|
Provinces Of The Republic Of New Granada
According to the constitution of 1832, the territory of the Republic of New Granada was divided into provinces. Each province was composed of one or more cantons, and each canton is several divided into districts parish. The provinces in 1832 were the same that made the Granadine Convention the same year and ratifying the constitution gave the republic. These were: Provinces 1851 For the year 1851 the changes of government and political-economic ideologies of these, added to the existing strong regional trends, led to the division of the republic in 36 provinces, which were: Territories Likewise, the Republic cover some territories in the peripheries of the country: * Caquetá Territory, capital in Mocoa * San Martín Territory, capital in San Martín, between Meta River The Meta River is a major left tributary of the Orinoco River in eastern Colombia and southern Venezuela, South America. The Meta originates in the Cordillera Oriental (Colombia), Eastern Rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombia In 1835
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuela to the east and northeast, Brazil to the southeast, Peru and Ecuador to the south and southwest, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and Panama to the northwest. Colombia is divided into 32 Departments of Colombia, departments. The Capital District of Bogotá is also the List of cities in Colombia by population, country's largest city hosting the main financial and cultural hub. Other major urban areas include Medellín, Cali, Barranquilla, Cartagena, Colombia, Cartagena, Santa Marta, Cúcuta, Ibagué, Villavicencio and Bucaramanga. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers (440,831 sq mi) and has a population of around 52 million. Its rich cultural heritage—including language, religion, cuisine, and art—reflects its history as a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
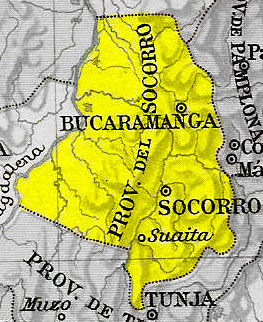
Socorro, Santander
Socorro is a town and municipality in the Santander Department in northeastern Colombia. It was founded in 1681 by José de Archila and José Díaz Sarmiento. The town was very influential in the history of Colombia. There began the Revolt of the Comuneros (New Granada), revolt of the Comuneros of 1781 against the oppression of Spanish rule. Socorro was the capital of Santander between 1862 and 1886. History The origin of the population was much more prosaic and simple. Broadly it can be argued that formed beside the road leading from Velez to Giron, the exact site where today is located. Jose de Archila and José Díaz Sarmiento, wealthy landowners chanchona Valley, donated the land to the Virgen de Nuestra Senora del Socorro, to set the village on 16 June 1683. Blas García Cabrera, influential and neighboring potentate representing many settlers, requested the erection of the parish to the metropolitan curia Santa Fe, with such good fortune, that the Archbishop Antonio Sanz Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socorro Province
Socorro Province was one of the provinces of Gran Colombia. It belonged to the Boyacá Department which was created in 1824. See also *Revolt of the Comuneros (New Granada) The Revolt of the Comuneros was a popular uprising in the Viceroyalty of New Granada (now Colombia and parts of Venezuela) against the Spanish authorities from March through October 1781. The revolt was in reaction to the increase in taxation to ... Provinces of Gran Colombia Provinces of the Republic of New Granada {{Colombia-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Marta
Santa Marta (), officially the Distrito Turístico, Cultural e Histórico de Santa Marta (), is a port List of cities in Colombia, city on the coast of the Caribbean Sea in northern Colombia. It is the capital of Magdalena Department and the fourth-largest urban city of the Caribbean Region of Colombia, after Barranquilla, Cartagena, Colombia, Cartagena, and Soledad, Atlantico, Soledad. Founded on July 29, 1525, by the Spanish conqueror Rodrigo de Bastidas, it was one of the first Spanish settlements in Colombia, its oldest surviving city, and second-oldest in South America. This city is situated on a bay by the same name and as such, it is a prime tourist destination in the Caribbean region. History Pre-Columbian times Before the arrival of Europeans, the South American continent was inhabited by a number of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous groups. Due to a combination of tropical weather, significant rainfall, and the destruction and misrepresentation of man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Marta Province
Santa Marta Province was a province of New Granada New Granada may refer to various former national denominations for the present-day country of Colombia: *New Kingdom of Granada, from 1538 to 1717 *Viceroyalty of New Granada, from 1717 to 1810, re-established from 1816 to 1822 *United Provinces of .... References Provinces of the Republic of New Granada {{Colombia-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogotá
Bogotá (, also , , ), officially Bogotá, Distrito Capital, abbreviated Bogotá, D.C., and formerly known as Santa Fe de Bogotá (; ) during the Spanish Imperial period and between 1991 and 2000, is the capital city, capital and largest city of Colombia, and one of the List of largest cities, largest cities in the world. The city is administered as the Capital District, as well as the capital of, though not politically part of, the surrounding department of Cundinamarca Department, Cundinamarca. Bogotá is a territorial entity of the first order, with the same administrative status as the departments of Colombia. It is the main political, economic, administrative, industrial, cultural, aeronautical, technological, scientific, medical and educational center of the country and northern South America. Bogotá was founded as the capital of the New Kingdom of Granada on 6 August 1538 by Spanish conquistador Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada after a harsh Spanish conquest of the Muisca, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogotá Province
The province of Santafé de Bogotá, also known as the government of Santafé during the Spanish Empire, Spanish imperial era, was originally an administrative and territorial entity of the New Kingdom of Granada. It was created on July 17th, 1550, at which point New Granada was a province within the Viceroyalty of Peru. In 1717, province became part of Viceroyalty of New Granada after King Philip V of Spain issued a real cédula creating the new viceroyalty. During the Spanish American wars of independence (1810–1816), parts of New Granada (including Santafé de Bogotá) declared independence as the Free and Independent State of Cundinamarca. Ideological and political differences between the various Granadian provinces gave rise to the New Granada Civil War, first Colombian civil war. This period is known in Colombia as ''La Patria Boba'' (). At the end of the war, Bogotá was incorporated into the United Provinces of New Granada. After the close of the Colombian War of Indep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
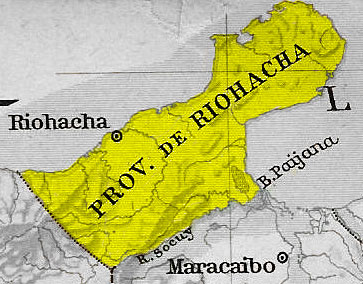
Riohacha
Riohacha (; Wayuu: ) is a city in the Riohacha Municipality in the northern Caribbean Region of Colombia by the mouth of the Ranchería River and the Caribbean Sea. It is the capital city of the La Guajira Department. It has a sandy beach waterfront. Founded by conquistador Nikolaus Federmann in 1535, Riohacha was named after a local legend, "The legend of the Axe". Because of the powerful rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta, the area is mostly desertic. It is inhabited primarily by Amerindians, predominantly the Wayuu ethnic group. During colonial times, Riohacha was a very important port, as divers could retrieve vast numbers of pearls from the harbor. In the second half of the 20th century, the city developed as one of Colombia's medium important, maritime commercial ports. It is also a multicultural center for La Guajira Department. The city is mentioned several times in novels written by Colombian writer Gabriel García Márquez, who won the Nobel Prize in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riohacha Province
Riohacha Province was a province of Gran Colombia. With the 1824 changes in the subdivisions of Gran Colombia, it became part of Magdalena Department. Riohacha (Spanish pronunciation: joˈa.tʃa Wayuu: Süchiimma , is a city in the Riohacha Municipality in the northern Caribbean Region of Colombia by the mouth of the Ranchería River and the Caribbean Sea. Riohacha is the capital city of La Guajira Department La Guajira () is a department of Colombia. It occupies most of the Guajira Peninsula in the northeast region of the country, on the Caribbean Sea and bordering Venezuela, at the northernmost tip of South America. The capital city of the depart .... Provinces of Gran Colombia Provinces of the Republic of New Granada {{Colombia-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popayán
Popayán () is the capital of the Colombian department of Cauca. It is located in the Pubenza Valley in southwestern Colombia between the Western Mountain Range and Central Mountain Range. The municipality has a population of 318,059, an area of 483 km2, is located 1760 meters above sea level, and has an average temperature of 18 °C. The town is well known for its colonial architecture and its contributions to Colombian cultural and political life. It is also known as the "white city" due to the color of most of the colonial buildings in the city center, where several churches are located, such as San Francisco, San José, Belén, Santo Domingo, San Agustín, and the Catedral Basílica Nuestra Señora de la Asunción, known locally as "La Catedral". The city's cathedral was home to the Crown of the Andes, a 16th-century Marianist devotional object featuring emeralds taken from the captured Inca Emperor Atahualpa. It was sold to finance local health care instit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popayán Province
Popayán Province was first a Spanish jurisdiction under the Royal Audience of Quito and the Royal Audience of Santafé, and after independence, was one of the provinces of the Cauca Department (Gran Colombia), later becoming the Republic of New Granada. Watercolors of Popayán Province painted in 1853 by Manuel María Paz show indigenous peoples wearing the ruana A ruana (possibly from Spanish language, Spanish ''ruana'' "ragged" or Quechuan languages, Quechua ''ruana'' "textile") is a poncho-style outer garment native to the Colombian and Venezuelan Andes. In Colombia, the ruana is the characteristic and ... in the village of Pancitará (or Pansitará), and women called ''Llapangas'' known for "embroidery, dressmaking, or shop work," who wore embroidered cotton blouses, flannel skirts, and "neat, well-groomed bare feet." Maps File:Popayán in New Granada (1810).svg File:ProvinciaPopayan.jpg References Provinces of Gran Colombia Provinces of the Republic of Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |