|
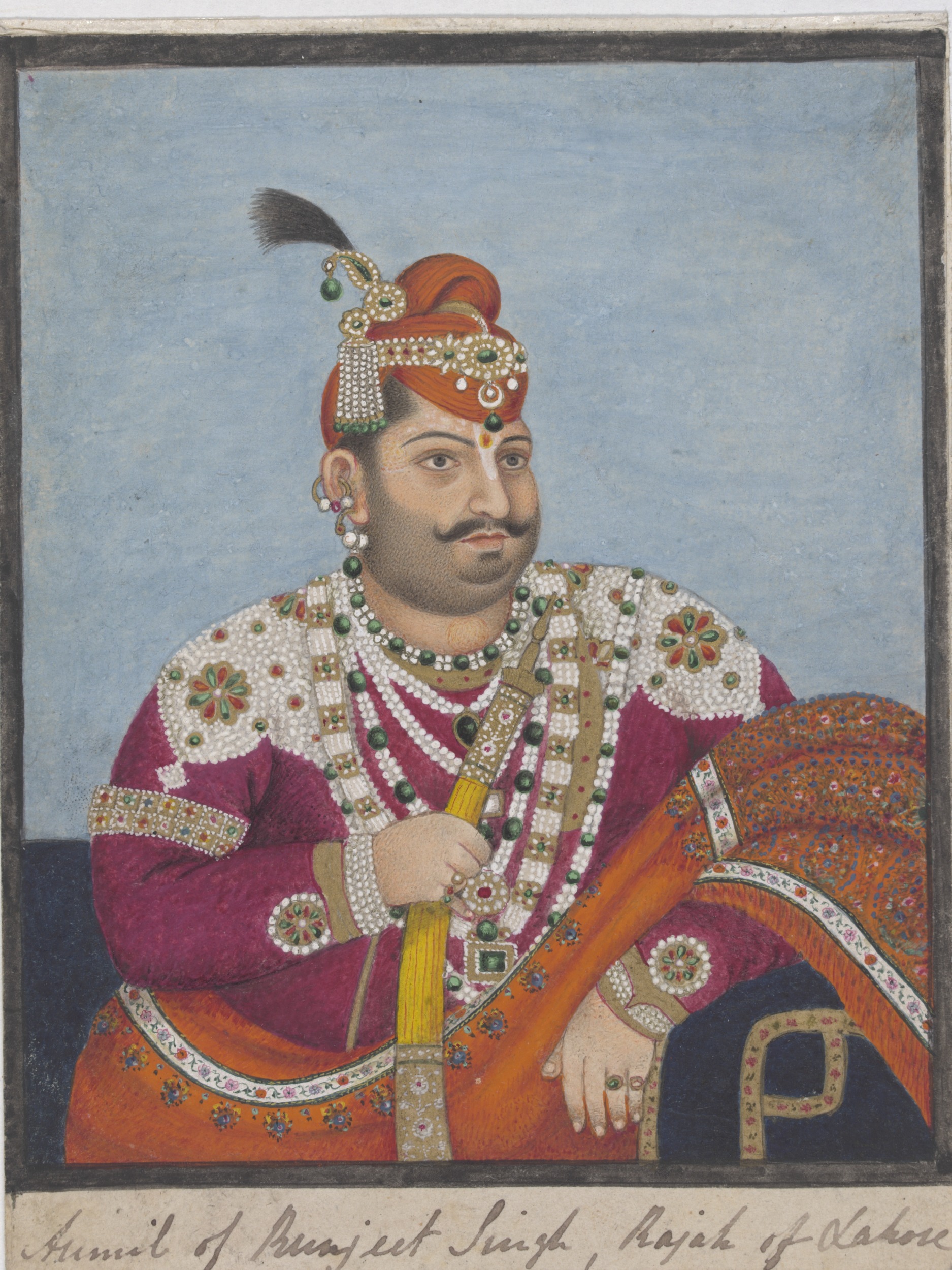
Rāja
Raja (; from , IAST ') is a noble or royal Sanskrit title historically used by some Indian rulers and monarchs and highest-ranking nobles. The title was historically used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested from the ''Rigveda'', where a ' is a ruler, see for example the ', the "Battle of Ten Kings". The title has equivalent cognates in other Indo-European languages, notably the Latin Rex and the Celtic Rix. Raja-ruled Indian states While most of the Indian salute states (those granted a gun salute by the British Crown) were ruled by a Maharaja (or variation; some promoted from an earlier Raja- or equivalent style), even exclusively from 13 guns up, a number had Rajas: ; Hereditary salutes of 11-guns : * the Raja of Ali Rajpur * the Raja of Bilaspur * the Raja of Chamba * the Raja of Faridkot * the Raja of Jhabua * the Raja of Mandi * the Raja of Manipur * the Raja of Narsing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Maharaja
Maharaja (also spelled Maharajah or Maharaj; ; feminine: Maharani) is a royal title in Indian subcontinent, Indian subcontinent of Sanskrit origin. In modern India and Medieval India, medieval northern India, the title was equivalent to a prince. However, in late ancient India and History of South India, medieval south India, the title denoted a king. The form "Maharaj" (without "-a") indicates a separation of noble and religious offices, although since in Marathi the suffix ''-a'' is silent, the two titles are near homophones. Historically, the title "Maharaja" has been used by kings since Vedic period, Vedic times and also in the second century by the Indo-Greek Kingdom, Indo-Greek rulers (such as the kings Apollodotus I and Menander I) and then later by the Indo-Scythians (such as the king Maues), and also the Kushans as a higher ranking variant of "Raja". Eventually, during the medieval era, the title "Maharaja" came to be used by sovereignty, sovereign princes and vassal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
History Of Southeast Asia
The history of Southeast Asia covers the people of Southeast Asia from prehistory to the present in two distinct sub-regions: Mainland Southeast Asia (or Indochina) and Maritime Southeast Asia (or Insular Southeast Asia). Mainland Southeast Asia comprises Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar (or Burma), Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam whereas Maritime Southeast Asia comprises Brunei, Cocos (Keeling) Islands, Christmas Island, East Malaysia, East Timor, Indonesia, Philippines and Singapore. The earliest ''Homo sapiens'' presence in Mainland Southeast Asia can be traced back to 70,000 years ago and to at least 50,000 years ago in Maritime Southeast Asia. Since 25,000 years ago, East Asian-related (Basal East Asian) groups expanded southwards into Maritime Southeast Asia from Mainland Southeast Asia. As early as 10,000 years ago, Hoabinhian settlers from Mainland Southeast Asia had developed a tradition and culture of distinct artefact and tool production. During the Neolithic, Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rex (title)
The Latin title has the meaning of "king, ruler" (monarch). It is derived from Proto-Indo-European ''*h₃rḗǵs''. Its cognates include Sanskrit ''rājan'', Gothic ''reiks'', and Old Irish ''rí'', etc. Its Greek equivalent is (), "leader, ruler, chieftain". The chief magistrate of the Roman Kingdom was titled ''Rex Romae'' (King of Rome). See also *R. (other), R. *Reich *Dux *Basileus *Germanic king References Latin words and phrases Roman historiography Royal titles Kings {{Latin-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Shakha of the many survive today, namely the Shakala Shakha, Śakalya Shakha. Much of the contents contained in the remaining Shakhas are now lost or are not available in the public forum. The ''Rigveda'' is the oldest known Vedic Sanskrit text. Its early layers are among the oldest extant texts in any Indo-European language. Most scholars believe that the sounds and texts of the ''Rigveda'' have been orally transmitted with precision since the 2nd millennium BCE, through Indian mathematics#Styles of memorisation, methods of memorisation of exceptional complexity, rigour and fidelity, though the dates are not confirmed and remain contentious till concrete evidence surfaces. Philolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jai Singh And Shivaji
Jai or JAI may refer to: Abbreviations and codes * Jaipur International Airport (IATA: JAI), in Jaipur, India * Java Advanced Imaging, an API for the Java platform * Jet Airways (ICAO: JAI), an Indian airline * Jewish Agency for Israel * Denys Wilkinson Building#John_Adams_Institute_for_Accelerator_Science, John Adams Institute for Accelerator Science * Journal of Astronomical Instrumentation, a peer-reviewed academic journal by World Scientific People * Jason Rowe (born 1969), British pop/soul singer who recorded under the name ''Jai'' in the late 1990s * Jai (actor) (born 1985), Indian Tamil film actor * Jai Brooks, comedian from the Australian YouTube group, The Janoskians * Jai Courtney (born 1986), Australian actor * Jai Ingham (born 1993), Australian football player * Jai Koutrae (born 1975), Australian actor * Jai Lucas (born 1988), American basketball coach and former professional and collegiate basketball player * Jai McDowall (born 1986), Scottish singer who won the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
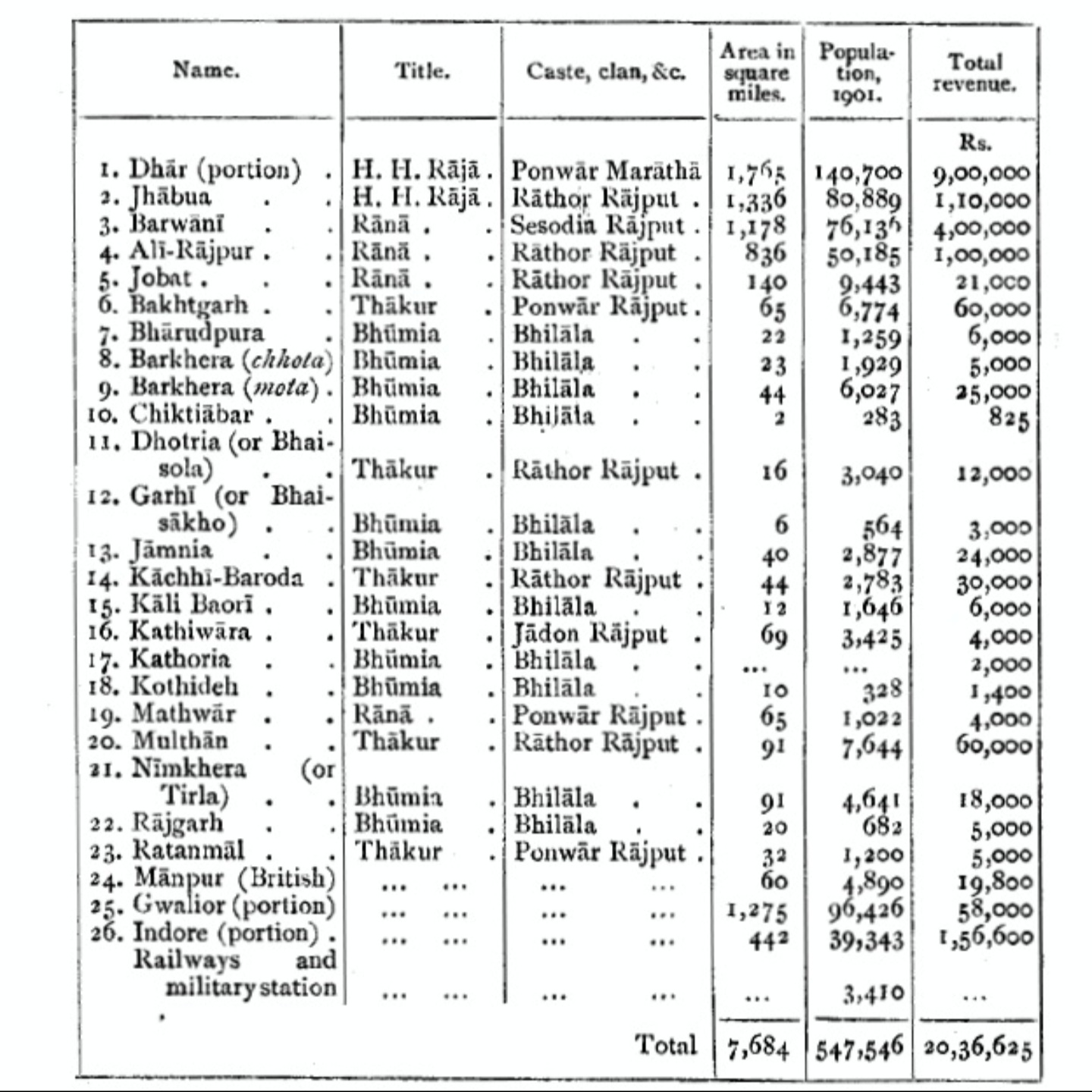
Jhabua State
Jhabua State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. It had its capital in Jhabua town. Most of the territory of the princely state was inhabited by the Bhil people, who constituted a majority of the population. The revenue of the state in 1901 was Rs.1,10,000. History The state of Jhabua was founded by Kesho Das or Kishan Das, in 1584. He was granted the title of ''Raja'' by Mughal Emperor Akbar as a reward for a successful campaign in Bengal, and for punishing the Bhil Chiefs of Jhabua, who had murdered the wife and daughters of the Imperial Viceroy of Gujarat. Kesho Das was killed by his own son called Karan Singh which threw the state into disorder. After Karan, Man Singh became the raja and after Man, Khushal Singh was the ruler of Jhabua. During 1698, Khushal gave much of his lands to his brothers and sons and was too weak to rule his state effectively. This allowed the Maratha The Marathi people (; Marathi: , ''Marāṭ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bilaspur State
Bilaspur State or Kahlur State, sometimes Kahloor Riyasat, was a kingdom (697–1849) and later princely state (1849–1948) in the Punjab Province ruled by a separate branch of Chandravanshi Chandel rajput dynasty. Raja Bir Chand 697–730 was the founder of the state but it was named Kahlur only after the Construction of Kahlur Fort by Raja Kahal Chand around 890–930CE and Raja Anand Chand the 44th Raja was the last ruler. The state was earlier known as Kahlur Riyasat and was later renamed Bilaspur. It covered an area of , on the name of Sage Bias (from Biaspur later became Bilaspur) and had a population of 100,994 according to the 1931 Census of India. The last ruler of Bilaspur State acceded to the Indian Union on 12 October 1948. Bilaspur State remained Bilaspur Province in independent India until 1950 when the province was briefly renamed "Bilaspur State" before it was merged with Himachal Pradesh state as a district in 1954. In the pre-partitioned Punjab, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chamba State
Chamba State was one of the oldest princely states in present-day Republic of India, having been founded during the late 6th century. It was part of the States of the Punjab Hills of the Punjab Province (British India), Punjab Province in British Raj, India from 1859 to 1947. Its last ruler signed the instrument of accession to the Dominion of India, Indian Union of 15 April 1948. History According to tradition, the ancient name of Chamba was Champa, and its predecessor state was known as Brahmpur. This site later became Bharmour around 550 AD when Raja Maru Verman came from Kalpagram to the Chamba Hills. Around 920 CE, the capital was shifted from Bharmour to present day Chamba Town. The rulers of Chamba State patronized artists of the Pahari painting style. Between 1809 and 1846 Chamba was tributary to Sikh Empire & come under its The Kangra hills province of lahore durbar. In 1821, Chamba annexed Bhadrawah State. After the First Anglo-Sikh War, the British gained a large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Faridkot State
Faridkot State was a self-governing princely state of Punjab ruled by Brar Jats outside British India during the British Raj period in the Indian sub-continent until Indian independence. The state was located in the south of the erstwhile Firozpur district, Ferozepore district during the British period. The former state had an area of around 1649.82 square kilometres (637 sq mi). It population in 1941 was around 199,000 thousand. The state's rulers had cordial relations with the British. History Origin The formation of a state of Faridkot took many years in the making, with various rulers governing the area with no single authority. It is said that Raja Mokalsi was the founder of the locality of Faridkot and he constructed a fort in Mohalkar in the 12th century. He was succeeded by various rulers of the same dynasty but at some point the dynasty ceased to govern the Faridkot region. The Manj chief, Isa Khan Munj, Nawab Isa Khan, killed Kapura Singh Brar, Kapura Brar, the ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Narsinghgarh State
The Kingdom of Narsinghgarh also known as Narsinghgarh State was a princely state located in present-day Madhya Pradesh, India with its capital at Narsinghgarh, Rajgarh, Narsinghgarh from which the state was named. The ruling family was a cadet branch of the royal family of Rajgarh State. It formed an enclave within Rajgarh State and was placed administratively under the Bhopal Agency subdivision of the Central India Agency. The state covered an area of and had a population of 92,093 and an average revenue of Rs.5,00,000 in 1901. The state capital was the town of the same name, Narsinghgarh, Rajgarh, Narsinghgarh. History The State of Narsinghgarh was carved out of the state of Rajgarh State by Paras Ramji, the younger brother of the then Ruler of Rajgarh, Rawat Mohan Singhji in 1681. During the 18th century, the state was a feudatory to the House of Holkar, Holkar rulers of Indore State, but in 1872 Narsinghgarh was recognized as a princely state by British India . Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mandi State
Mandi State was a princely state within (British India), with the town of Mandi, Himachal Pradesh, Mandi as its capital. The state of Mandi (the name means "market" in Hindi), which included two towns and 3,625 villages, was part of the States of the Punjab Hills. It was located in the Himalayan range, bordering to the west, north, and east on the British Punjabi district of Kangra State, Kangra; to the south, on Suket State, Suket; and to the southwest, on Bilaspur State, Bilaspur. As of 1941, population of Mandi State was 232,598 and area of the state was . History The predecessor state of Suket was founded in 1527. Formerly part of the Kingdom of Suket in the Punjab Hills, the dynasty traditionally goes back to 765AD. In about 1100, Vijaya Sen had two sons, Sahu Sen who ruled over Suket and Bahu Sen who ruled over Kullu. Bahu Sen’s descendants emigrated to Kullu until the tenth descendant, Kabakha Sen was killed by the Raja of Kullu and his son had to flee to Suket, not v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Manipur Kingdom
The Manipur Kingdom, also known as Meckley, was an ancient kingdom at the India–Burma frontier. Historically, Manipur was an independent kingdom ruled by a Ningthouja dynasty, Meitei dynasty. But it was also invaded and ruled over by Konbaung dynasty, Burmese kingdom at various point of time. It became a protectorate of the British Company Rule in India, East India Company from 1824, and a princely state of British Raj in 1891. The princely state bordered the Assam Province in the west and British Burma in the east, and in the 20th century covered an area of 22,327 square kilometres (8,621 sq mi) and contained 467 villages. The capital of the state was Imphal. Kangleipak State The early history of Manipur is composed of mythical narratives . The location of the Kangla Fort on the banks of the Imphal River is believed to be where King Pakhangba built his first palace. :simple:Loyumba Shinyen, Loyumba Shinyen, the written constitution of Kangleipak was formally dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |