|
Sea Surface Skin Temperature
The sea surface skin temperature (SSTskin), or ocean skin temperature, is the temperature of the sea surface as determined through its infrared spectrum (3.7–12 μm) and represents the temperature of the sublayer of water at a depth of 10–20 μm. High-resolution data of skin temperature gained by satellites in passive infrared measurements is a crucial constituent in determining the sea surface temperature (SST). Since the skin layer is in radiative equilibrium with the atmosphere and the sun, its temperature underlies a daily cycle. Even small changes in the skin temperature can lead to large changes in atmospheric circulation. This makes skin temperature a widely used quantity in weather forecasting and climate science. Remote Sensing Large-scale sea surface skin temperature measurements started with the use of satellites in remote sensing. The underlying principle of this kind of measurement is to determine the surface temperature via its black body spectrum. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retrieval Algorithms
Retrieval may refer to: Computer science * RETRIEVE, Tymshare database that inspired dBASE and others * Data retrieval * Document retrieval * Image retrieval * Information retrieval Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the task of identifying and retrieving information system resources that are relevant to an Information needs, information need. The information need can be specified in the form ... * Knowledge retrieval * Medical retrieval * Music information retrieval * Text retrieval Psychology *The process of recall (memory), recalling information that is stored in memory ("memory retrieval") Film * Retrieval (film), ''Retrieval'' (film), a 2006 Polish film * ''The Retrieval'', a 2013 American drama film by Chris Eska Television * Retrieval (Star Wars: The Bad Batch), "Retrieval" (''Star Wars: The Bad Batch'') {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
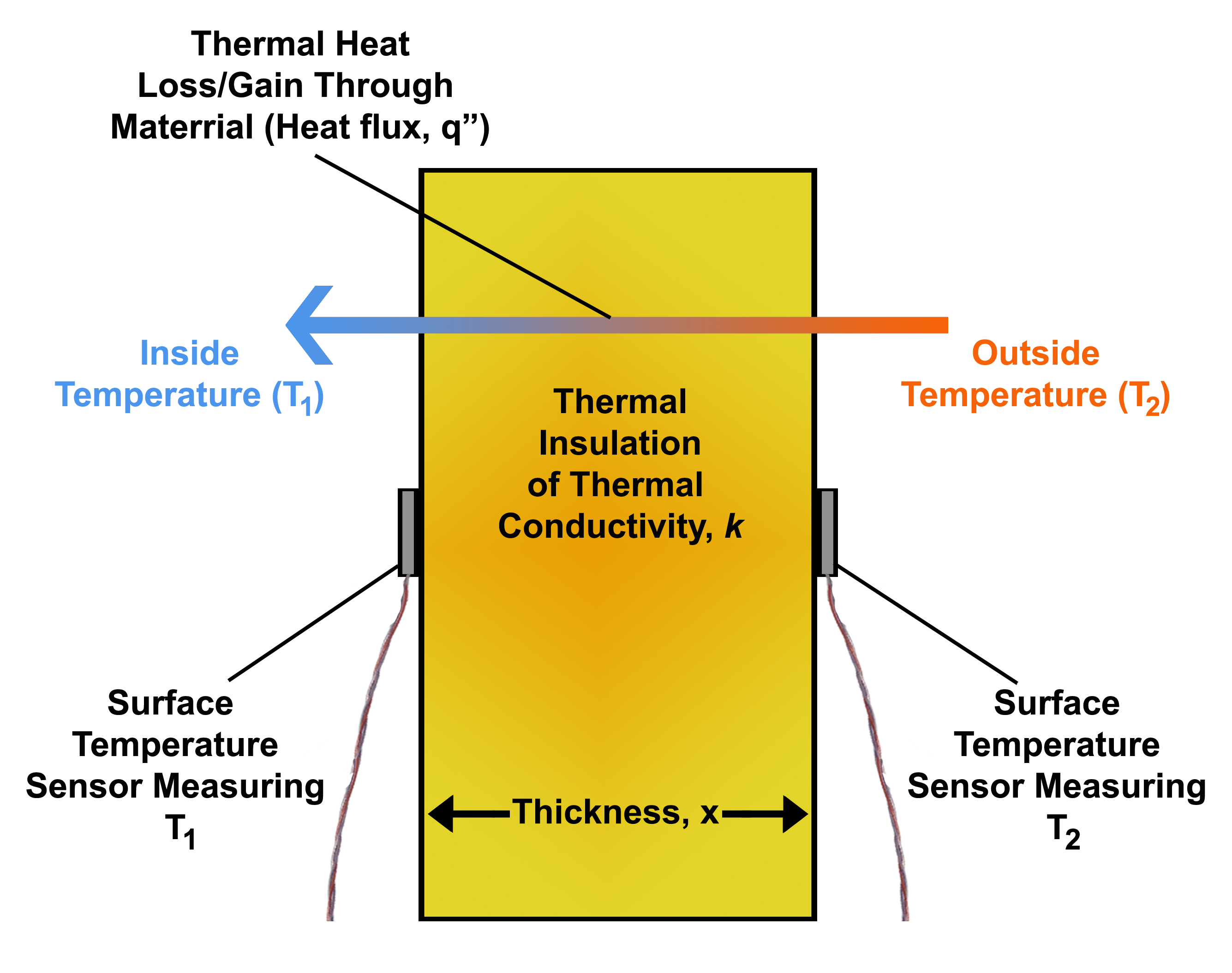
Heat Flux
In physics and engineering, heat flux or thermal flux, sometimes also referred to as heat flux density, heat-flow density or heat-flow rate intensity, is a flow of energy per unit area per unit time (physics), time. Its SI units are watts per square metre (W/m2). It has both a direction and a magnitude, and so it is a Vector (geometric), vector quantity. To define the heat flux at a certain point in space, one takes the Limiting case (mathematics), limiting case where the size of the surface becomes infinitesimally small. Heat flux is often denoted \vec_\mathrm, the subscript specifying ''heat'' flux, as opposed to ''Mass flux, mass'' or Transport phenomena, ''momentum'' flux. Heat conduction#Fourier's law, Fourier's law is an important application of these concepts. Fourier's law For most solids in usual conditions, heat is transported mainly by thermal conduction, conduction and the heat flux is adequately described by Fourier's law. Fourier's law in one dimension \phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electronic, molecular, and lattice oscillations in a material. Kinetic energy is converted to electromagnetism due to charge-acceleration or dipole oscillation. At room temperature, most of the emission is in the infrared (IR) spectrum, though above around 525 °C (977 °F) enough of it becomes visible for the matter to visibly glow. This visible glow is called incandescence. Thermal radiation is one of the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer, along with conduction and convection. The primary method by which the Sun transfers heat to the Earth is thermal radiation. This energy is partially absorbed and scattered in the atmosphere, the latter process being the reason why the sky is visibly blue. Much of the Sun's radiation tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensible Heat
Sensible heat is heat exchanged by a body or thermodynamic system in which the exchange of heat changes the temperature of the body or system, and some macroscopic variables of the body or system, but leaves unchanged certain other macroscopic variables of the body or system, such as volume or pressure. Usage The term is used in contrast to a latent heat, which is the amount of heat exchanged that is hidden, meaning it occurs without change of temperature. For example, during a phase change such as the melting of ice, the temperature of the system containing the ice and the liquid is constant until all ice has melted. Latent and sensible heat are complementary terms. The sensible heat of a thermodynamic process may be calculated as the product of the body's mass (''m'') with its specific heat capacity (''c'') and the change in temperature (\Delta T): : Q_ = m c \Delta T \, . ''Sensible heat'' and ''latent heat'' are not special forms of energy. Rather, they describe exchanges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Heat
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process—usually a first-order phase transition, like melting or condensation. Latent heat can be understood as hidden energy which is supplied or extracted to change the state of a substance without changing its temperature or pressure. This includes the latent heat of fusion (solid to liquid), the latent heat of vaporization (liquid to gas) and the latent heat of sublimation (solid to gas). The term was introduced around 1762 by Scottish chemist Joseph Black. Black used the term in the context of calorimetry where a heat transfer caused a volume change in a body while its temperature was constant. In contrast to latent heat, sensible heat is energy transferred as heat, with a resultant temperature change in a body. Usage The terms ''sensible heat'' and ''latent heat'' refer to energy transferred between a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
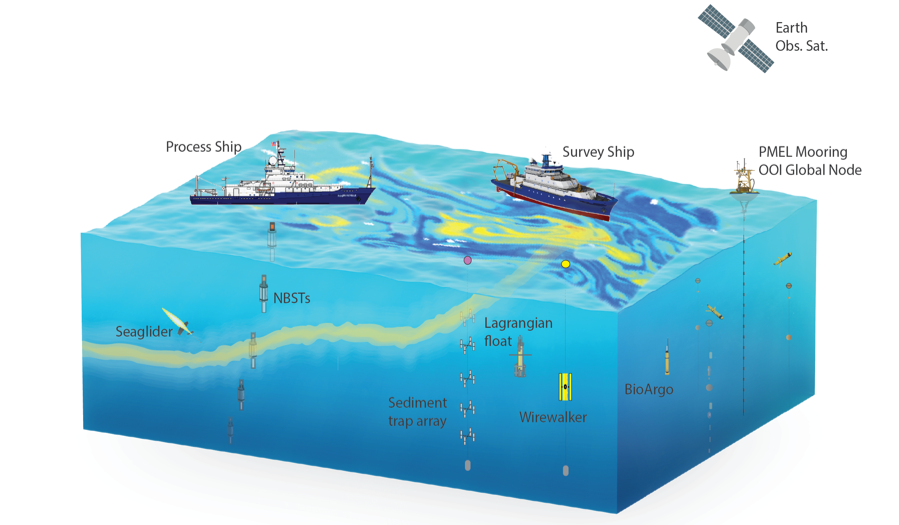
Research Vessel
A research vessel (RV or R/V) is a ship or boat designed, modified, or equipped to carry out research at sea. Research vessels carry out a number of roles. Some of these roles can be combined into a single vessel but others require a dedicated vessel. Due to the demanding nature of the work, research vessels may be constructed around an icebreaker hull, allowing them to operate in polar waters. History The research ship had origins in the early voyages of exploration. By the time of James Cook's ''Endeavour'', the essentials of what today we would call a research ship are clearly apparent. In 1766, the Royal Society hired Cook to travel to the Pacific Ocean to observe and record the transit of Venus across the Sun. The ''Endeavour'' was a sturdy vessel, well designed and equipped for the ordeals she would face, and fitted out with facilities for her "research personnel", Joseph Banks. As is common with contemporary research vessels, ''Endeavour'' also carried out more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Buoy
Weather buoys are instruments which collect weather and ocean data within the world's oceans, as well as aid during emergency response to chemical spills, legal proceedings, and engineering design. Moored buoys have been in use since 1951, while drifting buoys have been used since 1979. Moored buoys are connected with the ocean bottom using either chains, nylon, or buoyant polypropylene. With the decline of the weather ship, they have taken a more primary role in measuring conditions over the open seas since the 1970s. During the 1980s and 1990s, a network of buoys in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean helped study the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Moored weather buoys range from in diameter, while drifting buoys are smaller, with diameters of . Drifting buoys are the dominant form of weather buoy in sheer number, with 1250 located worldwide. Wind data from buoys has smaller error than that from ships. There are differences in the values of sea surface tempe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbulent Heat Transport
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers with no disruption between those layers. Turbulence is commonly observed in everyday phenomena such as surf, fast flowing rivers, billowing storm clouds, or smoke from a chimney, and most fluid flows occurring in nature or created in engineering applications are turbulent. Turbulence is caused by excessive kinetic energy in parts of a fluid flow, which overcomes the damping effect of the fluid's viscosity. For this reason, turbulence is commonly realized in low viscosity fluids. In general terms, in turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear of many sizes which interact with each other, consequently drag due to friction effects increases. The onset of turbulence can be predicted by the dimensionless Reynolds number, the ratio of kinetic energy to viscous damping in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscous Heat Transport
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Thus its SI units are newton-seconds per metre squared, or pascal-seconds. Viscosity quantifies the internal frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's center line than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube with a constant rate of flow, the strengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |