|
Reductive Dehalogenation
In organochlorine chemistry, reductive dechlorination describes any chemical reaction which cleaves the covalent bond between carbon and chlorine via reductants, to release chloride ions. Many modalities have been implemented, depending on the application. Reductive dechlorination is often applied to remediation of chlorinated pesticides or dry cleaning solvents. It is also used occasionally in the synthesis of organic compounds, e.g. as pharmaceuticals. Chemical Dechlorination is a well-researched reaction in organic synthesis, although it is not often used. Usually stoichiometric amounts of dechlorinating agent are required. In one classic application, the Ullmann reaction, chloroarenes are coupled to biphenyls. For example, the activated substrate 2-chloronitrobenzene is converted into 2,2'-dinitrobiphenyl with a copper - bronze alloy. Zerovalent iron effects similar reactions. Organophosphorus(III) compounds effect gentle dechlorinations. The products are alkenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organochlorine Compound
Organochlorine chemistry is concerned with the properties of organochlorine compounds, or organochlorides, organic compounds that contain one or more carbon–chlorine bonds. The chloroalkane class (alkanes with one or more hydrogens substituted by chlorine) includes common examples. The wide structural variety and divergent chemical properties of organochlorides lead to a broad range of names, applications, and properties. Organochlorine compounds have wide use in many applications, though some are of profound environmental concern, with TCDD being one of the most notorious. Organochlorides such as trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, dichloromethane and chloroform are commonly used as solvents and are referred to as "chlorinated solvents". Physical and chemical properties Chlorination modifies the physical properties of hydrocarbons in several ways. These compounds are typically denser than water due to the higher atomic weight of chlorine versus hydrogen. They have highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Bacteria
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenated environment. Anaerobes may be unicellular (e.g. protozoans, bacteria) or multicellular. Most fungi are obligate aerobes, requiring oxygen to survive. However, some species, such as the Chytridiomycota that reside in the rumen of cattle, are obligate anaerobes; for these species, anaerobic respiration is used because oxygen will disrupt their metabolism or kill them. The sea floor is possibly one of the largest accumulation of anaerobic organisms on Earth, where microbes are primarily concentrated around hydrothermal vents. These microbes produce energy in absence of sunlight or oxygen through a process called chemosynthesis, whereby inorganic compounds such as hydrogen gas, hydrogen sulfide or ferrous ions are converted into organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichloroethylene
Trichloroethylene (TCE) is an organochloride with the formula C2HCl3, commonly used as an industrial metal-degreasing solvent. It is a clear, colourless, non-flammable, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like pleasant mild smell and sweet taste.Trichloroethylene (TCE) on ATSDR Its name is trichloroethene. Trichloroethylene has been sold under a variety of trade names. Industrial abbreviations include trichlor, Trike, Tricky and tri. Under the trade names Trimar and Trilene, it was used as a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrachloroethylene
Tetrachloroethylene, also known as perchloroethylene or under the systematic name tetrachloroethene, and abbreviations such as perc (or PERC), and PCE, is a chlorocarbon with the formula . It is a non-flammable, stable, colorless and heavy liquid widely used for dry cleaning of fabrics and occasionally as a highly effective automotive brake cleaner. It has a mildly sweet, sharp odor, detectable by most people at a concentration of 50 ppm. Tetrachloroethylene is regarded as a toxic substance, a human health hazard, and an environmental hazard. In 2020, the United States Environmental Protection Agency stated that "tetrachloroethylene exposure may harm the nervous system, liver, kidneys, and reproductive system, and may be harmful to unborn children", and reported that numerous toxicology agencies regard it as a carcinogen. History and production French chemist Henri Victor Regnault first synthesized tetrachloroethylene in 1839 by thermal decomposition of hexachloroethane f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
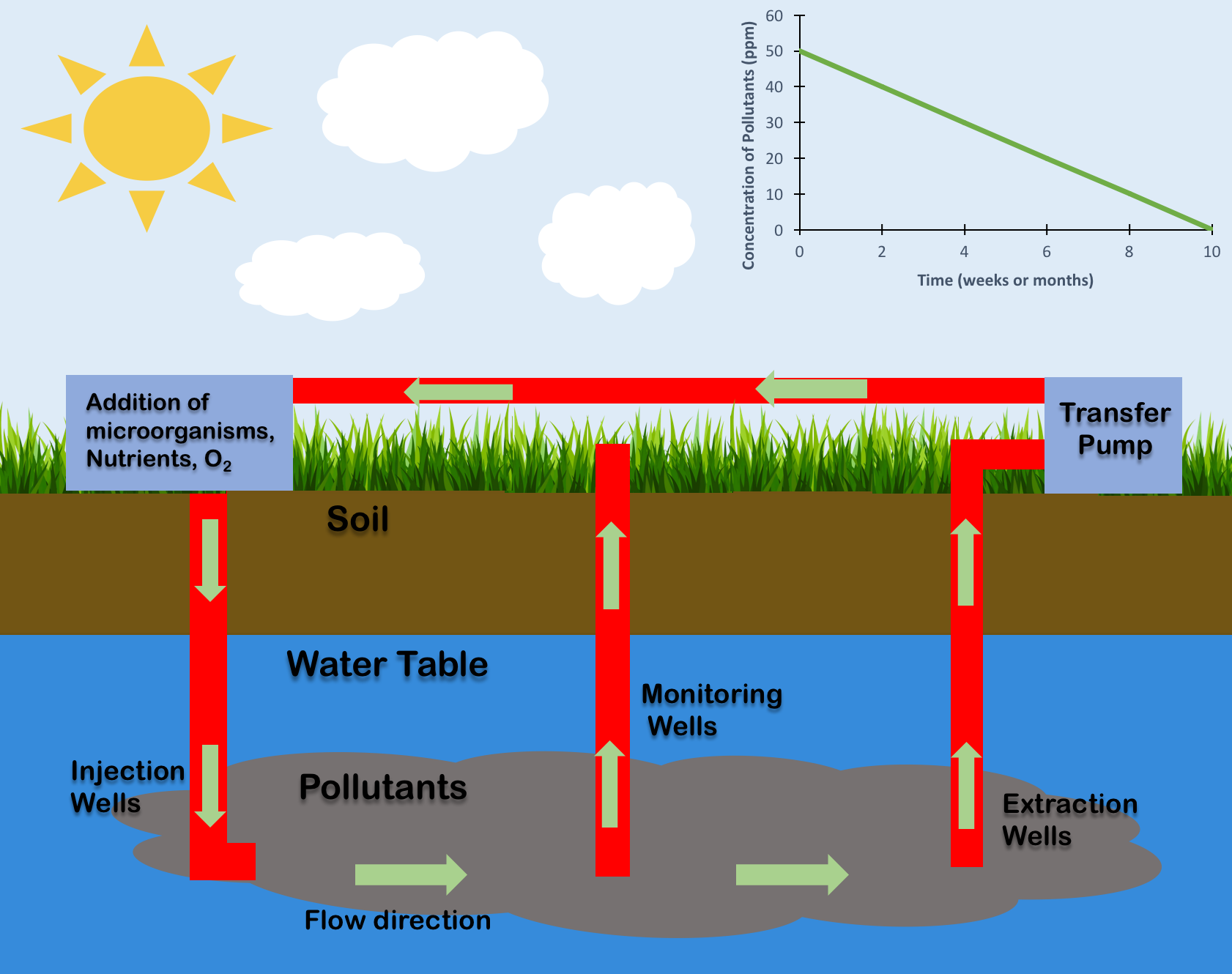
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, fuel gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. This technology is rarely implemented however because it is slow or inefficient. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote their growt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It plays an essential role in the nervous system by supporting myelinogenesis, myelin synthesis and is critical for the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. While animals require B12, plants do not, relying instead on alternative enzymatic pathways. Vitamin B12 is the most chemically complex of all vitamins, and is synthesized exclusively by certain archaea and bacteria. Natural food sources include meat, shellfish, liver, fish, poultry, Egg as food, eggs, and dairy products. It is also added to many breakfast cereals through food fortification and is available in dietary supplement and pharmaceutical forms. Supplements are commonly taken orally but may be administered via intramuscular injection to treat defic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehalobacter
''Dehalobacter'' is a genus in the phylum Bacillota (Bacteria). Etymology The generic name ''Dehalobacter'' derives from Latin ''de'', from; ''halogenum'' from Swedish, coined by Swedish chemist Baron Jöns Jakob Berzelius (1779–1848) from Greek ''hals'', ''halos'' "salt" + ''gen'' "to produce", so called because a salt is formed in reactions involving these elements; a rod '' bacter'', nominally meaning "a rod", but in effect meaning a bacterium, a rod; giving ''Dehalobacter'', a halogen-removing, rod-shaped bacterium. Species The genus contains a single species, namely '' D. restrictus'' (Holliger ''et al''. 1998), type species of the genus. The specific name is from Latin ''restrictus'', limited, restricted, confined, referring to the limited substrate range used. Recently, ''Dehalobacter'' sp. UNSWDHB, which dechlorinate chloroform to dichloromethane, and its reductive dehalogenase were identified. See also * Bacterial taxonomy * Microbiology * List of bacterial or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehalococcoides
''Dehalococcoides'' is a genus of bacteria within class Dehalococcoidia that obtain energy via the oxidation of hydrogen and subsequent reductive dehalogenation of halocarbon, halogenated organic compounds in a mode of anaerobic respiration called organohalide respiration. They are well known for their great potential to remediate halogenated ethenes and aromatics. They are the only bacteria known to transform highly chlorinated dioxins, PCBs. In addition, they are the only known bacteria to transform tetrachloroethene (Tetrachloroethylene, perchloroethene, PCE) to ethene. Microbiology The first member of the genus ''Dehalococcoides'' was described in 1997 as ''Dehalococcoides ethenogenes'' strain 195 (nom. inval.). Additional ''Dehalococcoides'' members were later described as strains CBDB1, BAV1, FL2, VS, and GT. In 2012 all yet-isolated ''Dehalococcoides'' strains were summarized under the new taxonomic name ''Dehalococcoides mccartyi, D. mccartyi'', with strain 195 as the type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) Preferred IUPAC name, recommends using the name "alkene" only for Open-chain compound, acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for Cyclic compound, cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with ''n'' being a >1 natural number (which is two hydrogens less than the corresponding alkane). When ''n'' is four or more, isomers are possible, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |