|
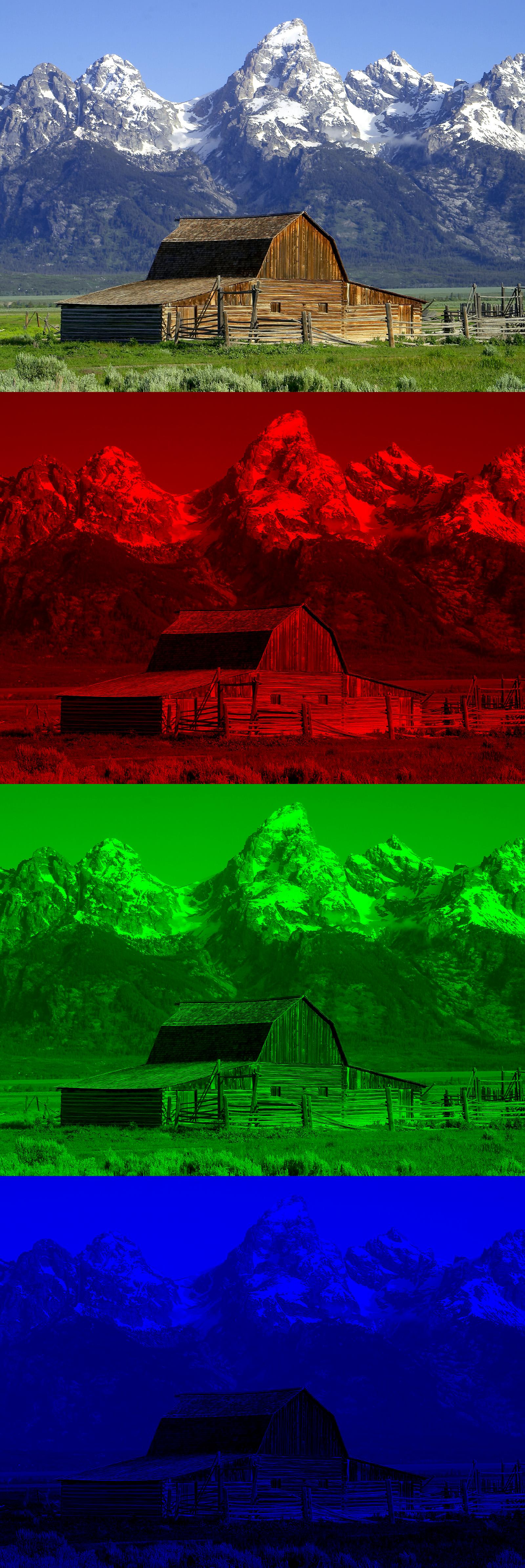
RGBA
RGBA stands for red green blue alpha. While it is sometimes described as a color space, it is actually a three-channel RGB color model supplemented with a fourth ''alpha channel''. Alpha indicates how opaque each pixel is and allows an image to be combined over others using alpha compositing, with transparent areas and anti-aliasing of the edges of opaque regions. Each pixel is a 4D vector. The term does ''not'' define what RGB color space is being used. It also does not state whether or not the colors are premultiplied by the alpha value, and if they are it does not state what color space that premultiplication was done in. This means more information than just "RGBA" is needed to determine how to handle an image. In some contexts the abbreviation "RGBA" means a specific memory layout (called RGBA8888 below), with other terms such as "BGRA" used for alternatives. In other contexts "RGBA" means any layout. Representation In computer graphics, pixels encoding the RGBA c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Compositing
In computer graphics, alpha compositing or alpha blending is the process of combining one image with a background to create the appearance of partial or full transparency. It is often useful to render picture elements (pixels) in separate passes or layers and then combine the resulting 2D images into a single, final image called the composite. Compositing is used extensively in film when combining computer-rendered image elements with live footage. Alpha blending is also used in 2D computer graphics to put rasterized foreground elements over a background. In order to combine the picture elements of the images correctly, it is necessary to keep an associated '' matte'' for each element in addition to its color. This matte layer contains the coverage information—the shape of the geometry being drawn—making it possible to distinguish between parts of the image where something was drawn and parts that are empty. Although the most basic operation of combining two images is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portable Network Graphics
Portable Network Graphics (PNG, officially pronounced , colloquially pronounced ) is a raster graphics, raster-graphics file graphics file format, format that supports lossless data compression. PNG was developed as an improved, non-patented replacement for Graphics Interchange Format (GIF). PNG supports palette-based images (with palettes of 24-bit RGB color model, RGB or 32-bit RGBA color space, RGBA colors), grayscale images (with or without an Alpha compositing, alpha channel for transparency), and full-color non-palette-based RGB or RGBA images. The PNG working group designed the format for transferring images on the Internet, not for professional-quality print graphics; therefore, non-RGB color spaces such as CMYK color model, CMYK are not supported. A PNG file contains a single image in an extensible structure of ''chunks'', encoding the basic pixels and other information such as textual comments and Integrity checker, integrity checks documented in Request for Comments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4D Vector
In computer science, a 4D vector is a 4-component vector data type. Uses include homogeneous coordinates for 3-dimensional space in computer graphics, and ''red green blue alpha'' (RGBA) values for bitmap images with a color and alpha channel (as such they are widely used in computer graphics). They may also represent quaternions (useful for rotations) although the algebra they define is different. Computer hardware support Some microprocessors have hardware support for 4D vectors with instructions dealing with 4 lane ''single instruction, multiple data'' (SIMD) instructions, usually with a 128-bit data path and 32-bit floating point fields. Specific instructions (e.g., 4 element dot product) may facilitate the use of one 128-bit register to represent a 4D vector. For example, in chronological order: Hitachi SH4, PowerPC VMX128 extension, and Intel x86 SSE4. Some 4-element vector engines (e.g., the PS2 vector units) went further with the ability to broadcast components a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netpbm
Netpbm (formerly Pbmplus) is an open-source software, open-source package of graphics programs and a programming library. It is used primarily in Unix, where it is found in all major open-source operating system distributions, but also works on Microsoft Windows, macOS, and other operating systems. File formats Several graphics formats are used and defined by the Netpbm project: * portable bitmap format (PBM) * portable graymap format (PGM) * portable pixmap format (PPM) PBM, PGM and PPM, sometimes collectively referred to as the portable anymap format (PNM) are image file formats designed to be easily exchanged between platforms. The Magic number (programming), magic number at the beginning of a file determines the type. PNM files use a magic number of an ASCII "P" followed by a number defining the file type. The PBM format was invented by Jef Poskanzer in the 1980s. The format allowed monochrome bitmaps to be transmitted within an email message as plain ASCII text, so that it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital representation. A color space may be arbitrary, i.e. with physically realized colors assigned to a set of physical color swatches with corresponding assigned color names (including discrete numbers infor examplethe Pantone collection), or structured with mathematical rigor (as with the NCS System, Adobe RGB and sRGB). A "color space" is a useful conceptual tool for understanding the color capabilities of a particular device or digital file. When trying to reproduce color on another device, color spaces can show whether shadow/highlight detail and color saturation can be retained, and by how much either will be compromised. A "color model" is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers (e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RGB Color Model
The RGB color model is an additive color, additive color model in which the red, green, and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three additive primary colors, red, green, and blue. The main purpose of the RGB color model is for the sensing, representation, and display of images in electronic systems, such as televisions and computers, though it has also been used in conventional photography and Light-emitting diode#RGB systems, colored lighting. Before the electronic age, the RGB color model already had a solid theory behind it, based in Trichromacy, human perception of colors. RGB is a ''device-dependent'' color model: different devices detect or reproduce a given RGB value differently, since the color elements (such as phosphors or dyes) and their response to the individual red, green, and blue levels vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, or even in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transparency (graphic)
Transparency in computer graphics is possible in a number of file formats. The term " transparency" is used in various ways by different people, but at its simplest there is "full transparency" i.e. something that is completely invisible. Only part of a graphic should be fully transparent, or there would be nothing to see. More complex is "partial transparency" or "translucency" where the effect is achieved that a graphic is partially transparent in the same way as colored glass. Since ultimately a printed page or computer or television screen can only be one color at a point, partial transparency is always simulated at some level by mixing colors. There are many different ways to mix colors, so in some cases transparency is ambiguous. In addition, transparency is often an "extra" for a graphics format, and some graphics programs will ignore the transparency. Raster file formats that support transparency include GIF, PNG, WebP, BMP, TIFF, TGA and JPEG 2000, through e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLTK
Fast Light Toolkit (FLTK) is a cross-platform widget (graphical control element) library for graphical user interfaces (GUIs), developed by Bill Spitzak and others. Made to accommodate 3D graphics programming, it has an interface to OpenGL, but it is also suitable for general GUI programming. Using its own widget, drawing and event systems abstracted from the underlying system-dependent code, it allows for writing programs which look the same on all supported operating systems. FLTK is free and open-source software, licensed under GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) with an added clause permitting static linking from applications with incompatible licenses. In contrast to user interface libraries like GTK, Qt, and wxWidgets, FLTK uses a more lightweight design and restricts itself to GUI functionality. Because of this, the library is very small (the FLTK "Hello World" program is around 100 KiB), and is usually statically linked. It also avoids complex macros, separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Graphics
Silicon Graphics, Inc. (stylized as SiliconGraphics before 1999, later rebranded SGI, historically known as Silicon Graphics Computer Systems or SGCS) was an American high-performance computing manufacturer, producing computer hardware and software. Founded in Mountain View, California, in November 1981 by James H. Clark, the computer scientist and entrepreneur perhaps best known for founding Netscape (with Marc Andreessen). Its initial market was 3D graphics computer workstations, but its products, strategies and market positions developed significantly over time. Early systems were based on the RealityEngine, Geometry Engine that Clark and Marc Hannah had developed at Stanford University, and were derived from Clark's broader background in computer graphics. The Geometry Engine was the first very-large-scale integration (VLSI) implementation of a geometry pipeline, specialized hardware that accelerated the "inner-loop" geometric computations needed to display three-dimensional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexadecimal
Hexadecimal (also known as base-16 or simply hex) is a Numeral system#Positional systems in detail, positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of sixteen. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using ten symbols, hexadecimal uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols "0"–"9" to represent values 0 to 9 and "A"–"F" to represent values from ten to fifteen. Software developers and system designers widely use hexadecimal numbers because they provide a convenient representation of binary code, binary-coded values. Each hexadecimal digit represents four bits (binary digits), also known as a nibble (or nybble). For example, an 8-bit byte is two hexadecimal digits and its value can be written as to in hexadecimal. In mathematics, a subscript is typically used to specify the base. For example, the decimal value would be expressed in hexadecimal as . In programming, several notations denote hexadecimal numbers, usually involving a prefi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |