|
Raw Fish
Raw fish or shellfish dishes include marinated raw fish (soaked in a seasoned liquid) and raw fish which is lightly cured such as gravlax, but not fish which is fully cured (fermented, pickled, smoked or otherwise preserved). __TOC__ Raw fish dishes Health concerns Parasites in fish are a natural occurrence and common. Though not a health concern in thoroughly cooked fish, parasites are a concern when consumers eat raw or lightly preserved fish such as sashimi, sushi, ceviche, and gravlax. The popularity of such raw fish dishes makes it important for consumers to be aware of this risk. Raw fish should be frozen to an internal temperature of −20 °C (−4 °F) for at least 7 days to kill parasites. It is important to be aware that home freezers may not be cold enough to kill parasites. Traditionally, fish that live all or part of their lives in fresh water were considered unsuitable for sashimi due to the possibility of parasites (see sashimi article). Para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herring
Herring are various species of forage fish, belonging to the Order (biology), order Clupeiformes. Herring often move in large Shoaling and schooling, schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific Ocean, North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, including the Baltic Sea, as well as off the west coast of South America. Three species of ''Clupea'' (the type genus of the herring family Clupeidae) are recognised, and comprise about 90% of all herrings captured in fisheries. The most abundant of these species is the Atlantic herring, which comprises over half of all herring capture. Fish called herring are also found in the Arabian Sea, Indian Ocean, and Bay of Bengal. Herring played an important role in the history of marine fisheries in Europe, and early in the 20th century, their study was fundamental to the development of fisheries science. These oily fish also have a long history as an important food fish, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravlax
Gravlax (), gravlaks or graved salmon is a Nordic dish consisting of salmon that is cured using a mix of salt, sugar and dill. It is garnished with fresh dill or sprucetwigs and may occasionally be cold- smoked afterwards. Gravlax is usually served as an appetizer, sliced thinly and accompanied by a dill and mustard sauce known as (Also known in Sweden as , in Norway as , literally 'mustard sauce', in Denmark as , literally 'fox sauce', in Iceland as , and in Finland as , literally 'butler's sauce'), either on bread or with boiled potatoes. Etymology The word comes from the Northern Germanic word ('to dig'; modern sense 'to cure (fish)') which goes back to the Proto-Germanic , ('hole in the ground; ditch, trench; grave') and the Indo-European root 'to dig, to scratch, to scrape', and ''/'', 'salmon'. History During the Middle Ages, gravlax was made by fishermen, who salted the salmon and lightly fermented it by burying it in the sand above the high-tide line. Perhap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swordfish Hinava
The swordfish (''Xiphias gladius''), also known as the broadbill in some countries, are large, highly migratory predatory fish characterized by a long, flat, pointed bill. They are the sole member of the family Xiphiidae. They are a popular sport fish of the billfish category. Swordfish are elongated, round-bodied, and lose all teeth and scales by adulthood. These fish are found widely in tropical and temperate parts of the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans, and can typically be found from near the surface to a depth of , and exceptionally up to depths of 2,234 m. They commonly reach in length, and the maximum reported is in length and in weight. Taxonomy and etymology The swordfish is named after its long pointed, flat bill, which resembles a sword. The species name, ''Xiphias gladius'', derives from Greek (''xiphias'', "swordfish"), itself from (''xiphos'', "sword") and from Latin ("sword"). This makes it superficially similar to other billfish such as marlin, but u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinava
Hinava is a traditional native dish of the Kadazan-Dusun people in the state of Sabah. It is made from fish and mixed with lime juice, bird's eye chili, sliced shallots and grated ginger. While the Kadazan are famous with their ''Hinava tongii''. See also * Umai, a similar dish from neighbouring state of Sarawak * Kinilaw, a similar dish from the Philippines * Ceviche * List of raw fish dishes Raw fish or shellfish dishes include marinated raw fish (soaked in a seasoned liquid) and raw fish which is lightly cured such as gravlax, but not fish which is fully cured (fermented, pickled, smoked or otherwise preserved). __TOC__ Raw fis ... References External links Hinava Ginapan(Kadazan-Dusun) Malaysian cuisine Uncooked fish dishes {{Malaysia-cuisine-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grouper
Groupers are a diverse group of marine ray-finned fish in the family Epinephelidae, in the order Perciformes. Groupers were long considered a subfamily of the seabasses in Serranidae, but are now treated as distinct. Not all members of this family are called "groupers". The common name "grouper" is usually given to fish in one of two large genera: ''Epinephelus'' and '' Mycteroperca''. In addition, the species classified in the small genera ''Anyperidon'', ''Cromileptes'', ''Dermatolepis'', ''Graciela'', ''Saloptia'', and ''Triso'' are also called "groupers". Fish in the genus '' Plectropomus'' are referred to as "coral groupers". These genera are all classified in the subfamily Epiphelinae. However, some of the hamlets (genus ''Alphestes''), the hinds (genus ''Cephalopholis''), the lyretails (genus ''Variola''), and some other small genera (''Gonioplectrus'', ''Niphon'', ''Paranthias'') are also in this subfamily, and occasional species in other serranid genera have common na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skipjack Tuna
The skipjack tuna (''Katsuwonus pelamis'') is a perciform fish in the tuna family, Scombridae, and is the only member of the genus ''Katsuwonus''. It is also known as katsuo, arctic bonito, mushmouth, oceanic bonito, striped tuna or victor fish. It grows up to in length. It is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan pelagic fish found in tropical and warm-temperate waters. It is a very important species for fisheries. It is also the namesake of the nuclear submarine USS Skipjack (SSN-585), USS ''Skipjack''. Description It is a streamlined, fast-swimming pelagic fish common in tropical waters throughout the world, where it inhabits surface waters in large Shoaling and schooling, shoals (up to 50,000 fish, often in combination with other Scombridae, scombridaes), feeding on fish, crustaceans, cephalopods, and Mollusk, mollusks. It is an important prey species for sharks and large pelagic fishes and is often used as live bait when fishing for marlin. It has no scales, except on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brine
Brine (or briny water) is a high-concentration solution of salt (typically sodium chloride or calcium chloride) in water. In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawater, on the lower end of that of solutions used for brining foods) up to about 26% (a typical saturated solution, depending on temperature). Brine forms naturally due to evaporation of ground saline water but it is also generated in the mining of sodium chloride. Brine is used for food processing and cooking (pickling and brining), for de-icing of roads and other structures, and in a number of technological processes. It is also a by-product of many industrial processes, such as desalination, so it requires wastewater treatment for proper disposal or further utilization (fresh water recovery). In nature Brines are produced in multiple ways in nature. Modification of seawater via evaporation results in the concentration of salts in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
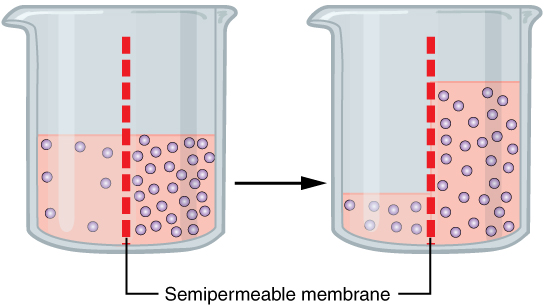
Osmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane, selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do Work (physics), work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to prevent net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative properties, colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity. Osmosis is a vital process in biology, bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—once part of the Byzantine Empire� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appetizer
An hors d'oeuvre ( ; ), appetiser, appetizer or starter is a small dish served before a meal in European cuisine. Some hors d'oeuvres are served cold, others hot. Hors d'oeuvres may be served at the dinner table as a part of the meal, or they may be served before seating, such as at a reception or cocktail party. Formerly, hors d'oeuvres were also served between courses.''Oxford English Dictionary'', First Edition, 189''s.v.'' Typically smaller than a main dish, an hors d'oeuvre is often designed to be eaten by hand. Hors d'oeuvre are typically served at parties as a small "snack" before a main course. Etymology in French literally means 'outside the work', that is "not part of the ordinary set of courses in a meal". In practice, it is a dish which stands on its own as a snack or supports the main course. The French spelling is the same for singular and plural usage. In English, the typographic ligature is usually replaced by the digraph and two plural forms are acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dill
Dill (''Anethum graveolens'') is an annual herb in the celery family Apiaceae. It is native to North Africa, Iran, and the Arabian Peninsula; it is grown widely in Eurasia, where its leaves and seeds are used as a herb or spice for flavouring food. Etymology The word ''dill'' and its close relatives are found in most of the Germanic languages; its ultimate origin is unknown. Taxonomy The genus name ''Anethum'' is the Latin form of Greek ἄνῑσον / ἄνησον / ἄνηθον / ἄνητον, which meant both "dill" and " anise". The form 'anīsum' came to be used for anise, and 'anēthum' for dill. The Latin word is the origin of dill's names in the Western Romance languages ('anet', 'aneldo' etc.), and also of the obsolete English 'anet'. Botany Dill grows up to from a taproot like a carrot. Its stems are slender and hollow with finely divided, softly delicate leaves; the leaves are alternately arranged, long with ultimate leaf divisions measuring broad, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |