|
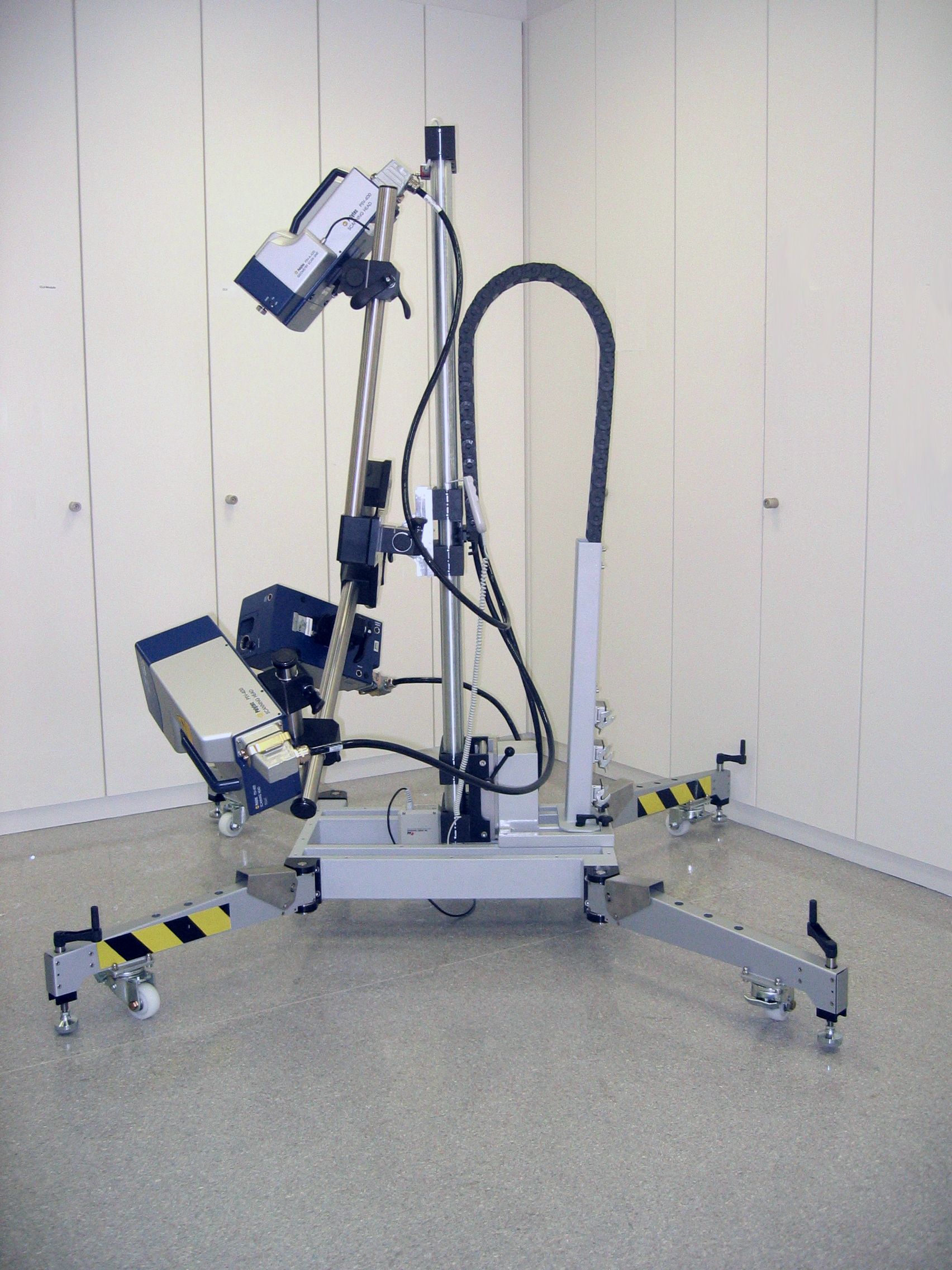
Scanning Laser Doppler Vibrometry
The scanning laser vibrometer or scanning laser Doppler vibrometer, was first developed by the British loudspeaker company, Celestion, around 1979, further developed in the 1980s,Stoffregen, B., Felske, A., “Scanning Laser Doppler Analysis System,” SAE Paper No. 850327, 1985. and commercially introduced by Ometron, Ltd around 1986. It is an instrument for rapid non-contact measurement and imaging of vibration. Fields where they are applied include automotive, medical, aerospace, micro system and information technology as well as for quality and production control. The optimization of vibration and acoustic behavior are important goals of product development in all of these fields because they are often among the key characteristics that determine a product's success in the market. They are also in widespread use throughout many universities conducting basic and applied research in areas that include structural dynamics, modal analysis, acoustic optimization and non-destruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler Effect
The Doppler effect (also Doppler shift) is the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. The ''Doppler effect'' is named after the physicist Christian Doppler, who described the phenomenon in 1842. A common example of Doppler shift is the change of pitch heard when a vehicle sounding a horn approaches and recedes from an observer. Compared to the emitted frequency, the received frequency is higher during the approach, identical at the instant of passing by, and lower during the recession. When the source of the sound wave is moving towards the observer, each successive cycle of the wave is emitted from a position closer to the observer than the previous cycle. Hence, from the observer's perspective, the time between cycles is reduced, meaning the frequency is increased. Conversely, if the source of the sound wave is moving away from the observer, each cycle of the wave is emitted from a position farther from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metrology
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of Unit of measurement, units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in France when a length standard taken from a natural source was proposed. This led to the creation of the decimal-based metric system in 1795, establishing a set of standards for other types of measurements. Several other countries adopted the metric system between 1795 and 1875; to ensure conformity between the countries, the ''International Bureau of Weights and Measures, Bureau International des Poids et Mesures'' (BIPM) was established by the Metre Convention. This has evolved into the International System of Units (SI) as a result of a resolution at the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) in 1960. Metrology is divided into three basic overlapping activities: * The definition of units of measurement * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Validation
In statistics, model validation is the task of evaluating whether a chosen statistical model is appropriate or not. Oftentimes in statistical inference, inferences from models that appear to fit their data may be flukes, resulting in a misunderstanding by researchers of the actual relevance of their model. To combat this, model validation is used to test whether a statistical model can hold up to permutations in the data. Model validation is also called model criticism or model evaluation. This topic is not to be confused with the closely related task of model selection, the process of discriminating between multiple candidate models: model validation does not concern so much the conceptual design of models as it tests only the consistency between a chosen model and its stated outputs. There are many ways to validate a model. Residual plots plot the difference between the actual data and the model's predictions: correlations in the residual plots may indicate a flaw in the model. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Element
Finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential. Computers are usually used to perform the calculations required. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved and are often required to solve the largest and most complex problems. FEM is a general numerical method for solving partial differential equations in two- or three-space variables (i.e., some boundary value problems). There are also studies about using FEM to solve high-dimensional problems. To solve a problem, FEM subdivides a large system into smaller, simpler parts called finite elements. This is achieved by a particular space discretization in the space dimensions, which is implemented by the construction of a mesh of the object: the numerica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula 1
Formula One (F1) is the highest class of worldwide racing for open-wheel single-seater formula Auto racing, racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one of the world's premier forms of motorsport since its 1950 Formula One season, inaugural running in 1950 and is often considered to be the pinnacle of motorsport. The word ''Formula racing, formula'' in the name refers to Formula One regulations, the set of rules all participant cars must follow. A Formula One season consists of a series of races, known as List of Formula One Grands Prix, Grands Prix. Grands Prix take place in multiple countries and continents on either purpose-built List of Formula One circuits, circuits or closed roads. A List of Formula One World Championship points scoring systems, points scoring system is used at Grands Prix to determine two annual World Championships: List of Formula One World Drivers' Champions, one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microstructure
Microstructure is the very small scale structure of a material, defined as the structure of a prepared surface of material as revealed by an optical microscope above 25× magnification. The microstructure of a material (such as metals, polymers, ceramics or composites) can strongly influence physical properties such as strength, toughness, ductility, hardness, corrosion resistance, high/low temperature behaviour or wear resistance. These properties in turn govern the application of these materials in industrial practice. Microstructure at scales smaller than can be viewed with optical microscopes is often called nanostructure, while the structure in which individual atoms are arranged is known as crystal structure. The nanostructure of biological specimens is referred to as ultrastructure. A microstructure's influence on the mechanical and physical properties of a material is primarily governed by the different defects present or absent of the structure. These defects can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Propagation
In physics, mathematics, engineering, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from equilibrium) of one or more quantities. '' Periodic waves'' oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (resting) value at some frequency. When the entire waveform moves in one direction, it is said to be a travelling wave; by contrast, a pair of superimposed periodic waves traveling in opposite directions makes a '' standing wave''. In a standing wave, the amplitude of vibration has nulls at some positions where the wave amplitude appears smaller or even zero. There are two types of waves that are most commonly studied in classical physics: mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. In a mechanical wave, stress and strain fields oscillate about a mechanical equilibrium. A mechanical wave is a local deformation (strain) in some physical medium that propagates from particle to particle by creating local stresses that cause strain in neighboring particles too ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Domain
In mathematics and signal processing, the time domain is a representation of how a signal, function, or data set varies with time. It is used for the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental data. In the time domain, the independent variable is time, and the dependent variable is the value of the signal. This contrasts with the frequency domain, where the signal is represented by its constituent frequencies. For continuous-time signals, the value of the signal is defined for all real numbers representing time. For discrete-time signals, the value is known at discrete, often equally-spaced, time intervals. It is commonly visualized using a graph where the x-axis represents time and the y-axis represents the signal's value. An oscilloscope is a common tool used to visualize real-world signals in the time domain. Though most precisely referring to time in physics, the term ''time domain'' may occasionally informally ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Domain
In mathematics, physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency (and possibly phase), rather than time, as in time series. While a time-domain graph shows how a signal changes over time, a frequency-domain graph shows how the signal is distributed within different frequency bands over a range of frequencies. A complex valued frequency-domain representation consists of both the magnitude and the phase of a set of sinusoids (or other basis waveforms) at the frequency components of the signal. Although it is common to refer to the magnitude portion (the real valued frequency-domain) as the frequency response of a signal, the phase portion is required to uniquely define the signal. A given function or signal can be converted between the time and frequency domains with a pair of mathematical operators called transforms. An example is the Fourier transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrometer
A laser Doppler vibrometer (LDV) is a scientific instrument that is used to make non-contact vibration measurements of a surface. The laser beam from the LDV is directed at the surface of interest, and the vibration amplitude and frequency are extracted from the Doppler shift of the reflected laser beam frequency due to the motion of the surface. The output of an LDV is generally a continuous analog voltage that is directly proportional to the target velocity component along the direction of the laser beam. Some advantages of an LDV over similar measurement devices such as an accelerometer are that the LDV can be directed at targets that are difficult to access, or that may be too small or too hot to attach a physical transducer. Also, the LDV makes the vibration measurement without mass-loading the target, which is especially important for MEMS devices. Principles of operation A vibrometer is generally a two beam laser interferometer that measures the frequency (or phase) diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-destructive Evaluation
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definition is invasive, and many operations requiring incisions of some size are referred to as ''open surgery''. Incisions made during open surgery can sometimes leave large wounds that may be painful and take a long time to heal. Advancements in medical technologies have enabled the development and regular use of minimally invasive procedures. For example, endovascular aneurysm repair, a minimally invasive surgery, has become the most common method of repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in the US as of 2003. The procedure involves much smaller incisions than the corresponding open surgery procedure of open aortic surgery. Interventional radiologists were the forerunners of minimally invasive procedures. Using imaging techniques, radiolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |