|
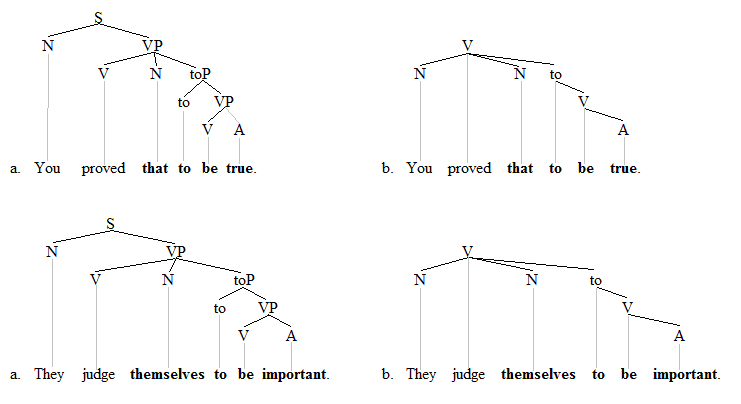
Raising Verb
In linguistics, raising constructions involve the movement of an argument from an embedded or subordinate clause to a matrix or main clause. A raising predicate/verb appears with a syntactic argument that is not its semantic argument but rather the semantic argument of an embedded predicate. In other words, the sentence is expressing something about a phrase taken as a whole. For example, in ''they seem to be trying'', ''"to be trying"'' (the predicand of ''trying'') is the subject of ''seem''. English has raising constructions, unlike some other languages. The term ''raising'' has its origins in the transformational analysis of such constructions; the constituent in question is seen as being "raised" from its initial deep structure position, as the subject of the embedded predicate, to its surface structure position in the matrix predicate/verb. Raising predicates/verbs are related to control predicates, although there are important differences between the two predicate/ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Selection (linguistics)
In linguistics, selection denotes the ability of predicates to determine the semantic content of their arguments. Predicates select their arguments, which means they limit the semantic content of their arguments. A distinction may sometimes be drawn between types of selection; viz., ''s(emantic)-selection'' versus ''c(ategory)-selection''. Selection in general stands in contrast to subcategorization: selection is a semantic concept, whereas subcategorization is a syntactic one; predicates both ''select'' and ''subcategorize'' for their complement arguments, but only ''select'' their subject arguments. Selection is closely related to valency, a term used in grammars other than the Chomskian generative grammar for a similar phenomenon. Examples The following pairs of sentences illustrate the concept of selection; the # indicates semantic deviance: ::a. ''The plant is wilting.'' ::b. ''#The building is wilting.'' – The argument ''the building'' violates the selectional restric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Right Node Raising
In linguistics, the term right node raising (RNR) denotes a sharing mechanism that sees the material to the immediate right of parallel structures being in some sense "shared" by those parallel structures, e.g. '' am likesbut red dislikesthe debates''. The parallel structures of RNR are typically the conjuncts of a coordinate structure, although the phenomenon is not limited to coordination, since it can also appear with parallel structures that do not involve coordination. The term ''right node raising'' itself is due to Postal (1974). Postal assumed that the parallel structures are complete clauses below the surface. The shared constituent was then raised rightward out of each conjunct of the coordinate structure and attached as a single constituent to the structure above the level of the conjuncts, hence "right node raising" was occurring in a literal sense. While the term ''right node raising'' survives, the actual analysis that Postal proposed is not (or no longer) widely ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phrase Structure Grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue ( Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in the Chomsky hierarchy: context-sensitive grammars or context-free grammars. In a broader sense, phrase structure grammars are also known as ''constituency grammars''. The defining character of phrase structure grammars is thus their adherence to the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation of dependency grammars. History In 1956, Chomsky wrote, "A phrase-structure grammar is defined by a finite vocabulary (alphabet) Vp, and a finite set Σ of initial strings in Vp, and a finite set F of rules of the form: X → Y, where X and Y are strings in Vp." Constituency relation In linguistics, phrase structure grammars are all those grammars that are based on the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Exceptional Case Marking
Exceptional case-marking (ECM), in linguistics, is a phenomenon in which the subject of an embedded infinitival verb seems to appear in a superordinate clause and, if it is a pronoun, is unexpectedly marked with object case morphology (''him'' not ''he'', ''her'' not ''she'', etc.). The unexpected object case morphology is deemed "exceptional". The term ''ECM'' itself was coined in the Government and Binding grammar framework although the phenomenon is closely related to the accusativus cum infinitivo constructions of Latin. ECM-constructions are also studied within the context of raising. The verbs that license ECM are known as ''raising-to-object'' verbs. Many languages lack ECM-predicates, and even in English, the number of ECM-verbs is small. The structural analysis of ECM-constructions varies in part according to whether one pursues a relatively flat structure or a more layered one. Examples The ECM-construction is licensed by a relatively small number of verbs in English (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern Grammar, grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of Phrase structure grammar, phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a Head (linguistics), head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb, finite verb phrase constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Control (linguistics)
In linguistics, control is a construction in which the understood Subject (linguistics), subject of a given predicate (grammar), predicate is determined by some expression in context. Stereotypical instances of control involve verbs. A superordinate verb "controls" the arguments of a subordinate, nonfinite verb. Control was intensively studied in the Government and binding theory, government and binding framework in the 1980s, and much of the terminology from that era is still used today. In the days of Transformational Grammar, control phenomena were discussed in terms of ''Equi-NP deletion''. Control is often analyzed in terms of a null pronoun called ''PRO (linguistics), PRO''. Control is also related to Raising (syntax), raising, although there are important differences between control and raising. Examples Standard instances of (obligatory) control are present in the following sentences: ::Susan promised to help us. - Subject control with the obligatory control predicate ''pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Negative Raising
In linguistics, negative raising is a phenomenon that concerns the Raising (syntax), raising of negation from the embedded or subordinate clause of certain Predicate (grammar), predicates to the matrix or Independent clause, main clause. The higher copy of the negation, in the matrix clause, is pronounced; but the semantic meaning is interpreted as though it were present in the embedded clause. Background The NEG-element was first introduced by Edward Klima, but the term ''neg raising'' has been accredited to the early transformational analysis as an instance of movement. Charles J. Fillmore was the first to propose a syntactic approach called ''neg transportation'' but is now known solely as ''negative raising.'' This syntactic approach was supported in the early beginnings by evidence provided by Robin Lakoff, who used, in part, strong/strict polarity items as proof. Laurence R. Horn and Robin Lakoff have written on the theory of negative raising, which is now considered to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Syntactic Expletive
An expletive is a word or phrase inserted into a sentence that is not needed to express the basic meaning of the sentence. It is regarded as semantically null or a placeholder. Expletives are not insignificant or meaningless in all senses; they may be used to give emphasis or tone, to contribute to the meter in verse, or to indicate tense. The word "expletive" derives from the Latin word : serving to fill out or take up space. In these examples ''in fact'' and ''indeed'' are expletives: :*The teacher was not, in fact, present. :*Indeed, the teacher was absent. In conversation the expressions ''like'' and ''you know'', when they are not meaningful, are expletives. The word ''so'', used as an introductory particle (especially when used in answer to a question), has become a common modern expletive. Oaths or profanities may be expletives, as occurs in William Shakespeare, Shakespeare: :"Yes, ''by Saint Patrick'', but there is, Horatio." :: ''Hamlet,'' act 1, scene 5, line 134 :" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |