|
Rights Of Nature Law
Rights of nature law is the codification and other implementations of the legal and jurisprudential theory of the rights of nature. This legal school of thought describes inherent rights as associated with ecosystems and species, similar to the concept of fundamental human rights. The early 2000s saw a significant expansion of rights of nature law, in the form of constitutional provisions, treaty agreements, national and subnational statutes, local laws, and court decisions. As of 2022, nature's rights laws exist at the local to national levels in 39 countries, including in Canada, at least seven Tribal Nations in the U.S. and Canada, and over 60 cities and counties throughout the United States. The total number of initiatives was 409 as of June 2021 and 495 as of May 2024. The EcoJurisprudence Monitor lists over 540 as of early 202 Treaties New Zealand Legal standing for natural systems in New Zealand arose alongside new attention paid to long-ignored treaty agreements with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rights Of Nature
Rights of nature or Earth rights is a legal and jurisprudential theory that describes inherent rights as associated with ecosystems and species, similar to the concept of fundamental human rights. The rights of nature concept challenges twentieth-century laws as generally grounded in a flawed frame of nature as "resource" to be owned, used, and degraded. Proponents argue that laws grounded in rights of nature direct humanity to act appropriately and in a way consistent with modern, system-based science, which demonstrates that humans and the natural world are fundamentally interconnected. This school of thought is underpinned by two basic lines of reasoning. First, since the recognition of human rights is based in part on the philosophical belief that those rights emanate from humanity's own existence, logically, so too do inherent rights of the natural world arise from the natural world's own existence. A second and more pragmatic argument asserts that the survival of humans de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrato River
The Atrato River () is a river of northwestern Colombia. It rises in the slopes of the Western Cordillera and flows almost due north to the Gulf of Urabá (or Gulf of Darién), where it forms a large, swampy delta. Its course crosses the Chocó Department, forming that department's border with neighboring Antioquia in two places. Its total length is about , and it is navigable as far as Quibdó (400 km / 250 mi), the capital of the department. In 2016, the Constitutional Court of Colombia granted the river legal rights of personhood after years of degradation of the river basin from large-scale mining and illegal logging practices, which severely impacted the traditional ways of life for Afro-Colombians and Indigenous people. Drainage area The river’s total length is about , and it is navigable as far as Quibdó (400 km / 250 mi), the capital of the department. The basin occupies an area of and has an average annual precipitation of >5,000 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
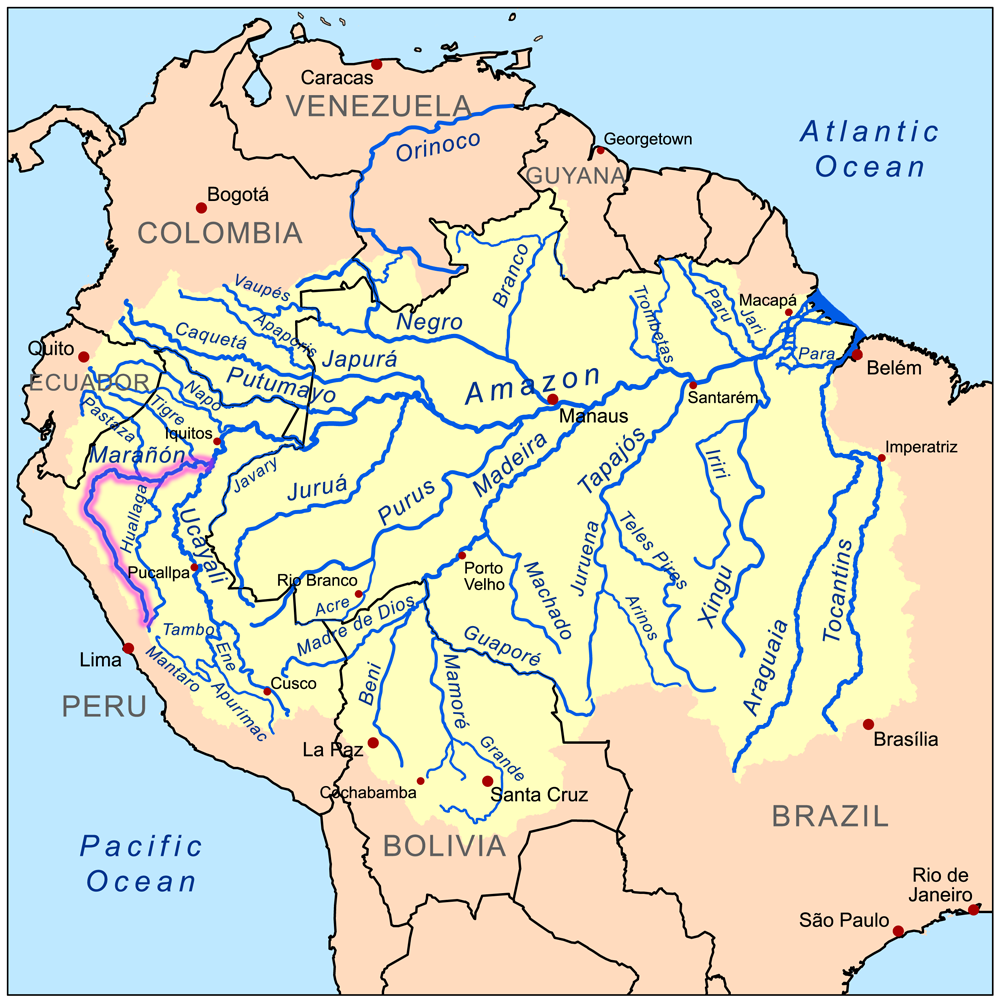
Marañón River
The Marañón River (, , ) is the principal or mainstem source of the Amazon River, arising about 160 km (100 miles) to the northeast of Lima, Peru, and flowing northwest across plateaus 3,650 m (12,000 feet) high, it runs through a deeply eroded Andean valley, along the eastern base of the Cordillera of the Andes, as far as 5° 36′ southern latitude; from where it makes a great bend to the northeast, and cuts through the jungle Ande in its midcourse, until at the Pongo de Manseriche it flows into the flat Amazon basin. Although historically, the term "Marañón River" often was applied to the river all the way to the Atlantic Ocean, nowadays the Marañón River is generally thought to end at the confluence with the Ucayali River, after which most cartographers label the ensuing waterway the Amazon River. As the Marañón passes through high jungle in its midcourse, it is marked by a series of unnavigable rapids and falls. The Marañón was the subject of a landmark legal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personhood
Personhood is the status of being a person. Defining personhood is a controversial topic in philosophy and law and is closely tied with legal and political concepts of citizenship, equality, and liberty. According to law, only a legal person (either a natural or a juridical person) has rights, protections, privileges, responsibilities, and legal liability. Personhood continues to be a topic of international debate and has been questioned critically during the abolition of human and nonhuman slavery, in debates about abortion and in fetal rights and/or reproductive rights, in animal rights activism, in theology and ontology, in ethical theory, and in debates about corporate personhood, and the beginning of human personhood. In the 21st century, corporate personhood is an existing Western concept; granting non-human entities personhood, which has also been referred to a "personhood movement", can bridge Western and Indigenous legal systems. Processes through which personhood i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain, Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly River. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma River, Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna River (Bangladesh), Jamuna, the lower str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttarakhand High Court
The Uttarakhand High Court is the High courts of India, High Court of the States and union territories of India, state of Uttarakhand in India. The Uttarakhand High Court was established on 9 November 2000 after the separation of the state of Uttarakhand from Uttar Pradesh. The Judiciary of India#Judge strength, sanctioned judge strength at the time of creation in 2000 was 7; this was increased to 9 in 2003. Justice Ashok Desai (judge), Ashok Desai was the inaugural holder of the office. Former Chief Justices of Uttarakhand Sarosh Homi Kapadia and Jagdish Singh Khehar later went on to become Chief Justice of India. History The Uttarakhand High Court is a relatively new addition to India's judiciary system. The building of Uttarakhand High Court was constructed by Santoni MacDonald in 1900. Uttarakhand was carved out from the state of Uttar Pradesh on 9 November 2000 under the Uttar Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2000. At the time of the creation of the state, the High Court o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Justice
Environmental justice is a social movement that addresses injustice that occurs when poor or marginalized communities are harmed by hazardous waste, resource extraction, and other land uses from which they do not benefit. The movement has generated hundreds of studies showing that exposure to environmental harm is inequitably distributed. Additionally, many marginalized communities, including the LGBTQ community, are disproportionately impacted by natural disasters. The movement Environmental racism in the United States, began in the United States in the 1980s. It was heavily influenced by the Civil rights movement, American civil rights movement and focused on environmental racism within rich countries. The movement was later expanded to consider gender, LGBTQ people, international environmental injustice, and inequalities within marginalized groups. As the movement achieved some success in rich countries, environmental burdens were shifted to the Global North and Global Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of India is the supreme judiciary of India, judicial authority and the supreme court, highest court of the Republic of India. It is the final Appellate court, court of appeal for all civil and criminal cases in India. It also has the power of Judicial review in India, judicial review. The Supreme Court, which consists of the Chief Justice of India and a maximum of fellow 33 judges, has extensive powers in the form of original jurisdiction, original, appellate jurisdiction, appellate and Advisory opinion, advisory jurisdictions. As the apex constitutional court, it takes up appeals primarily against verdicts of the List of High Courts of India, High Courts of various states and tribunals. As an advisory court, it hears matters which are referred by the President of India#Judicial powers, president of India. Under judicial review, the court invalidates both ordinary laws as well as Amendment of the Constitution of India, constitutional amendments as per the basi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |