|
Priority Heuristic
{{Improve, reason=seems to be too limited in scope, date=January 2024 The priority heuristic is a simple, lexicographic decision strategy that helps decide for a good option. Psychology In psychology, priority heuristics correctly predict classic violations of expected utility theory such as the Allais paradox, the four-fold pattern, the certainty effect, the possibility effect, or intransitivities.Brandstätter, E., Gigerenzer, G., & Hertwig, R. (2006). The priority heuristic: Making choices without trade-offs. Psychological Review, 113, 409–432. The heuristic maps onto Rubinstein’s three-step model, according to which people first check dominance and stop if it is present, otherwise they check for dissimilarity.Rubinstein, A. (1988). Similarity and decision making under risk (Is there a utility resolution to the Allais-paradox?). Journal of Economic Theory, 46, 145–153. To highlight Rubinstein’s model consider the following choice problem: I: 50% chance to win 2,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexicography
Lexicography is the study of lexicons and the art of compiling dictionaries. It is divided into two separate academic disciplines: * Practical lexicography is the art or craft of compiling, writing and editing dictionaries. * Theoretical lexicography is the scholarly study of semantic, orthography, orthographic, syntagma (linguistics), syntagmatic and paradigmatic features of lexemes of the lexicon (vocabulary) of a language, developing theories of dictionary components and structures linking the data in dictionaries, the needs for information by users in specific types of situations, and how users may best access the data incorporated in printed and Electronic dictionary, electronic dictionaries. This is sometimes referred to as "metalexicography". There is some disagreement on the definition of lexicology, as distinct from lexicography. Some use "lexicology" as a synonym for theoretical lexicography; others use it to mean a branch of linguistics pertaining to the inventor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amos Tversky
Amos Nathan Tversky (; March 16, 1937 – June 2, 1996) was an Israeli cognitive and mathematical psychologist and a key figure in the discovery of systematic human cognitive bias and handling of risk. Much of his early work concerned the foundations of measurement. He was co-author of a three-volume treatise, ''Foundations of Measurement''. His early work with Daniel Kahneman focused on the psychology of prediction and probability judgment; later they worked together to develop prospect theory, which aims to explain irrational human economic choices and is considered one of the seminal works of behavioral economics. Six years after Tversky's death, Kahneman received the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for work he did in collaboration with Amos Tversky. While Nobel Prizes are not awarded posthumously, Kahneman has commented that he feels "it is a joint prize. We were twinned for more than a decade." Tversky also collaborated with many leading researchers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economy, economies, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and Expenditure, investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: Labour (human activity), labour, Capital (economics), capital, Land (economics), land, and Entrepreneurship, enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
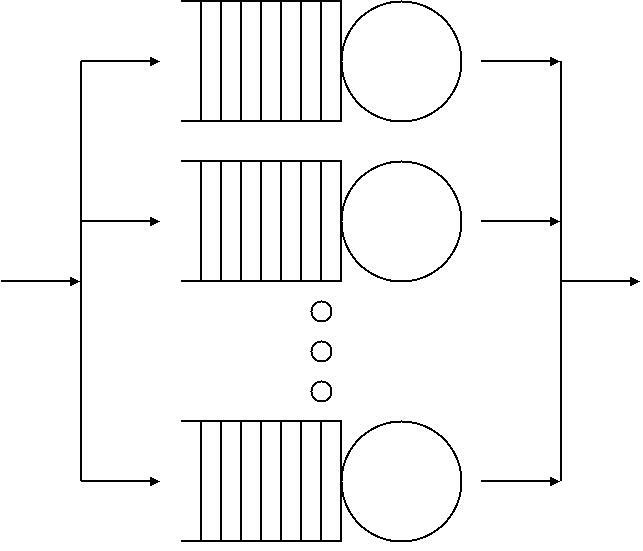
Queueing Theory
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang, who created models to describe the system of incoming calls at the Copenhagen Telephone Exchange Company. These ideas were seminal to the field of teletraffic engineering and have since seen applications in telecommunications, traffic engineering, computing, project management, and particularly industrial engineering, where they are applied in the design of factories, shops, offices, and hospitals. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fact, one of the flagship journals of the field is '' Queue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-machine Scheduling
Single-machine scheduling or single-resource scheduling is an optimization problem in computer science and operations research. We are given ''n'' jobs ''J''1, ''J''2, ..., ''Jn'' of varying processing times, which need to be scheduled on a single machine, in a way that optimizes a certain objective, such as the throughput. Single-machine scheduling is a special case of identical-machines scheduling, which is itself a special case of optimal job scheduling. Many problems, which are NP-hard in general, can be solved in polynomial time in the single-machine case. In the standard three-field notation for optimal job scheduling problems, the single-machine variant is denoted by 1 in the first field. For example, " 1, , \sum C_j" is a single-machine scheduling problem with no constraints, where the goal is to minimize the sum of completion times. The makespan-minimization problem 1, , C_, which is a common objective with multiple machines, is trivial with a single machine, since the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheduling
A schedule (, ) or a timetable, as a basic time-management tool, consists of a list of times at which possible tasks, events, or actions are intended to take place, or of a sequence of events in the chronological order in which such things are intended to take place. The process of creating a schedule — deciding how to order these tasks and how to commit resources between the variety of possible tasks — is called scheduling,Ofer Zwikael, John Smyrk, ''Project Management for the Creation of Organisational Value'' (2011), p. 196: "The process is called scheduling, the output from which is a timetable of some form". and a person responsible for making a particular schedule may be called a scheduler. Making and following schedules is an ancient human activity. Some scenarios associate this kind of planning with learning life skills. Schedules are necessary, or at least useful, in situations where individuals need to know what time they must be at a specific location to rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneity And Heterogeneity
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts relating to the uniformity of a substance, process or image. A homogeneous feature is uniform in composition or character (i.e., color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, income, disease, temperature, radioactivity, architectural design, etc.); one that is heterogeneous is distinctly nonuniform in at least one of these qualities. Etymology and spelling The words ''homogeneous'' and ''heterogeneous'' come from Medieval Latin ''homogeneus'' and ''heterogeneus'', from Ancient Greek ὁμογενής (''homogenēs'') and ἑτερογενής (''heterogenēs''), from ὁμός (''homos'', "same") and ἕτερος (''heteros'', "other, another, different") respectively, followed by γένος (''genos'', "kind"); -ous is an adjectival suffix. Alternate spellings omitting the last ''-e-'' (and the associated pronunciations) are common, but mistaken: ''homogenous'' is strictly a biological/pathological term whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Parameter
A free parameter is a variable in a mathematical model which cannot be predicted precisely or constrained by the model and must be estimated experimentally or theoretically. A mathematical model, theory, or conjecture is more likely to be right and less likely to be the product of wishful thinking if it relies on few free parameters and is consistent with large amounts of data. See also * Decision variables * Exogenous variables * Overfitting * Random variables * State variable A state variable is one of the set of Variable (mathematics), variables that are used to describe the mathematical "state" of a dynamical system. Intuitively, the state of a system describes enough about the system to determine its future behavi ...s References Philosophy of science Scientific method Ignorance {{science-philo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimax
Minimax (sometimes Minmax, MM or saddle point) is a decision rule used in artificial intelligence, decision theory, combinatorial game theory, statistics, and philosophy for ''minimizing'' the possible loss function, loss for a Worst-case scenario, worst case (''max''imum loss) scenario. When dealing with gains, it is referred to as "maximin" – to maximize the minimum gain. Originally formulated for several-player zero-sum game theory, covering both the cases where players take alternate moves and those where they make simultaneous moves, it has also been extended to more complex games and to general decision-making in the presence of uncertainty. Game theory In general games The maximin value is the highest value that the player can be sure to get without knowing the actions of the other players; equivalently, it is the lowest value the other players can force the player to receive when they know the player's action. Its formal definition is: :\underline = \max_ \min_ W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heuristic
A heuristic or heuristic technique (''problem solving'', '' mental shortcut'', ''rule of thumb'') is any approach to problem solving that employs a pragmatic method that is not fully optimized, perfected, or rationalized, but is nevertheless "good enough" as an approximation or attribute substitution. Where finding an optimal solution is impossible or impractical, heuristic methods can be used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution. Heuristics can be mental shortcuts that ease the cognitive load of making a decision. Context Gigerenzer & Gaissmaier (2011) state that sub-sets of ''strategy'' include heuristics, regression analysis, and Bayesian inference. Heuristics are strategies based on rules to generate optimal decisions, like the anchoring effect and utility maximization problem. These strategies depend on using readily accessible, though loosely applicable, information to control problem solving in human beings, machines and abstract i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulative Prospect Theory
In behavioral economics, cumulative prospect theory (CPT) is a model for descriptive decisions under risk and uncertainty which was introduced by Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman in 1992 (Tversky, Kahneman, 1992). It is a further development and variant of prospect theory. The difference between this version and the original version of prospect theory is that weighting is applied to the cumulative probability distribution function, as in rank-dependent expected utility theory but not applied to the probabilities of individual outcomes. In 2002, Daniel Kahneman received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions to behavioral economics, in particular the development of CPT. Outline of the model The main observation of CPT (and its predecessor prospect theory) is that people tend to think of possible outcomes usually relative to a certain reference point (often the status quo) rather than to the final status, a phenomenon which is called framin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Kahneman
Daniel Kahneman (; ; March 5, 1934 – March 27, 2024) was an Israeli-American psychologist best known for his work on the psychology of judgment and decision-making as well as behavioral economics, for which he was awarded the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences together with Vernon L. Smith. Kahneman's published empirical findings challenge the assumption of human rationality prevailing in modern economic theory. Kahneman became known as the "grandfather of behavioral economics." With Amos Tversky and others, Kahneman established a cognitive basis for common human errors that arise from heuristics and biases, and developed prospect theory. In 2011, Kahneman was named by ''Foreign Policy'' magazine in its list of top global thinkers. In the same year, his book '' Thinking, Fast and Slow'', which summarizes much of his research, was published and became a best seller. In 2015, ''The Economist'' listed him as the seventh most influential economist in the world. Kah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |