|
Salt Tectonics
upright=1.7 Salt tectonics, or halokinesis, or halotectonics, is concerned with the geometries and processes associated with the presence of significant thicknesses of evaporites containing rock salt within a stratigraphic sequence of rocks. This is due both to the low density of salt, which does not increase with burial, and its low strength. Salt structures (excluding undeformed layers of salt) have been found in more than 120 sedimentary basins around the world. Passive salt structures Structures may form during continued sedimentary loading, without any external tectonic influence, due to gravitational instability. Pure halite has a density of 2160 kg/m3. When initially deposited, sediments generally have a lower density of 2000 kg/m3, but with loading and compaction their density increases to 2500 kg/m3, which is greater than that of salt. Once the overlying layers have become denser, the weak salt layer will tend to deform into a characteristic series of rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Tectonics
Thrust tectonics or contractional tectonics is concerned with the structures formed by, and the Tectonics, tectonic processes associated with, the shortening and thickening of the Crust (geology), crust or lithosphere. It is one of the three main types of tectonic regime, the others being extensional tectonics and strike-slip tectonics. These match the three types of plate tectonics, plate boundary, convergent boundary, convergent (thrust), divergent boundary, divergent (extensional) and transform fault, transform (strike-slip). There are two main types of thrust tectonics, thin-skinned and thick-skinned, depending on whether or not basement rocks are involved in the deformation. The principle geological environments where thrust tectonics is observed are zones of continental collision, restraining bends on strike-slip faults and as part of detached fault systems on some passive margins. Deformation styles In areas of thrust fault, thrust tectonics, two main processes are recognize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for separating the New World of the Americas (North America and South America) from the Old World of Afro-Eurasia (Africa, Asia, and Europe). Through its separation of Afro-Eurasia from the Americas, the Atlantic Ocean has played a central role in the development of human society, globalization, and the histories of many nations. While the Norse were the first known humans to cross the Atlantic, it was the expedition of Christopher Columbus in 1492 that proved to be the most consequential. Columbus's expedition ushered in an age of exploration and colonization of the Americas by European powers, most notably Portugal, Spain, France, and the United Kingdom. From the 16th to 19th centuries, the Atlantic Ocean was the center of both an epo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq. The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western European nations in the early 20th century as a replacement of the term Near East (both were in contrast to the Far East). The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions. Since the late 20th century, it has been criticized as being too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of West Asia, but without the South Caucasus. It also includes all of Egypt (not just the Sinai Peninsula, Sinai) and all of Turkey (including East Thrace). Most Middle Eastern countries (13 out of 18) are part of the Arab world. The list of Middle Eastern countries by population, most populous countries in the region are Egypt, Turkey, and Iran, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southwest and south by the Mexican states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatán, and Quintana Roo; and on the southeast by Cuba. The coastal areas along the Southern U.S. states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, which border the Gulf on the north, are occasionally referred to as the "Third Coast" of the United States (in addition to its Atlantic and Pacific coasts), but more often as "the Gulf Coast". The Gulf of Mexico took shape about 300 million years ago (mya) as a result of plate tectonics. The Gulf of Mexico basin is roughly oval and is about wide. Its floor consists of sedimentary rocks and recent sediments. It is connected to part of the Atlantic Ocean through the Straits of Florida between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
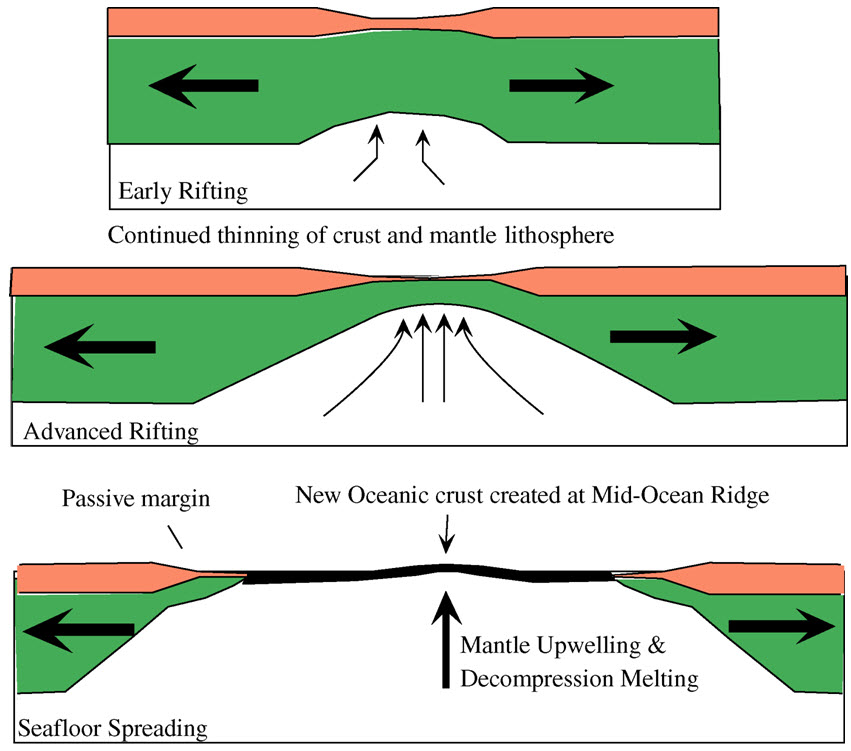
Passive Margin
A passive margin is the transition between Lithosphere#Oceanic lithosphere, oceanic and Lithosphere#Continental lithosphere, continental lithosphere that is not an active plate continental margin, margin. A passive margin forms by sedimentation above an ancient rift, now marked by transitional lithosphere. Continental rifting forms new ocean basins. Eventually the continental rift forms a mid-ocean ridge and the locus of extensional tectonics, extension moves away from the continent-ocean boundary. The transition between the continental and oceanic lithosphere that was originally formed by rifting is known as a passive margin. Global distribution Passive margins are found at every ocean and continent boundary that is not marked by a Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults, strike-slip fault or a subduction, subduction zone. Passive margins define the region around the Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, and western Indian Ocean, and define the entire coasts of Africa, Australia, Greenla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Glacier
A salt glacier (or namakier) is a rare flow of salt that is created when a rising diapir in a salt dome breaches the surface of Earth. The name ‘salt glacier’ was given to this phenomenon due to the similarity of movement when compared with ice glaciers. The causes of these formations is primarily due to salt's unique properties and its surrounding geologic environment. A rising body of salt is referred to as a diapir; which rises to the surface and feeds the salt glacier. Salt structures are usually composed of halite, anhydrite, gypsum and clay minerals. Clays may be brought up with the salt, turning it dark. These salt flows are rare on Earth. In a more recent discovery, scientists have found that they also occur on Mars, but are composed of sulfates. A paper published in November 2023 suggests that salt glaciers composed of halite might also be present on Mercury. The salt glaciers of the Zagros Mountains in Iran are halite whereas the salt glacier of Lüneburg Kalkberg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually faint, and may be similar to that of gasoline or Naphtha, lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases (such as methane and propane), liquids (such as hexane and benzene), low melting solids (such as paraffin wax and naphthalene) or polymers (such as polyethylene and polystyrene). In the fossil fuel industries, ''hydrocarbon'' refers to naturally occurring petroleum, natural gas and coal, or their hydrocarbon derivatives and purified forms. Combustion of hydrocarbons is the main source of the world's energy. Petroleum is the dominant raw-material source for organic commodity chemicals such as solvents and polymers. Most anthropogenic (human-generated) emissions of greenhouse gases are eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormuz Formation
The Hormuz Formation, Hormuz Series, Hormuz Evaporites or Hormuz Group is a sequence of evaporites that were deposited during the Ediacaran (Late Neoproterozoic) to Early Cambrian, a period previously referred to as the Infra-Cambrian. Most exposures of this sequence are in the form of emergent salt diapirs within anticlines of the Zagros fold and thrust belt. As a result of their involvement in post-depositional salt tectonics, the internal stratigraphy of the sequence is relatively poorly understood. They are the lateral equivalent of the evaporite-bearing Ara Group in the South Oman Basin. Distribution The Hormuz Formation is known from a wide area of the Zagros Mountains and around and beneath the Persian Gulf. Two main depositional basins have been recognised, the North Gulf and South Gulf Basins, separated by the Qatar Arch. The basins were formed as a result of extensional tectonics towards the end of the Pan-African Orogeny. The main structure formed during this period were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 486.85 Ma. Most of the continents lay in the southern hemisphere surrounded by the vast Panthalassa Ocean. The assembly of Gondwana during the Ediacaran and early Cambrian led to the development of new convergent plate boundaries and continental-margin arc magmatism along its margins that helped drive up global temperatures. Laurentia lay across the equator, separated from Gondwana by the opening Iapetus Ocean. The Cambrian marked a profound change in life on Earth; prior to the Period, the majority of living organisms were small, unicellular and poorly preserved. Complex, multicellular organisms gradually became more common during the Ediacaran, but it was not until the Cambrian that fossil diversity seems to rapidly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the last of the three geologic eras of the Proterozoic geologic eon, eon, spanning from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago, and is the last era of the Precambrian "supereon". It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era and succeeded by the Paleozoic era of the Phanerozoic eon, and is further subdivided into three geologic period, periods, the Tonian, Cryogenian and Ediacaran. One of the most severe glaciation events known in the geologic record occurred during the Cryogenian period of the Neoproterozoic, when global ice sheets may have reached the equator and created a "Snowball Earth" lasting about 100 million years. The earliest fossils of complex life are found in the Tonian period in the form of ''Otavia'', a primitive sponge, and the earliest fossil evidence of metazoan evolutionary radiation, radiation are found in the Ediacaran period, which included the namesaked Ediacaran biota as well as the oldest definitive cnidarians and bilaterians in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zagros Fold And Thrust Belt
The Zagros fold and thrust belt (Zagros FTB) is an approximately long zone of deformed crustal rocks, formed in the foreland of the collision between the Arabian plate and the Eurasian plate. It is host to one of the world's largest petroleum provinces, containing about 49% of the established hydrocarbon reserves in fold and thrust belts (FTBs) and about 7% of all reserves globally. Plate tectonic setting The Zagros FTB is formed along a section of the plate boundary that is subject to oblique convergence with the Arabian plate moving northwards with respect to the Eurasian plate at about 3 cm per year. The degree of obliqueness reduces southwards along the Zagros, with the collision becoming near orthogonal within the Fars domain. The relative movement between the plates is only partly taken up within the Zagros, the remainder is taken up by deformation in the Alborz mountains and the Lesser Caucasus Mountains to the north of the Iranian plateau and along the zone f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |