|
Rhynchocephalian
Rhynchocephalia (; ) is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a diverse group including a wide array of morphologically distinct forms. The oldest record of the group is dated to the Middle Triassic around 238 to 240 million years ago, and they had achieved a worldwide distribution by the Early Jurassic. Most rhynchocephalians belong to the group Sphenodontia ('wedge-teeth'). Their closest living relatives are lizards and snakes in the order Squamata, with the two orders being grouped together in the superorder Lepidosauria. Many of the niches occupied by lizards today were held by sphenodontians during the Triassic and Jurassic, although lizard diversity began to overtake sphenodontian diversity in the Cretaceous, and they had disappeared almost entirely by the beginning of the Cenozoic. While the modern tuatar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
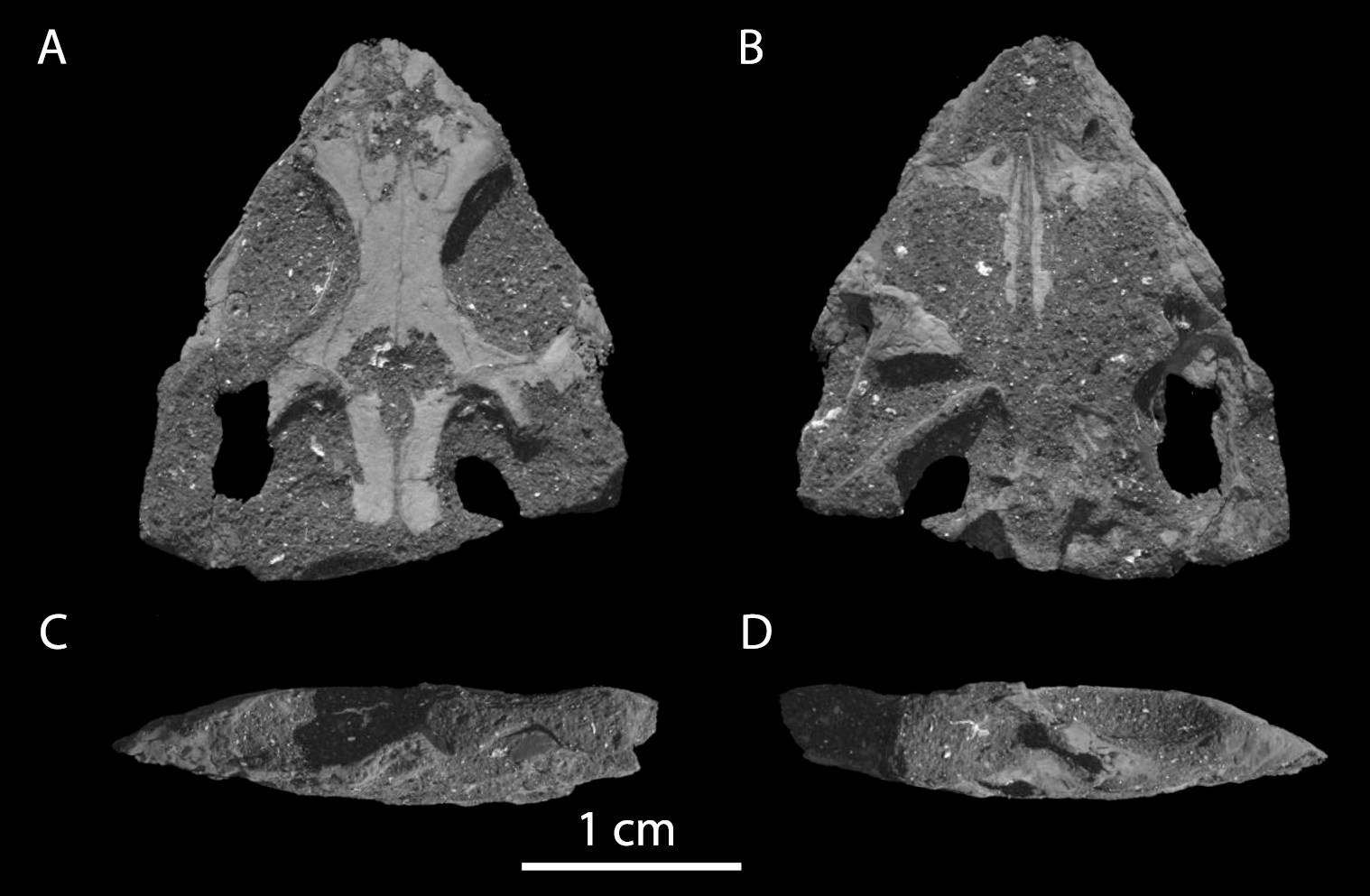
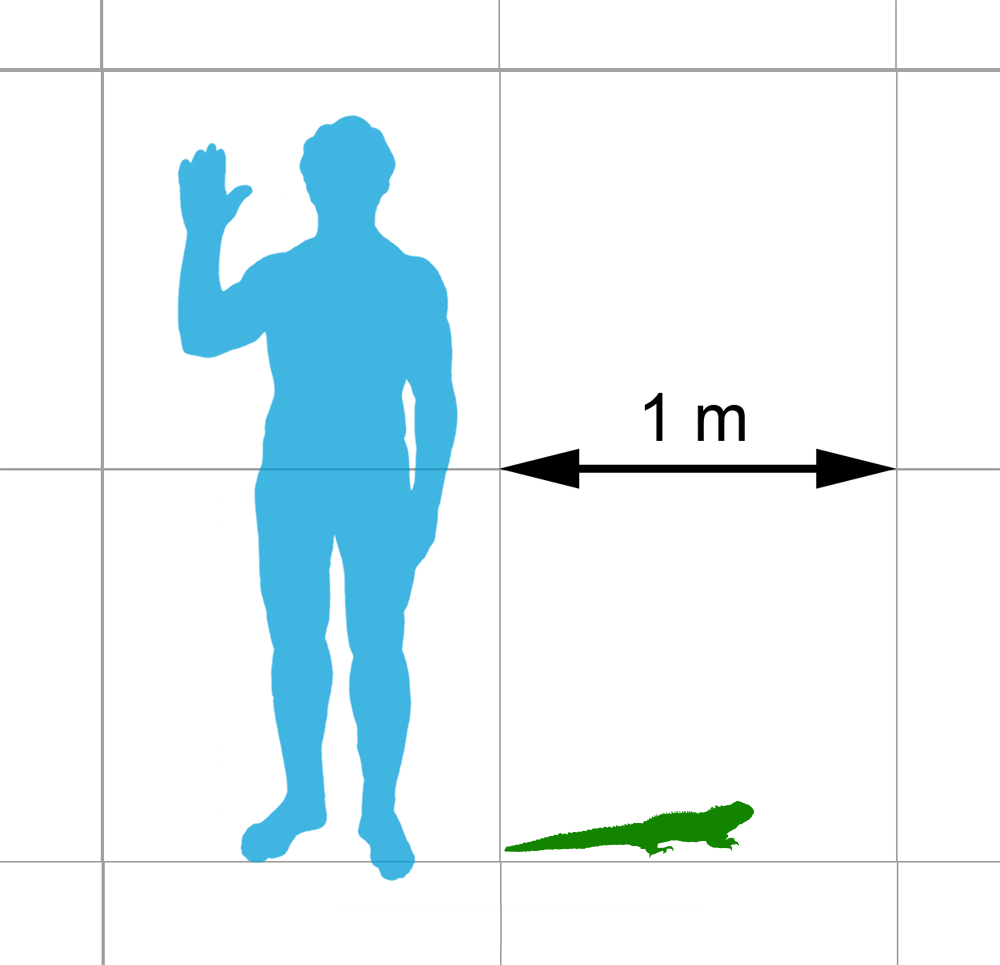
Colobops
''Colobops'' is a genus of reptile from the Late Triassic of Connecticut. Only known from a tiny skull (estimated total length of 2.8 centimeters or 1.1 inches long), this reptile has been interpreted to possess skull attachments for very strong jaw muscles. This may have given it a very strong bite, despite its small size. However, under some interpretations of the CT scan data, ''Colobopss bite force may not have been unusual compared to other reptiles. The generic name, ''Colobops'', is a combination of ''κολοβός'' (''kolobós''), meaning shortened, and ''ὤψ (ṓps),'' meaning face. This translation, "shortened face", refers to its short and triangular skull. ''Colobops'' is known from a single species, ''Colobops noviportensis''. The specific name, ''noviportensis'', is a latinization of New Haven, the name of both the geological setting of its discovery (the New Haven Arkose) as well as a nearby large city. The phylogenetic relations of ''Colobops'' are controve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapheosaur
Sapheosaurs are an extinct group of rhynchocephalian reptiles from the Late Jurassic period. "Sapheosaurs" is an informal name for a group of rhynchocephalians closely related to the genus '' Sapheosaurus''. It was first recognized as a group containing multiple genera by Hoffstetter in 1955. The group has sometimes been given a formal taxonomic name as the family Sapheosauridae, although in some analyses this group belongs to the family Sphenodontidae (which also contains the tuatara, the only living rhynchocephalian) and thus cannot be assigned its own family. They were fairly advanced rhynchocephalians which may have had semiaquatic habits. Classification The most well-known members of the group are ''Sapheosaurus'' and '' Kallimodon'', and most phylogenetic analyses on rhynchocephalians only study these two genera as representatives of sapheosaurs. Although a few early phylogenies in the 1990s did not find that these two formed a natural clade, the relation between these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthodontia (reptiles)
Opisthodontia is a proposed clade of sphenodontian reptiles, uniting '' Opisthias'' from the Late Jurassic-earliest Cretaceous of Europe and North America with the Elienodontinae, a group of herbivorous sphenodontians known from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous. Description Teeth and diet Like other sphenodonts, opisthodonts had acrodont teeth which grew directly from the bone. They had one row of teeth on the lower jaw and two rows on the roof of the mouth. When processing food, their mandibular teeth would have slid between the outer (maxillary) teeth and inner (palatine) teeth. Some opisthodonts, such as '' Sphenotitan'', also had clusters of small teeth on the pterygoid at the center of the mouth roof. Opisthodont teeth were wide, numerous, and tightly-packed for grinding and shredding tough plant matter. Although wide shredding teeth are also known in a few other sphenodontians, such as ''Clevosaurus'' and '' Pelecymala'', the most diverse and long-lasting group o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clevosaurus
''Clevosaurus'' (meaning "Gloucester lizard") is an extinct genus of rhynchocephalian reptile from the Late Triassic and the Early Jurassic periods. Species of ''Clevosaurus'' were widespread across Pangaea, and have been found on all continents except Australia and Antarctica. Five species of ''Clevosaurus'' have been found in ancient fissure fill deposits in south-west England and Wales, alongside other sphenodontians, early mammals and dinosaurs. In regards to its Pangaean distribution, ''C. hadroprodon'' is the oldest record of a sphenodontian from Gondwana, though its affinity to ''Clevosaurus'' has been questioned. History of discovery The first species of ''Clevosaurus'' to be described was ''C. hudsoni'', which was described by William Elgin Swinton in 1939 from a fissure fill deposit in Cromhall Quarry ( Magnesian Conglomerate Formation) in the county of Gloucestershire, England, with the name of the county lending its name to the genus. Description ''Clevosaurus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vadasaurus
''Vadasaurus'' is an extinct genus of rhynchocephalian closely related to the aquatic pleurosaurids. Although this genus was not as specialized as the eel-like pleurosaurs for aquatic life, various skeletal features support the idea that it had a semiaquatic lifestyle. The type species, ''Vadasaurus herzogi'', was described and named in 2017. It was discovered in the Solnhofen Limestone in Germany, which is dated to the Late Jurassic. The generic name "''Vadasaurus"'' is derived from "''vadare''", which is Latin for "to go" or "to walk forth", and "''saurus''", which means "lizard" (although rhynchocephalians are not lizards). "''Vadare"'' is the root of the English word "wade", which is the reason it was chosen for this genus, in reference to its perceived semiaquatic habits. The specific name, "''herzogi''", refers to Werner Herzog, a Bavarian filmmaker. Description The holotype of ''Vadasaurus herzogi'' is AMNH FARB 32768, a well-preserved but slightly flattened skeleton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenodon Punctatus
Tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') are reptiles endemic to New Zealand. Despite their close resemblance to lizards, they are part of a distinct lineage, the order Rhynchocephalia. The name ''tuatara'' is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order. Rhynchocephalians originated during the Triassic (~250 million years ago), reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic and, with the exception of tuatara, were extinct by 60 million years ago. Their closest living relatives are squamates (lizards and snakes). For this reason, tuatara are of interest in the study of the evolution of lizards and snakes, and for the reconstruction of the appearance and habits of the earliest diapsids, a group of amniote tetrapods that also includes dinosaurs (including birds) and crocodilians. Tuatara are greenish brown and grey, and measure up to from head to tail-tip and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphydontosaurus
''Diphydontosaurus'' is an extinct genus of rhynchocephalian reptile from the Late Triassic of England and Italy. This small animal was related to the living tuatara (''Sphenodon''). It may have grown to a length of . It is more derived than '' Gephyrosaurus'', yet more primitive than '' Planocephalosaurus'', and shares traits with both of them. Description ''Diphydontosaurus'' was a small sphenodontian, measuring up to long. It had long, sharp claws to help it catch its prey, and peg-like piercing teeth to help it eat insects. These features are shared with the other primitive rhynchocephalians '' Gephyrosaurus'' and '' Planocephalosaurus''. Classification ''Diphydontosaurus'' is known from many mostly complete specimens, which means that its classification as a rhynchocephalian is quite certain. In an analysis by Oliver Rahut and colleagues in 2012, it was found that ''Diphydontosaurus'' is the second most basal rhynchocephalian, after ''Gephyrosaurus'', and the most primi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthiamimus
''Opisthiamimus'' () is an extinct genus of small-bodied eusphenodontian rhynchocephalian from the Upper Jurassic Morrison Formation of Northern Wyoming, United States. The type species, ''O. gregori'', is known from four specimens, which together preserve a nearly complete skeleton. It is amongst the smallest known rhynchocephalians, with a skull length of and a snout–vent length (the length from the tip of the snout to the cloaca In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds ...) of around . The genus was described in 2022 by DeMar, Jones & Carrano. It was found that it was only distantly related to '' Eilenodon'', '' Theretairus'' and '' Opisthias,'' the other known rhynchocephalians from the Morrison Formation''.'' References {{Reflist Sphenodontia Prehistoric reptile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planocephalosaurus
''Planocephalosaurus'' is an extinct genus of rhynchocephalian. Fossils of the genus were found in the Tecovas Formation of Texas and the Magnesian Conglomerate of England. ''Planocephalosaurus'' was one of the first sphenodonts and bore a strong resemblance to the extant tuatara, albeit much smaller, at only in length. The creature is presumed to have fed on large invertebrates and small vertebrates. Dentition ''Planocephalosaurus'' exhibits very interesting dentition. Initially, it was believed to have been attached to the bone via acrodont tooth implantation, however, after this specimen was exposed to X-radiography it was determined that this animal has a combination of different tooth implantation types. Similar to another rhynchocephalian, ''Diphydontosaurus'', it possesses acrodont teeth in the posterior portion of the jaw, and pleurodont dentition in the anterior portion. ''Planocephalosauruss teeth were also fused with the cartilage, unlike its only extant Extant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gephyrosauridae
Gephyrosauridae was a family of rhynchocephalians that lived in the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic. The members of Gephyrosauridae were named lepidosaurs in 1985 by Michael Benton.The Paleobiology Database They are considered to be the only rhynchocephalians that lie outside of Sphenodontia, and in some analyses they are recovered as more closely related to squamates than to sphenodontians. Distribution Members of Gephyrosauridae are known from the ,Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially t ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenodontidae
Sphenodontidae is a family within the reptile group Rhynchocephalia, comprising taxa most closely related to the living tuatara of the genus ''Sphenodon''. Historically the taxa included within Sphenodontidae have varied greatly between analyses, and the group has lacked a formal definition. '' Cynosphenodon'' from the Early Jurassic of Mexico has consistently been recovered as a close relative of the tuatara in most analyses, with the clade containing the two often called Sphenodontinae. The herbivorous Eilenodontinae, otherwise considered part of Opisthodontia, is also sometimes considered part of this family as the sister group to Sphenodontinae. Sphenodontines first appeared during the Early Jurassic, and are characterised by a complete lower temporal bar caused by the fusion of the quadrate/quadratojugal and the jugal The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitakersaurus
''Whitakersaurus'' is a genus of sphenodontid rhynchocephalian reptile dated to be late Triassic in age and is from the Ghost Ranch fossil quarry in New Mexico, USA. It is named after the discoverer of the Ghost Ranch quarry, George O. Whitaker. The fossil was described in 2007. Features The left and right dentary are preserved, along with a fragmentary left maxilla and probable palatal bone, on two blocks of stone. Dentary bones The left dentary is fragmented but still has almost all teeth present, whereas the right dentary is incomplete and has most of the teeth. The left dentary is 11 mm long and has multiple broken teeth or tooth positions. The coronoid process is missing, but there may be a suture present where the dentary was joined to the surangular. A small groove is present on the lingual side of teeth 16-18. The right dentary is only partial, unlike the left dentary where all the fragments are present, but the piece preserved is 9 mm long. The posterior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_601758.jpg)