|
Retinalophototroph
A retinalophototroph is one of two different types of phototrophs, and are named for retinal-binding proteins (microbial rhodopsins) they utilize for cell signaling and converting light into energy. Like all phototrophs, retinalophototrophs absorb photons to initiate their cellular processes. In contrast with chlorophototrophs, retinalophototrophs do not use chlorophyll or an electron transport chain to power their chemical reactions. This means retinalophototrophs are incapable of traditional carbon fixation, a fundamental photosynthetic process that transforms inorganic carbon (carbon contained in molecular compounds like carbon dioxide) into organic compounds. For this reason, experts consider them to be less efficient than their chlorophyll-using counterparts, chlorophototrophs. Energy conversion Retinalophototrophs achieve adequate energy conversion via a proton-motive force. In retinalophototrophs, proton-motive force is generated from rhodopsin-like proteins, primarily bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1m0l Opm
{{Le ...
1M or 1-M may refer to: * 1m or 1 metre *1M as one million * Dinas Rekani *Astra 1M satellite * Mars 1M spacecraft *Northrop N-1M, an American experimental aircraft * Globus-1M No.12L, a Russian military communications satellite *UH-1M, model of Bell UH-1 Iroquois *TAC-1M, variant of the semi-automatic carbine Demro TAC-1 *SPP-1M, a variant of the SPP-1 underwater pistol *PDM-1M mine, a variant of the PDM series of amphibious mines *VO-1M, an early designation of the Marine Attack Squadron VMA-231 *YaK-1M, a variant of the Yakovlev Yak-1 *SSH 1M (WA), an early name of Washington State Route 121 *BWP-1M, a BMP-1 variant *BMW 1M, a BMW 1 Series M Coupe See also *M1 (other) *LM (other) *IM (other) IM or Im may refer to: Arts and entertainment * I.M, South Korean rapper and singer; member of boy band Monsta X * "I.M" (song), a song by Israeli singer Michael Ben David * Iron Maiden, a British heavy metal band * Iron Man, a comic book super ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
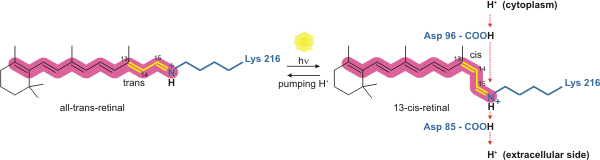
Bacteriorhodopsin
Bacteriorhodopsin (Bop) is a protein used by Archaea, most notably by Haloarchaea, a class of the Euryarchaeota. It acts as a proton pump; that is, it captures light energy and uses it to move protons across the membrane out of the cell. The resulting proton gradient is subsequently converted into chemical energy. Function Bacteriorhodopsin is a light-driven H+ ion transporter found in some Haloarchaea, most notably ''Halobacterium salinarum'' (formerly known as syn. ''H. halobium''). The proton-motive force generated by the protein is used by ATP synthase to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP). By expressing Bacteriorhodopsin, the archaea cells are able to synthesise ATP in the absence of a carbon source. Structure Bacteriorhodopsin is a 27'' '' kDa integral membrane protein usually found in two-dimensional crystalline patches known as "purple membrane", which can occupy almost 50% of the surface area of the archaeal cell. The repeating element of the hexa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophic Ecology
Trophic, from Ancient Greek wikt:τροφικός, τροφικός (''trophikos'') "pertaining to food or nourishment", may refer to: * Trophic cascade * Trophic coherence * Trophic egg * Trophic function * Trophic hormone * Trophic level index * Trophic level * Trophic mutualism * Trophic pyramid * Trophic species * Trophic state index See also * Food * Tropic (other) {{bca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabolism. ''Photosynthesis'' usually refers to oxygenic photosynthesis, a process that produces oxygen. Photosynthetic organisms store the chemical energy so produced within intracellular organic compounds (compounds containing carbon) like sugars, glycogen, cellulose and starches. To use this stored chemical energy, an organism's cells metabolize the organic compounds through cellular respiration. Photosynthesis plays a critical role in producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and it supplies most of the biological energy necessary for complex life on Earth. Some bacteria also perform anoxygenic photosynthesis, which uses bacteriochlorophyll to split hydrogen sulfide as a reductant instead of water, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the evolution of many organisms. HGT is influencing scientific understanding of higher-order evolution while more significantly shifting perspectives on bacterial evolution. Horizontal gene transfer is the primary mechanism for the spread of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and plays an important role in the evolution of bacteria that can degrade novel compounds such as human-created Bactericide, pesticides and in the evolution, maintenance, and transmission of virulence. It often involves Temperateness (virology), temperate bacteriophages and plasmids. Genes responsible for antibiotic resistance in one species of bacteria can be transferred to another species of bacteria through various mechanisms of HGT such as Transformation (genetics), tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malate
Malic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a dicarboxylic acid that is made by all living organisms, contributes to the sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms (L- and D-enantiomers), though only the L-isomer exists naturally. The salts and esters of malic acid are known as malates. The malate anion is a metabolic intermediate in the citric acid cycle. Etymology The word 'malic' is derived from Latin , meaning 'apple'. The related Latin word , meaning 'apple tree', is used as the name of the genus '' Malus'', which includes all apples and crabapples; and is the origin of other taxonomic classifications such as Maloideae, Malinae, and Maleae. Biochemistry L-Malic acid is the naturally occurring form, whereas a mixture of L- and D-malic acid is produced synthetically. File:L-Äpfelsäure.svg, L-Malic acid (''S'') File:D-Äpfelsäure.svg, D-Malic acid (''R'') Malate plays an important role ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaplerotic Reactions
Anaplerotic reactions, a term coined by Hans Kornberg and originating from the Greeἀνά 'up' anπληρόω 'to fill', are chemical reactions that form intermediates of a metabolic pathway. Examples of such are found in the citric acid cycle (TCA cycle). In normal function of this cycle for respiration, concentrations of TCA intermediates remain constant; however, many biosynthetic reactions also use these molecules as a substrate. Anaplerosis is the act of replenishing TCA cycle intermediates that have been extracted for biosynthesis (in what are called anaplerotic reactions). The TCA cycle is a hub of metabolism, with central importance in both energy production and biosynthesis. Therefore, it is crucial for the cell to regulate concentrations of TCA cycle metabolites in the mitochondria. Anaplerotic flux must balance cataplerotic flux in order to retain homeostasis of cellular metabolism. Reactions of anaplerotic metabolism There are five major reactions classed as anaple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoheterotroph
Photoheterotrophs (''Greek language, Gk'': ''photo'' = light, ''hetero'' = (an)other, ''troph'' = nourishment) are heterotrophic phototrophs—that is, they are organisms that use light for energy, but cannot use carbon dioxide as their sole carbon source. Consequently, they use organic compounds from the environment to satisfy their carbon requirements; these compounds include carbohydrates, fatty acids, and Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols. Examples of photoheterotrophic organisms include Purple bacteria, purple non-sulfur bacteria, Chloroflexota, green non-sulfur bacteria, and heliobacteria. These microorganisms are ubiquitous in aquatic habitats, occupy unique niche-spaces, and contribute to global biogeochemical cycling. Recent research has also indicated that the oriental hornet and some aphids may be able to use light to supplement their energy supply. Some recent research has even found hints of photoheterotrophy in a few eukaryotes, though it’s still being studied. Research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteorhodopsin
Proteorhodopsin (PR or pRhodopsin) belongs to the Protein family, family of Bacteria, bacterial Transmembrane protein, transmembrane Rhodopsin, rhodopsins (Retinylidene protein, retinylidene proteins). In 1971, the first Microorganism, microbial Transmembrane protein, transmembrane rhodopsin - Bacteriorhodopsin was discovered in Archaea, archea domain by Dieter Oesterhelt and Walther Stoeckenius. Later in 2000, the first Bacteria, bacterial Transmembrane protein, transmembrane Rhodopsin, rhodopsins was discovered by Oded Beja, Oded Béjà and Edward DeLong. The Proteorhodopsin is widely expressed in various type of aquatic habitats. It functions as light-driven Proton pump, proton pumps with the help of retinal chromophore at the active site. The light-driven proton pump gives bacteria energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Discovery Efforts by Oded Beja, Oded Béjà from Edward DeLong research group in pioneering bacterial artificial chromosome metagenomics analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton-motive Force
Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions across a semipermeable membrane bound structure, down their electrochemical gradient. An important example is the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the movement of hydrogen ions (H+) across a membrane during cellular respiration or photosynthesis. Hydrogen ions, or protons, will diffuse from a region of high proton concentration to a region of lower proton concentration, and an electrochemical concentration gradient of protons across a membrane can be harnessed to make ATP. This process is related to osmosis, the movement of water across a selective membrane, which is why it is called "chemiosmosis". ATP synthase is the enzyme that makes ATP by chemiosmosis. It allows protons to pass through the membrane and uses the free energy difference to convert phosphorylate adenosine diphosphate (ADP) into ATP. The ATP synthase contains two parts: CF0 (present in thylakoid membrane) and CF1 (protrudes on the outer surface of thylakoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phototroph
Phototrophs () are organisms that carry out photon capture to produce complex organic compounds (e.g. carbohydrates) and acquire energy. They use the energy from light to carry out various cellular metabolic processes. It is a list of common misconceptions, common misconception that phototrophs are obligatorily photosynthetic. Many, but not all, phototrophs often photosynthesize: they anabolism, anabolically convert carbon dioxide into organic material to be utilized structurally, functionally, or as a source for later catabolism, catabolic processes (e.g. in the form of starches, sugars and fats). All phototrophs either use electron transport chains or direct proton pumping to establish an electrochemical gradient which is utilized by ATP synthase, to provide the molecular energy currency for the cell. Phototrophs can be either autotrophs or heterotrophs. If their electron and hydrogen donors are inorganic compounds (e.g., , as in some purple sulfur bacteria, or , as in some gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |