 |
Right-click
A context menu (also called contextual, shortcut, and pop up or pop-up menu) is a menu in a graphical user interface (GUI) that appears upon user interaction, such as a right-click mouse operation. A context menu offers a limited set of choices that are available in the current state, or context, of the operating system or application to which the menu belongs. Usually the available choices are actions related to the selected object. From a technical point of view, such a context menu is a graphical control element. History Context menus first appeared in the Smalltalk environment on the Xerox Alto computer, where they were called ''pop-up menus''; they were invented by Dan Ingalls in the mid-1970s. Microsoft Office v3.0 introduced the context menu for copy and paste functionality in 1990. Borland demonstrated extensive use of the context menu in 1991 at the Second Paradox Conference in Phoenix Arizona. Lotus 1-2-3/G for OS/2 v1.0 added additional formatting options in 1991 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Middle-click
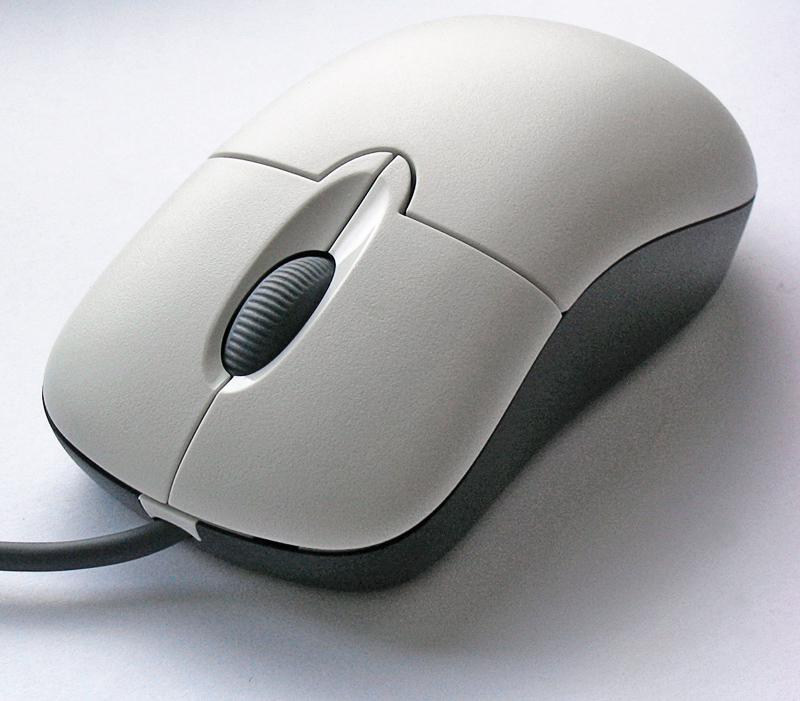
A computer mouse (plural mice; also mouses) is a hand-held pointing device that detects two-dimensional motion relative to a surface. This motion is typically translated into the motion of the pointer (called a cursor) on a display, which allows a smooth control of the graphical user interface of a computer. The first public demonstration of a mouse controlling a computer system was done by Doug Engelbart in 1968 as part of the Mother of All Demos. Mice originally used two separate wheels to directly track movement across a surface: one in the x-dimension and one in the Y. Later, the standard design shifted to use a ball rolling on a surface to detect motion, in turn connected to internal rollers. Most modern mice use optical movement detection with no moving parts. Though originally all mice were connected to a computer by a cable, many modern mice are cordless, relying on short-range radio communication with the connected system. In addition to moving a cursor, comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Mouse (computing)
A computer mouse (plural mice; also mouses) is a hand-held pointing device that detects Plane (mathematics), two-dimensional motion relative to a surface. This motion is typically translated into the motion of the Cursor (user interface)#Pointer, pointer (called a cursor) on a computer monitor, display, which allows a smooth control of the graphical user interface of a computer. The first public demonstration of a mouse controlling a computer system was done by Doug Engelbart in 1968 as part of the Mother of All Demos. Mice originally used two separate wheels to directly track movement across a surface: one in the x-dimension and one in the Y. Later, the standard design shifted to use a ball rolling on a surface to detect motion, in turn connected to internal rollers. Most modern mice use optical mouse, optical movement detection with no moving parts. Though originally all mice were connected to a computer by a cable, many modern mice are cordless, relying on short-range rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Unix
Unix (, ; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley ( BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems ( SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE ( HP-UX), and IBM ( AIX). The early versions of Unix—which are retrospectively referred to as " Research Unix"—ran on computers such as the PDP-11 and VAX; Unix was commonly used on minicomputers and mainframes from the 1970s onwards. It distinguished itself from its predecessors as the first portable operating system: almost the entire operating system is written in the C programming language (in 1973), which allows U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
IceWM
IceWM is a stacking window manager for the X Window System, originally written by Marko Maček. It was written from scratch in C++ and is released under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License. It is customizable, relatively lightweight in terms of memory and CPU usage, and comes with themes that allow it to imitate the GUI of Windows 95, Windows XP, Windows 7, OS/2, Motif, and other graphical user interfaces. IceWM can be configured from plain text files stored in a user's home directory, making it easy to customize and copy settings. IceWM has an optional, built-in taskbar with a dynamic start menu, tasks display, system tray, network and CPU meters, mail check and configurable clock. It features a task list window and an Alt+Tab task switcher. Official support for GNOME and KDE menus used to be available as a separate package. In recent IceWM versions, support for them is built-in as well. External graphical programs for editing the configuration and the men ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Awesome (window Manager)
awesome is a dynamic window manager for the X Window System developed in the C and Lua programming languages. Lua is also used for configuring and extending the window manager. Its development began as a fork of dwm, though has differed considerably since. It aims to be extremely small and fast, yet extensively customizable. It makes it possible for the user to manage windows with the use of keyboard. The fork was initially nicknamed ''jdwm'', where "jd" denoted the principal programmer's initials and dwm denoted the software project it was forked from. The first git repository for what was to become awesome was set up in September 2007. jdwm was renamed to awesome, named after the same phrase used by the ''How I Met Your Mother'' character Barney Stinson. awesome was officially announced on the dwm mailing list on September 20, 2007. Aim awesome has emerged as a dwm fork featuring customization through external configuration files (see Configuration and customization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Window Manager
A window manager is system software that controls the placement and appearance of window (computing), windows within a windowing system in a graphical user interface. Most window managers are designed to help provide a desktop environment. They work in conjunction with the underlying graphical system that provides required functionality—support for graphics hardware, pointing devices, and a keyboard—and are often written and created using a widget toolkit. Few window managers are designed with a clear distinction between the windowing system and the window manager. Every graphical user interface based on a windows metaphor has some form of window management. In practice, the elements of this functionality vary greatly. Elements usually associated with window managers allow the user to open, close, minimize, maximize, move, resize, and keep track of running windows, including window decorators. Many window managers also come with various utilities and features such as task b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word is a word processor program, word processing program developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983, under the name Multi-Tool Word for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platforms including IBM PCs running DOS (1983), Apple Macintosh running the Classic Mac OS (1985), AT&T UNIX PC (1985), Atari ST (1988), OS/2 (1989), Microsoft Windows (1989), SCO Unix (1990), Handheld PC (1996), Pocket PC (2000), macOS (2001), Web browsers (2010), iOS (2014), and Android (operating system), Android (2015). Microsoft Word has been the ''de facto'' standard word processing software since the 1990s when it eclipsed WordPerfect. Commercial versions of Word are licensed as a standalone product or as a component of Microsoft Office, which can be purchased with a perpetual license, as part of the Microsoft 365 suite as a Software as a service, subscription, or as a one-time purchase with Office 2024. History In 1981, Microsoft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Focus (computing)
In a computing graphical user interface (GUI), a component has focus when it is selected to receive input from the user by an event such as a mouse button click or keypress. Moving the focus away from a specific user interface element is known as a blur event in relation to this element. Typically, the focus is withdrawn from an element by giving another element the focus. This means that focus and blur Event (computing), events are virtually simultaneous in relation to different user interface elements, one that becomes focused and one that is "blurred" (in the computing, not visual, sense). The concept is similar to a Cursor (user interface), cursor in a text-based environment. However, when considering a graphical interface, there is also a mouse pointer involved. Moving the mouse will typically move the mouse pointer without changing the focus. The focus can usually be changed by clicking on a component that can receive focus with the mouse. Many Desktop environment, desktops al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Menu Key
In computing, the menu key (), or application key, is a key with the primary function to launch a context menu with the keyboard rather than with the usual right-mouse button. It was previously found on Microsoft Windows-oriented computer keyboards and was introduced at the same time as the Windows key, Windows logo key. On keyboards including the key, its symbol would usually have been a small icon depicting a pointer (computing WIMP), pointer hovering above a menu; it would typically have been found on the right side of the keyboard between the right Windows key, Windows logo key and the right control key (or between the right AltGr key and the right control key). While the Windows key is present on the vast majority of keyboards intended for use with the Windows operating system, the menu key was frequently omitted in the interest of space, particularly on portable and laptop keyboards. It was able to be used when the right-mouse button was not present on a Mouse (computing) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for Wireless LAN, local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks, used globally in small office/home office, home and small office networks to link devices and to provide Internet access with wireless routers and wireless access points in public places such as coffee shops, restaurants, hotels, libraries, and airports. ''Wi-Fi'' is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance, which restricts the use of the term "''Wi-Fi Certified''" to products that successfully complete Interoperability Solutions for European Public Administrations, interoperability certification testing. Non-compliant hardware is simply referred to as WLAN, and it may or may not work with "''Wi-Fi Certified''" devices. the Wi-Fi Alliance consisted of more than 800 companies from ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
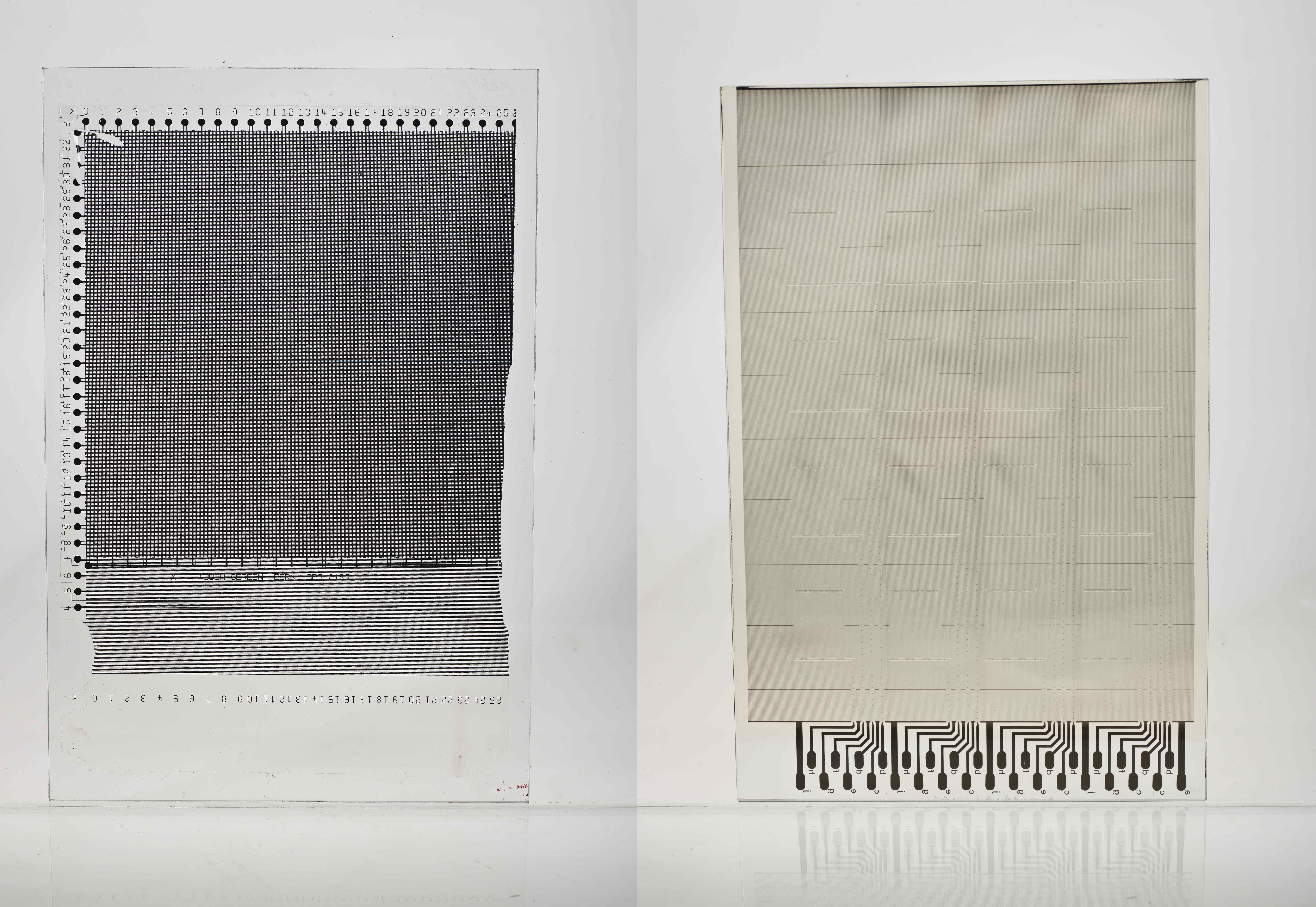 |
Multi-touch
In computing, multi-touch is technology that enables a surface (a touchpad or touchscreen) to recognize the presence of more than one somatosensory system, point of contact with the surface at the same time. The origins of multitouch began at CERN, MIT, University of Toronto, Carnegie Mellon University and Bell Labs in the 1970s. CERN started using multi-touch screens as early as 1976 for the controls of the Super Proton Synchrotron. Capacitive multi-touch displays were popularized by Apple Inc., Apple's iPhone in 2007. Multi-touch may be used to implement additional functionality, such as pinch to zoom or to activate certain subroutines attached to predefined gestures using gesture recognition. Several uses of the term multi-touch resulted from the quick developments in this field, and many companies using the term to market older technology which is called ''gesture-enhanced single-touch'' or several other terms by other companies and researchers. Several other similar or relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |