designed to operate on databases containing transactions (for example, collections of items bought by customers, or details of a website frequentation or IP addresses). Other algorithms are de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association Rule Learning
Association rule learning is a rule-based machine learning method for discovering interesting relations between variables in large databases. It is intended to identify strong rules discovered in databases using some measures of interestingness.Piatetsky-Shapiro, Gregory (1991), ''Discovery, analysis, and presentation of strong rules'', in Piatetsky-Shapiro, Gregory; and Frawley, William J.; eds., ''Knowledge Discovery in Databases'', AAAI/MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. In any given transaction with a variety of items, association rules are meant to discover the rules that determine how or why certain items are connected. Based on the concept of strong rules, Rakesh Agrawal, Tomasz Imieliński and Arun Swami introduced association rules for discovering regularities between products in large-scale transaction data recorded by point-of-sale (POS) systems in supermarkets. For example, the rule \ \Rightarrow \ found in the sales data of a supermarket would indicate that if a customer bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Alignment
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural biology, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are typically represented as rows within a matrix (mathematics), matrix. Gaps are inserted between the Residue (chemistry), residues so that identical or similar characters are aligned in successive columns. Sequence alignments are also used for non-biological sequences such as calculating the Edit distance, distance cost between strings in a natural language, or to display financial data. Interpretation If two sequences in an alignment share a common ancestor, mismatches can be interpreted as point mutations and gaps as indels (that is, insertion or deletion mutations) introduced in one or both lineages in the time since they diverged from one another. In sequence ali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ClustalW
Clustal is a computer program used for multiple sequence alignment in bioinformatics. The software and its algorithms have gone through several iterations, with ClustalΩ (Omega) being the latest version . It is available as standalone software, via a web interface, and through a server hosted by the European Bioinformatics Institute. Clustal has been an important bioinformatic software, with two of its academic publications amongst the top 100 papers cited of all time, according to Nature in 2014. History Version history * Clustal: The original software for multiple sequence alignments, created by Des Higgins in 1988, was based on deriving a guide tree from pairwise sequences of amino acids or nucleotides. * ClustalV: The second generation of Clustal, released in 1992. It introduced the ability to create new alignments from existing alignments in a process known as phylogenetic tree reconstruction. ClustalV also added the option to create trees using the neighbor joini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BLAST (biotechnology)
In bioinformatics, BLAST (basic local alignment search tool) is an algorithm and program for comparing Primary structure, primary biological sequence information, such as the amino acid, amino-acid sequences of proteins or the nucleotides of DNA sequence, DNA and/or RNA sequences. A BLAST search enables a researcher to compare a subject protein or nucleotide sequence (called a query) with a library or database of sequences, and identify database sequences that resemble the query sequence above a certain threshold. For example, following the discovery of a previously unknown gene in the Mus musculus, mouse, a scientist will typically perform a BLAST search of the human genome to see if humans carry a similar gene; BLAST will identify sequences in the human genome that resemble the mouse gene based on similarity of sequence. Background BLAST is one of the most widely used bioinformatics programs for sequence searching. It addresses a fundamental problem in bioinformatics research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Approximate String Matching
In computer science, approximate string matching (often colloquially referred to as fuzzy string searching) is the technique of finding strings that match a pattern approximately (rather than exactly). The problem of approximate string matching is typically divided into two sub-problems: finding approximate substring matches inside a given string and finding dictionary strings that match the pattern approximately. Overview The closeness of a match is measured in terms of the number of primitive operations necessary to convert the string into an exact match. This number is called the edit distance between the string and the pattern. The usual primitive operations are: * insertion: ''cot'' → ''coat'' * deletion: ''coat'' → ''cot'' * substitution: ''coat'' → ''cost'' These three operations may be generalized as forms of substitution by adding a NULL character (here symbolized by *) wherever a character has been deleted or inserted: * insertion: ''co*t'' → ''coat'' * del ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |