|
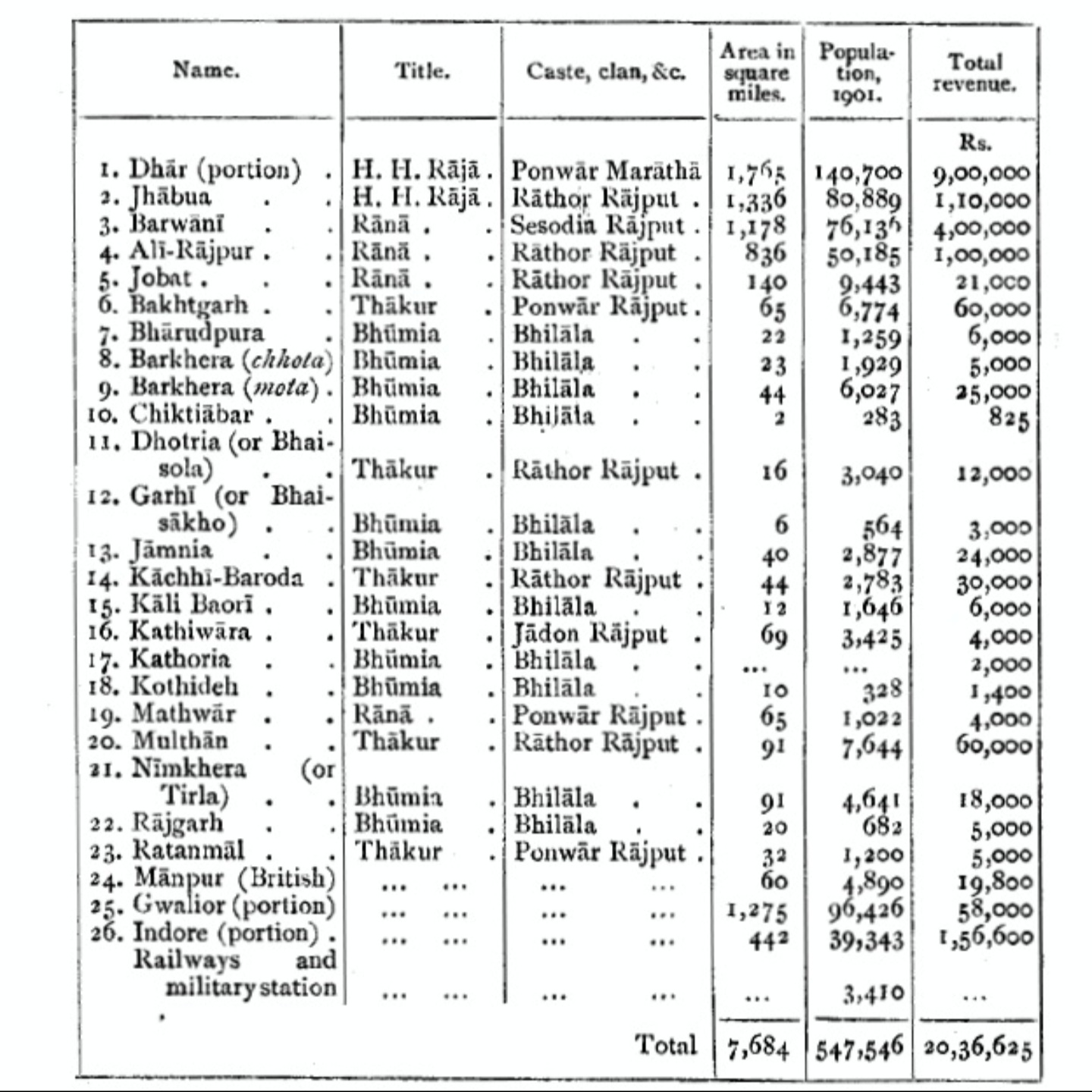
Jhabua State
Jhabua State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. It had its capital in Jhabua town. Most of the territory of the princely state was inhabited by the Bhil people, who constituted a majority of the population. The revenue of the state in 1901 was Rs.1,10,000. History The state of Jhabua was founded by Kesho Das or Kishan Das, in 1584. He was granted the title of ''Raja'' by Mughal Emperor Akbar as a reward for a successful campaign in Bengal, and for punishing the Bhil Chiefs of Jhabua, who had murdered the wife and daughters of the Imperial Viceroy of Gujarat. Kesho Das was killed by his own son called Karan Singh which threw the state into disorder. After Karan, Man Singh became the raja and after Man, Khushal Singh was the ruler of Jhabua. During 1698, Khushal gave much of his lands to his brothers and sons and was too weak to rule his state effectively. This allowed the Maratha The Marathi people (; Marathi: , ''Marāṭ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757, the East India Company set up "factories" (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century three ''Presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India, 1757–1858, the Company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "Presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government oversight, in effect sharing sovereig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailana
Sailana is a town in the Malwa region of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. Sailana is from Ratlam city and away from Banswara district of the neighboring state of Rajasthan. Sailana was once the capital of the Sailana State before it merged into India. A fort belonging to the former royal family still stands tall in Sailana. The Kedareshwar temple, situated from Sailana is a notable shrine. Demographics As of the 2011 Census of India, Sailana had a population of 1,34,959. There are 226 villages in Sailana block. Sailana has an average literacy rate of 86%, higher than the state average of 69%: male literacy is 93%, and female literacy is 78%. In Sailana, 11% of the population is under 6 years of age. The sub-district has a high population of Scheduled tribes. Geography Sailana is located at . It has an average elevation of 479 metres (1,571 feet). Foundation of Sailana Raja Jai Singh wanted to shift his capital from Raoti to a safer location, he ordered the cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1584 Establishments In India
Events January–March * January 11 – Sir Walter Mildmay is given a royal licence to found Emmanuel College, Cambridge in England. * January 16 – Roman Catholic priest George Haydock, imprisoned in the Tower of London since 1582, states during an interrogation that he claimed that Queen Elizabeth, leader of the Church of England, was a heretic. Convicted of treason, he is executed on February 12. * February 2 – (6th waning moon of the Magha, BE 2126) In what is now Thailand, Prince Naresuan, the Uparaja of the Ayutthaya Kingdom and the son of King Mahathammarachathirat carries out the orders of Burma's King Nanda Bayin, and leads an army to suppress a rebellion by the Viceroy of the Ava Kingdom, Thado Minsaw. Arriving in April, Naresuan learns that King Nanda has ordered Naresuan to be assassinated, and begins his own rebellion against Burma, the Burmese–Siamese War.''Hmannan Yazawin'' (Ministry of Information of Myanmar, 2003) * February ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rathore (clan) , a Hindu caste in Gujarat, India
{{disambiguation ...
Rathore or Rathod may refer * Rathore dynasty, a dynasty of India * Rathore (Rajput clan), a clan of Rajput caste * Rathore (surname), an Indian surname * Rathod (surname), an Indian surname See also * Rath (other) * Rather (other) * Rathodia The Rathodia are a Hindu caste found in the state of Gujarat in India. Origin and present circumstances The Rathodia are sub-division of the Halpati tribe. They are found mainly in the districts of Surat and Baroda. They speak Gujarati and Hindi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajput History
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the northern part of the Indian subcontinent. The term ''Rajput'' covers various patrilineal clans historically associated with warriorhood: several clans claim Rajput status, although not all claims are universally accepted. According to modern scholars, almost all Rajput clans originated from peasant or pastoral communities. Over time, the Rajputs emerged as a social class comprising people from a variety of ethnic and geographical backgrounds. From the 12th to 16th centuries, the membership of this class became largely hereditary, although new claims to Rajput status continued to be made in later centuries. Several Rajput-ruled kingdoms played a significant role in many regions of central and northern India from the seventh century o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely States Of Madhya Pradesh
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". In a related sense, now not commonly used, all more or less sovereign rulers over a state, including kings, were "princes" in the language of international politics. They normally had another title, for example king or duke. Many of these were Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, ), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the ''princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Integration Of India
Before it gained independence in 1947, India (also called the Indian Empire) was divided into two sets of territories, one under direct British rule (British India), and the other consisting of princely states under the suzerainty of the British Crown, with control over their internal affairs remaining to varying degrees in the hands of their hereditary rulers. The latter included 562 princely states which had different types of revenue-sharing arrangements with the British, often depending on their size, population and local conditions. In addition, there were several colonial enclaves controlled by France and Portugal. After independence, the political integration of these territories into an Indian Union was a declared objective of the Indian National Congress, and the Government of India pursued this over the next decade. Thus, a gradual unification of India was thus followed, Jawaharlal Nehru and Vallabhbhai Patel carried an expansionist movement, where they incorporated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dileep Singh Of Jhabua
Dileep Singh (or Dilip Singh) was the Raja of Jhabua from 1942 until his death in 1965. Education He had his education at Agra and Aligarh. He was subsequently placed at Indore for training in revenue and settlement work, and for judicial training, he was placed in the district court at Mhow. Early career He began his career as a railway magistrate and was thereafter appointed kamdar of Ratanmal by the Malwa Political Agency. When, on account of Udai Singh's inability to rule properly, the Government of India, on 29 September 1934, removed him from power and took Jhabua into administration, a Council of Administration was founded to govern the state's affairs. He was appointed its president. Under his supervision, the council restructured the administrative framework and operations of the state. He increased salaries for the revenue staff and assigned assistants to revenue officers and surveyors. He established two new patwari circles and appointed a new patwari in each tehsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udai Singh Of Jhabua
Udai Singh was the Raja of Jhabua from 1895 until his death in 1942. Birth and adoption He was born on 6 May 1875 as the second son of Raghunath Singh, Thakur of Khawasa. He was adopted by Gopal Singh, the Raja of Jhabua, sometime before the Raja's death, and his adoption was sanctioned by the Government of India. He was the twelfth in line of descent from Kesho Das, the founder of the Jhabua. Succession Upon the death of his adoptive father, he succeeded him as Raja of Jhabua on 22 January 1895. Reign He was granted full administrative powers in 1898. During the Indian famine of 1899–1900, he had to borrow Rs. 100,000 from the Maharaja Scindia of Gwalior through the British government and Rs. 377,000 directly from the British government to sustain the administration. Due to the disastrous effects of famine and mismanagement on the state's monetary resources, his powers were curtailed in 1900, and he was required to follow the advice of his Diwan. His powers were restored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gopal Singh Of Jhabua
Gopal Singh was the Raja of Jhabua from 1841 until his death in 1895. Birth Gopal Singh was born on 22 February 1841, four months after the death of his father, Ratan Singh. Succession He succeeded his late father as the Raja of Jhabua in October 1841. As he was a minor at the time, his grandmother served as regent and governed state affairs. Reign In 1841, while he was still a minor, disturbances arose in Thandla, and the aid of the Political Agent at Mandleshwar was sought. He brought a small force with him and quelled the disturbances. During the Indian Rebellion of 1857, when the Raja of Amjhera revolted and attacked Hutchinson, the Political Agent at Bhopawar, Hutchinson and his companions fled. Upon reaching Para, they sent a message to Gopal, requesting his protection and shelter. Gopal immediately sent an escort to bring them to Jhabua. When they arrived in Jhabua, he and his grandmother welcomed them kindly and ensured their safety and comfort. However, the local Arab f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salute State
A salute is usually a formal hand gesture or other action used to display respect in military situations. Salutes are primarily associated with the military and law enforcement, but many civilian organizations, such as Girl Guides, Scouting Movement, Boy Scouts and the The Salvation Army, Salvation Army use formal salutes. Ordinary civilians also salute informally to greet or acknowledge the presence of another person, such as a tip of the hat or a waving, hand wave to a friend or neighbor. Military salutes Throughout history, military organizations have used many methods to perform salutes. Depending on the situation a salute could be a hand or body gesture, cannon or rifle shots, hoisting of flags, removing headgear, or other means of showing respect or deference. Hand salutes Origins According to some modern military manuals, the modern Western salute originated in France when knights greeted each other to show friendly intentions by raising their Visor (armor), vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madhya Bharat
Madhya Bharat, also known as Malwa Union, was an Indian state in west-central India, created on 28 May 1948 from twenty-five princely states which until 1947 had been part of the Central India Agency, with Jiwajirao Scindia as its Rajpramukh. The union had an area of .Gwalior was made the capital and the first legislative assembly took place inside the Moti Mahal of Gwalior. It was bordered by the states of Bombay (presently Gujarat and Maharashtra) to the southwest, Rajasthan to the northwest, Uttar Pradesh to the north, and Vindhya Pradesh to the east, and Bhopal State and Madhya Pradesh to the southeast. The population was mostly Hindu and Hindi-speaking. On 1 November 1956, Madhya Bharat, together with the states of Vindhya Pradesh and Bhopal State, was merged into Madhya Pradesh. Districts Madhya Bharat comprised sixteen districts and these districts were initially divided into three Commissioners' Divisions, which were later reduced to two. The districts were: # Bhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |