|
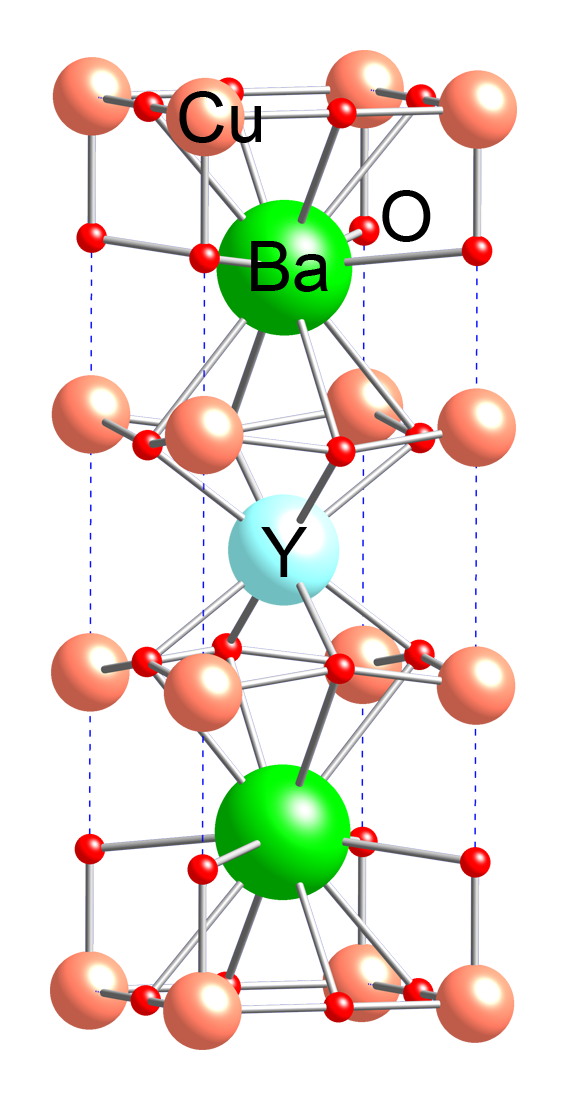
Rare-earth Barium Copper Oxide
Rare-earth barium copper oxide (ReBCO) is a family of chemical compounds known for exhibiting high-temperature superconductivity (HTS). ReBCO superconductors have the potential to sustain stronger magnetic fields than other superconductor materials. Due to their high critical temperature and critical magnetic field, this class of materials are proposed for use in technical applications where conventional low-temperature superconductors do not suffice. This includes magnetic confinement fusion reactors such as the ARC reactor, allowing a more compact and potentially more economical construction, and superconducting magnets to use in future particle accelerators to come after the Large Hadron Collider, which utilizes low-temperature superconductors. Materials Any rare-earth element can be used in a ReBCO; popular choices include yttrium (YBCO), lanthanum ( LBCO), samarium (Sm123), neodymium (Nd123 and Nd422), gadolinium (Gd123) and europium (Eu123), where the numbers among paren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europium
Europium is a chemical element; it has symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is a silvery-white metal of the lanthanide series that reacts readily with air to form a dark oxide coating. Europium is the most chemically reactive, least dense, and softest of the lanthanides. It is soft enough to be cut with a knife. Europium was discovered in 1896, provisionally designated as Σ; in 1901, it was named after the continent of Europe. Europium usually assumes the oxidation state +3, like other members of the lanthanide series, but compounds having oxidation state +2 are also common. All europium compounds with oxidation state +2 are slightly reducing. Europium has no significant biological role and is relatively non-toxic compared to other heavy metals. Most applications of europium exploit the phosphorescence of europium compounds. Europium is one of the rarest of the rare-earth elements on Earth.Stwertka, Albert. ''A Guide to the Elements'', Oxford University Press, 1996, p. 156. Ety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampere
The ampere ( , ; symbol: A), often shortened to amp,SI supports only the use of symbols and deprecates the use of abbreviations for units. is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). One ampere is equal to 1 coulomb (C) moving past a point per second. It is named after French mathematician and physicist André-Marie Ampère (1775–1836), considered the father of electromagnetism along with Danish physicist Hans Christian Ørsted. As of the 2019 revision of the SI, the ampere is defined by fixing the elementary charge to be exactly , which means an ampere is an electric current equivalent to elementary charges moving every seconds, or approximately elementary charges moving in a second. Prior to the redefinition, the ampere was defined as the current passing through two parallel wires 1 metre apart that produces a magnetic force of newtons per metre. The earlier CGS system has two units of current, one structured similarly to the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Fusion Systems
Commonwealth Fusion Systems (CFS) is an American fusion power company founded in 2018 in Cambridge, Massachusetts, after a spin-out from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Its stated goal is to build a small fusion power plant based on the ARC tokamak design. It has participated in the United States Department of Energy’s INFUSE public-private knowledge innovation scheme, with several national labs and universities. History CFS was founded in 2018 as a spin-off from the MIT Plasma Science and Fusion Center. After initial funding of $50 million in 2018 from the Italian multinational Eni, CFS closed its series A round of venture capital funding in 2019 with a total of US$ 115 million in funding from Eni, Bill Gates's Breakthrough Energy Ventures, Vinod Khosla's Khosla Ventures, and others. CFS raised an additional US$ 84 million in series A2 funding from Singapore's Temasek, Norway's Equinor, and Devonshire Investors, as well as from previous investors. As o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetragonal Crystal System
In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the cube becomes a rectangular prism with a square base (''a'' by ''a'') and height (''c'', which is different from ''a''). Bravais lattices There are two tetragonal Bravais lattices: the primitive tetragonal and the body-centered tetragonal. The body-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the primitive tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell, while the face-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the body-centered tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell. Crystal classes The point groups that fall under this crystal system are listed below, followed by their representations in international notation, Schoenflies notation, orbifold notation, Coxeter notation and mineral examples.Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, ''Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuprate
Cuprates are a class of compounds that contain copper (Cu) atom(s) in an anion. They can be broadly categorized into two main types: 1. Inorganic cuprates: These compounds have a general formula of . Some of them are non-stoichiometric. Many of these compounds are known for their superconducting properties. An example of an inorganic cuprate is the tetrachloridocuprate(II) or tetrachlorocuprate(II) (), an anionic coordination complex that features a copper atom in an oxidation state of +2, surrounded by four chloride ions. 2. Organic cuprates: These are organocopper compounds, some of which having a general formula of , where copper is in an oxidation state of +1, where at least one of the R groups can be any organic group. These compounds, characterized by copper bonded to organic groups, are frequently used in organic synthesis due to their reactivity. An example of an organic cuprate is dimethylcuprate(I) anion . One of the most studied cuprates is , a high-temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthorhombic Crystal System
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (''a'' by ''b'') and height (''c''), such that ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal In mathematics, orthogonality (mathematics), orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. Although many authors use the two terms ''perpendicular'' and ''orthogonal'' interchangeably, the term ''perpendic .... Bravais lattices There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic. For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;See , ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perovskite (structure)
A perovskite is a crystalline material of formula ABX3 with a crystal structure similar to that of the mineral perovskite, this latter consisting of calcium titanium oxide (CaTiO3). The mineral was first discovered in the Ural mountains of Russia by Gustav Rose in 1839 and named after Russian mineralogist L. A. Perovski (1792–1856). In addition to being one of the most abundant structural families, perovskites have wide-ranging properties and applications. Structure Perovskite structures are adopted by many compounds that have the chemical formula ABX3. 'A' and 'B' are positively charged ions (i.e. cations), often of very different sizes, and X is a negatively charged ion (an anion, frequently oxide) that bonds to both cations. The 'A' atoms are generally larger than the 'B' atoms. The ideal cubic structure has the B cation in 6-fold coordination, surrounded by an octahedron of anions, and the A cation in 12-fold cuboctahedral coordination. Additional perovskite for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
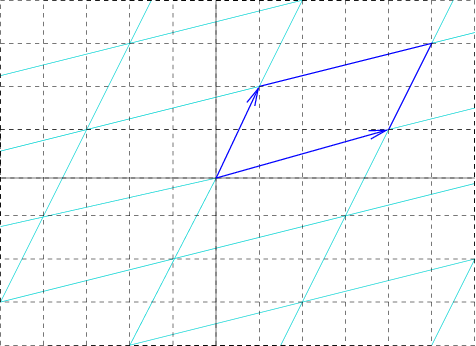
Unit Cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector In mathematics, a unit vector in a normed vector space is a Vector (mathematics and physics), vector (often a vector (geometry), spatial vector) of Norm (mathematics), length 1. A unit vector is often denoted by a lowercase letter with a circumfle ..., for example) does not necessarily have unit size, or even a particular size at all. Rather, the primitive cell is the closest analogy to a unit vector, since it has a determined size for a given lattice and is the basic building block from which larger cells are constructed. The concept is used particularly in describing crystal structure in two and three dimensions, though it makes sense in all dimensions. A lattice can be characterized by the geometry of its unit cell, which is a section of the tiling (a parallelogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole Fraction
In chemistry, the mole fraction or molar fraction, also called mole proportion or molar proportion, is a quantity defined as the ratio between the amount of a constituent substance, ''ni'' (expressed in unit of moles, symbol mol), and the total amount of all constituents in a mixture, ''n''tot (also expressed in moles): :x_i = \frac It is denoted ''xi'' (lowercase Roman letter '' x''), sometimes (lowercase Greek letter chi). (For mixtures of gases, the letter ''y'' is recommended.) It is a dimensionless quantity with dimension of \mathsf/\mathsf and dimensionless unit of moles per mole (mol/mol or molmol−1) or simply 1; metric prefixes may also be used (e.g., nmol/mol for 10−9). When expressed in percent, it is known as the mole percent or molar percentage (unit symbol %, sometimes "mol%", equivalent to cmol/mol for 10−2). The mole fraction is called amount fraction by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and amount-of-substance fractio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review Letters
''Physical Review Letters'' (''PRL''), established in 1958, is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal that is published 52 times per year by the American Physical Society. The journal is considered one of the most prestigious in the field of physics. Over a quarter of Physics Nobel Prize-winning papers between 1995 and 2017 were published in it. ''PRL'' is published both online and as a print journal. Its focus is on short articles ("letters") intended for quick publication. The Lead Editor is Hugues Chaté. The Managing Editor is Robert Garisto. History The journal was created in 1958. Samuel Goudsmit, who was then the editor of '' Physical Review'', the American Physical Society's flagship journal, organized and published ''Letters to the Editor of Physical Review'' into a new standalone journal'','' which became ''Physical Review Letters''. It was the first journal intended for the rapid publication of short articles, a format that eventually became popular in many other fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) is nitrogen in a liquid state at cryogenics, low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, mobile liquid whose viscosity is about one-tenth that of acetone (i.e. roughly one-thirtieth that of water at room temperature). Liquid nitrogen is widely used as a coolant. Physical properties The diatomic character of the N2 molecule is retained after liquefaction. The weak van der Waals interaction between the N2 molecules results in little interatomic attraction. This is the cause of nitrogen's unusually low boiling point. The temperature of liquid nitrogen can readily be reduced to its freezing point by placing it in a vacuum chamber pumped by a vacuum pump. Liquid nitrogen's efficiency as a coolant is limited by the fact that it boils immediately on contact with a warmer object, enveloping the object in an insulating layer of nitrogen gas bubbles. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |