|
Schistosoma Mansoni
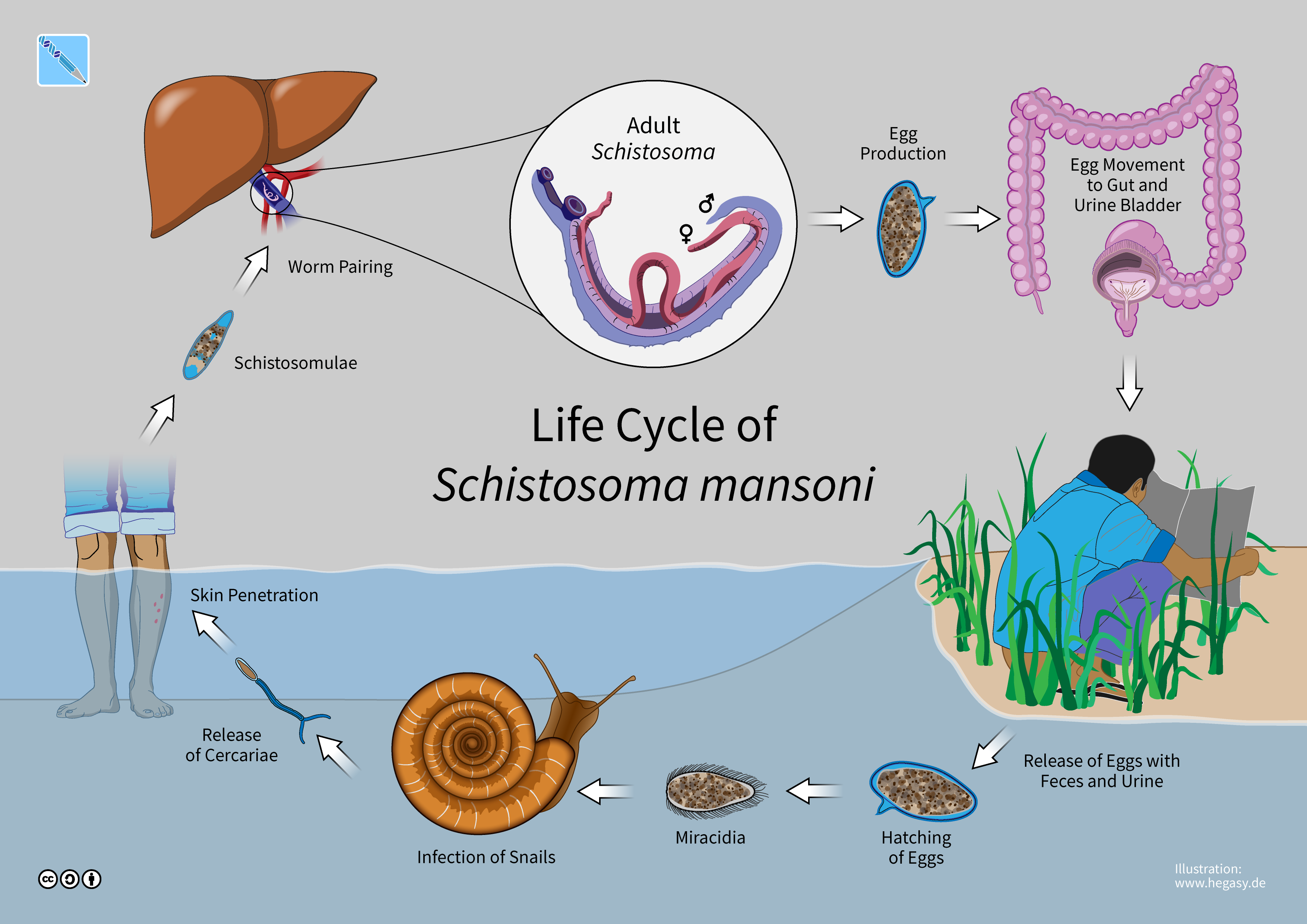
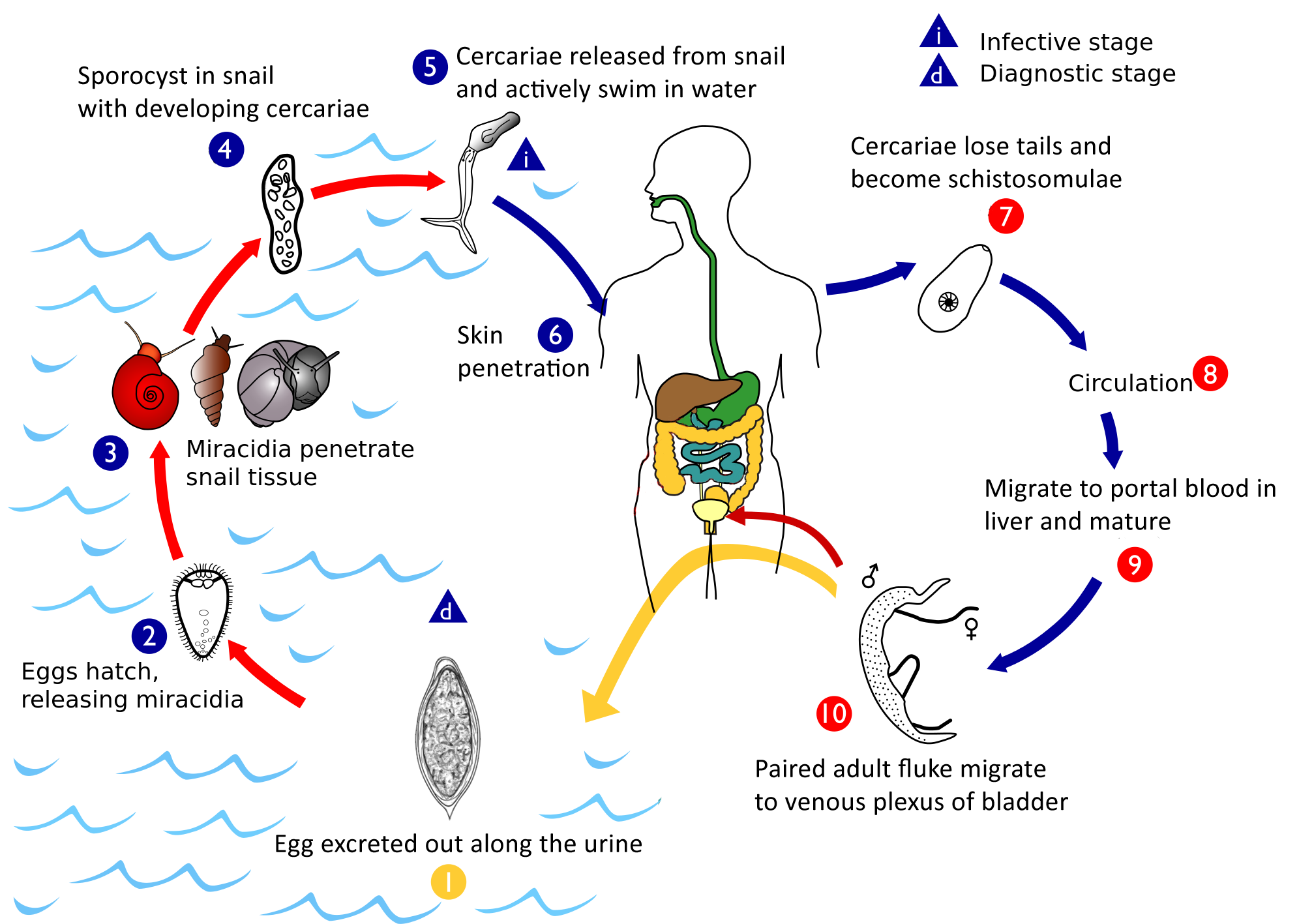
A paired couple of ''Schistosoma mansoni''. ''Schistosoma mansoni'' is a water-borne parasite of humans, and belongs to the group of blood flukes (''Schistosoma''). The adult lives in the blood vessels ( mesenteric veins) near the human intestine. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis (similar to '' S. japonicum'', '' S. mekongi'', ''S. guineensis'', and '' S. intercalatum''). Clinical symptoms are caused by the eggs. As the leading cause of schistosomiasis in the world, it is the most prevalent parasite in humans. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease. As of 2021, the World Health Organization reports that 251.4 million people have schistosomiasis and most of it is due to ''S. mansoni''. It is found in Africa, the Middle East, the Caribbean, Brazil, Venezuela and Suriname. Unlike other flukes (trematodes) in which sexes are not separate (monoecious), schistosomes are unique in that adults are divided into males and females, thus, gonochoric. However, a permanent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Westenra Sambon
Louis Westenra Sambon (original first name Luigi, 7 November 1867 – 30 August 1931) was an Italian-English physician who played important roles in understanding the causes (etiology) of diseases. He described many pathogenic protozoans, insects, and helminths including the name '' Schistosoma mansoni'' for a blood fluke. He was an authority on the classification of parasitic tongue worms called Pentastomida (Linguatulida), and one of the genus ''Sambonia'' is named after him. Sambon was born in Milan, Italy, and obtained an M.D. from the University of Naples Federico II. He moved to England to work at the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine. He originated theories on the nature of diseases such as sleeping sickness, malaria, pellagra, and cancer. Biography Sambon was born in Milan to an Italian father and an English mother. His father was an Italian soldier Commendatore (Commander) Jules Sambon, and her mother, Laura Elizabeth Day, was a distant relative of Charles Dickens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomphalaria
''Biomphalaria'' is a genus of air-breathing freshwater snails, aquatic pulmonates belonging to the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails and their allies. ''Biomphalaria'' is the type genus of the tribe Biomphalariini. Both ''Planorbis'' and ''Taphius'' are synonyms for ''Biomphalaria''. The shell of this species, like all planorbids is left coiling (sinistral), but is carried upside down and thus appears to be right coiling (dextral). Species There are a suspected 35 extant species in the genus ''Biomphalaria'' in total (21 American species and 14 Old World species). However, there are a large number of invalid taxa within the ''Biomphalaria'' literature, which is likely the result of several (if not all) species of ''Biomphalaria'' being subject to various sources of intraspecific variation such as ecophenotypic variation and indeterminate shell growth. This intraspecific variation can make two individuals of the same species appear as two taxonomically distinct ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will degenerate in the body. Normally, these are paired structures, but in birds and some cartilaginous fishes, one or the other side fails to develop (together with the corresponding ovary), and only one functional oviduct can be found. Except in teleosts, the oviduct is not directly in contact with the ovary. Instead, the most anterior portion ends in a funnel-shaped structure called the infundibulum, which collects eggs as they are released by the ovary into the body cavity. The only female vertebrates to lack oviducts are the jawless fishes. In these species, the single fused ovary releases eggs directly into the body cavity. The fish eventually extrudes the eggs through a small genital pore towards the rear of the body. Fish and amphibia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocrine glands, secreting various hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. Structure Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The ovaries are surrounded by a capsule, and have an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The capsule is of dense connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemozoin
Haemozoin is a disposal product formed from the digestion of blood by some blood-feeding parasites. These hematophagy, hematophagous organisms such as malaria parasites (''Plasmodium spp.''), ''Rhodnius'' and ''Schistosoma'' digest haemoglobin and release high quantities of free heme, which is the non-protein component of haemoglobin. Heme is a prosthetic group consisting of an iron atom contained in the center of a heterocyclic porphyrin ring. Free heme is toxic to cells, so the parasites convert it into an insoluble crystalline form called hemozoin. In malaria parasites, hemozoin is often called ''malaria pigment''. Since the formation of hemozoin is essential to the survival of these parasites, it is an attractive target for drug development, developing drugs and is much-studied in ''Plasmodium'' as a way to find drugs to treat malaria (malaria's Achilles' heel). Several currently used antimalarial drugs, such as chloroquine and mefloquine, are thought to kill malaria parasites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundworm
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (helminths) are the cause of soil-transmitted helminthiases. They are classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa. Unlike the flatworms, nematodes have a tubular digestive system, with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species are uncertain. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity suggested there are over 25,000. Estimates of the total number of extant species are subject to ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio De Janeiro, RJ
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the Rio de Janeiro (state), state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the List of cities in Brazil by population, second-most-populous city in Brazil (after São Paulo) and the Largest cities in the Americas, sixth-most-populous city in the Americas. Founded in 1565 by the Portuguese people, Portuguese, the city was initially the seat of the Captaincy of Rio de Janeiro, a domain of the Portuguese Empire. In 1763, it became the capital of the State of Brazil, a List of states of the Portuguese Empire, state of the Portuguese Empire. In 1808, when the Transfer of the Portuguese Court to Brazil, Portuguese Royal Court moved to Brazil, Rio de Janeiro became the seat of the court of Queen Maria I of Portugal. She subsequently, under the leadership of her son the prince regent John VI of Portugal, raised Brazil to the dignity of a kingdom, within the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves, United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil, and Algar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal. In plants A tubercle is generally a wart-like projection, but it has slightly different meaning depending on which family of plants or animals it is used to refer to. In the case of certain orchids and cacti, it denotes a round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on the lip. They are also known as podaria (singular ''podarium''). When referring to some members of the pea family, it is used to refer to the wart-like excrescences that are found on the roots. In fungi In mycology, a tubercle is used to refer to a mass of hyphae from which a mushroom is made. In animals When it is used in relation to certain dorid nudibranchs such as '' Peltodoris nobilis'', it means the nodules on the dorsum of the animal. The tubercles in nudibranchs can present themselves in different way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sucker (zoology)
A sucker in zoology is a specialised attachment organ of an animal. It acts as an adhesion device in parasitic worms, several flatworms, cephalopods, certain fishes, amphibians, and bats. It is a muscular structure for suction on a host or substrate. In parasitic annelids, flatworms and roundworms, suckers are the organs of attachment to the host tissues. In tapeworms and flukes, they are a parasitic adaptation for attachment on the internal tissues of the host, such as intestines and blood vessels. In roundworms and flatworms they serve as attachment between individuals particularly during mating. In annelids, a sucker can be both a functional mouth and a locomotory organ. The structure and number of suckers are often used as basic taxonomic diagnosis between different species, since they are unique in each species. In tapeworms there are two distinct classes of suckers, namely "bothridia" for true suckers, and " bothria" for false suckers. In digeneal flukes there are usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexually Dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, dioecious species, which consist of most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, color, markings, or behavioral or cognitive traits. Male-male reproductive competition has evolved a diverse array of sexually dimorphic traits. Aggressive utility traits such as "battle" teeth and blunt heads reinforced as battering rams are used as weapons in aggressive interactions between rivals. Passive displays such as ornamental feathering or song-calling have also evolved mainly through sexual selection. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', when both biological sexes are phenotype, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrick Manson
Sir Patrick Manson (3 October 1844 – 9 April 1922) was a Scottish physician who made important discoveries in parasitology, and was a founder of the field of tropical medicine. He graduated from the University of Aberdeen with degrees in Master of Surgery, Doctor of Medicine and Doctor of law, Doctor of Law. His medical career spanned mainland China, Hong Kong, Taiwan Island, Taiwan and London. He discovered that filariasis in humans is transmitted by mosquitoes. This is the foundation of modern tropical medicine, and he is recognized with an epithet "Father of Tropical Medicine". This also made him the first person to show pathogen transmission by a blood-feeding arthropod. His discovery directly invoked the mosquito-malaria theory, which became the foundation in malariology. He eventually became the first President of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. He founded the Hong Kong College of Medicine for Chinese (subsequently absorbed into the University of Hon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistosoma Haematobium
''Schistosoma haematobium'' (urinary blood fluke) is a species of digenetic trematode, belonging to a group (genus) of blood flukes (''Schistosoma''). It is found in Africa and the Middle East. It is the major agent of schistosomiasis, the most prevalent parasitic infection in humans. It is the only blood fluke that infects the urinary tract, causing urinary schistosomiasis, and is a leading cause of bladder cancer (only next to tobacco smoking). The diseases are caused by the eggs. Adults are found in the venous plexuses around the urinary bladder and the released eggs travel to the wall of the urine bladder causing haematuria and fibrosis of the bladder. The bladder becomes calcified, and there is increased pressure on ureters and kidneys otherwise known as hydronephrosis. Inflammation of the genitals due to ''S. haematobium'' may contribute to the propagation of HIV. ''S. haematobium'' was the first blood fluke discovered. Theodor Bilharz, a German surgeon working in Cai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |