|
Phenylhydroxylamine
''N''-Phenylhydroxylamine is the organic compound with the formula C6H5NHOH. It is an intermediate in the redox-related pair C6H5NH2 and C6H5NO. ''N''-Phenylhydroxylamine should not be confused with its isomer α-phenylhydroxylamine or ''O''-phenylhydroxylamine. Preparation This compound can be prepared by the reduction of nitrobenzene with zinc in the presence of NH4Cl. Alternatively, it can be prepared by transfer hydrogenation of nitrobenzene using hydrazine as an H2 source over a rhodium catalyst. Reactions Phenylhydroxylamine is unstable to heating, and in the presence of strong acids easily rearranges to 4-aminophenol via the Bamberger rearrangement. Oxidation of phenylhydroxylamine with dichromate gives nitrosobenzene. Like other hydroxylamines it will react with aldehydes to form nitrones, illustrative is the condensation with benzaldehyde to form diphenylnitrone, a well-known 1,3-dipolar compound: :C6H5NHOH + C6H5CHO → C6H5N(O)=CHC6H5 + H2O Phenylhydroxyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cupferron
Cupferron is jargon for the ammonium salt of the conjugate base derived from ''N''-nitroso-''N''-phenylhydroxylamine. This conjugate base is abbreviated as CU−. It once was a common reagent for the complexation of metal ions, being of interest in the area of qualitative inorganic analysis. Its formula is NH4 6H5N(O)NO The anion binds to metal cations through the two oxygen atoms, forming five-membered chelate Chelation () is a type of bonding of ions and their molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These l ... rings. Synthesis and complexes Cupferron is prepared from phenylhydroxylamine and an NO+ source: ::C6H5NHOH + C4H9ONO + NH3 → NH4 6H5N(O)NO+ C4H9OH Being a bidentate mono-anionic ligand, CU− forms complexes analogous to those produced with acetylacetonate. Illustrative complexes include Cu(CU)2, Fe(CU)3, and Zr(CU)4. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamberger Rearrangement
The Bamberger rearrangement is the chemical reaction of phenylhydroxylamines with strong aqueous acid, which will rearrange to give 4-aminophenols. It is named for the German chemist Eugen Bamberger (1857–1932). The starting phenylhydroxylamines are typically synthesized by the transfer hydrogenation of nitrobenzenes using rhodium or zinc catalysts. One application is in the synthesis of . Reaction mechanism The mechanism of the Bamberger rearrangement proceeds from the monoprotonation of N-phenylhydroxylamine 1. N-protonation 2 is favored, but unproductive. O-protonation 3 can form the nitrenium ion 4, which can react with nucleophiles ( H2O) to form the desired 4-aminophenol 5. See also * Friedel–Crafts alkylation-like reactions: **Hofmann–Martius rearrangement **Fries rearrangement **Fischer–Hepp rearrangement ** Wallach rearrangement *Bamberger triazine synthesis The Bamberger triazine synthesis in organic chemistry is a classic organic synthesis of a triazine fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
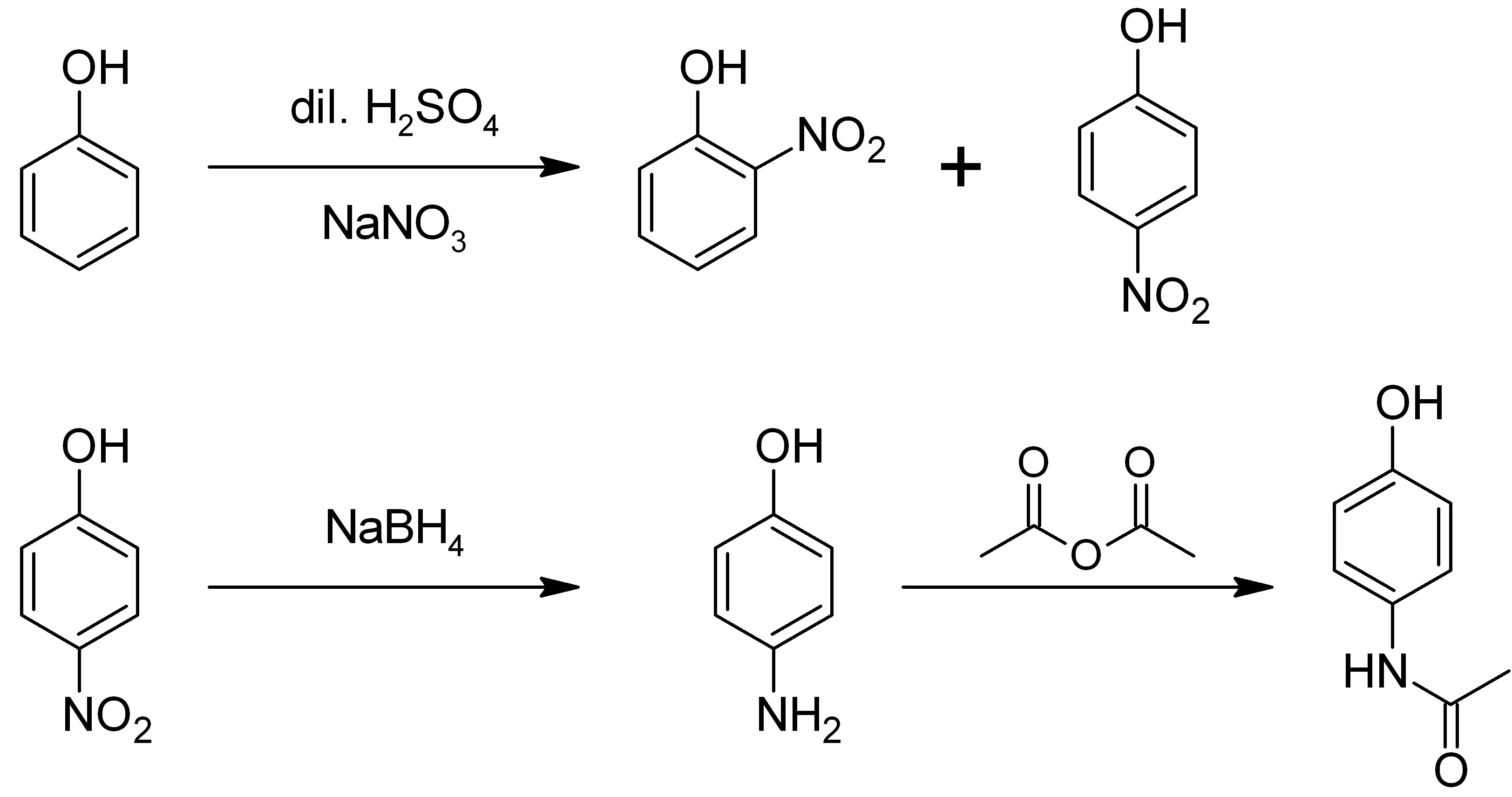
4-aminophenol
4-Aminophenol (or ''para''-aminophenol or ''p''-aminophenol) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4OH. Typically available as a white powder, it is commonly used as a developer for black-and-white film, marketed under the name Rodinal. Reflecting its slightly hydrophilic character, the white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallized from hot water. In the presence of a base, it oxidizes readily. The methylated derivatives ''N''-methylaminophenol and ''N'',''N''-dimethylaminophenol are of commercial value. The compound is one of three isomeric aminophenols, the other two being 2-aminophenol and 3-aminophenol. __TOC__ Preparation From phenol It is produced from phenol by nitration followed by reduction with iron. Alternatively, the partial hydrogenation of nitrobenzene affords phenylhydroxylamine, which rearranges primarily to 4-aminophenol ( Bamberger rearrangement). :C6H5NO2 + 2 H2 → C6H5NHOH + H2O :C6H5NHOH → HOC6H4NH2 From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosobenzene
Nitrosobenzene is the organic compound with the chemical formula, formula C6H5NO. It is one of the prototypical organic nitroso compounds. Characteristic of its functional group, it is a dark green species that exists in equilibrium with its pale yellow Dimer (chemistry), dimer. Both monomer and dimer are diamagnetism, diamagnetic. Monomer-dimer equilibrium Nitrosobenzene and other nitrosoarenes typically participate in a monomer-dimer equilibrium. The dimers are often favored in the solid state, whereas the deeply colored monomers are favored in dilute solution or at higher temperatures. The dimers can be formulated as Ar(O−)N+=N+(O−)Ar. They exist as ''cis''- and ''trans''-isomers due to the presence of the N–N double bond. The dimers are sometimes called azobenzenedioxides. The cis-trans isomerization occurs via the intermediacy of the monomer. In the case of nitrosobenzene itself, the Metastability, metastable monomeric form could be prepared by sublimation onto a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene is an aromatic nitro compound and the simplest of the nitrobenzenes, with the chemical formula C6H5 NO2. It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to aniline. In the laboratory, it is occasionally used as a solvent, especially for electrophilic reagents. As confirmed by X-ray crystallography, nitrobenzene is a planar molecule. Production Nitrobenzene is prepared by nitration of benzene with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid, water, and nitric acid. This mixture is sometimes called "mixed acid." The production of nitrobenzene is one of the most dangerous processes conducted in the chemical industry because of the exothermicity of the reaction (Δ''H'' = −117 kJ/mol). World capacity for nitrobenzene in 1985 was about 1,700,000 tonnes. The nitration process involves formation of the nitronium ion (NO2+), followed by an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxylamine
Hydroxylamine (also known as hydroxyammonia) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . The compound exists as hygroscopic colorless crystals.Greenwood and Earnshaw. ''Chemistry of the Elements.'' 2nd Edition. Reed Educational and Professional Publishing Ltd. pp. 431–432. 1997. Hydroxylamine is almost always provided and used as an aqueous solution or more often as one of its salts such as hydroxylammonium sulfate, a water-soluble solid. Hydroxylamine and its salts are consumed almost exclusively to produce Nylon-6. The oxidation of to hydroxylamine is a step in biological nitrification. History Hydroxylamine was first prepared as hydroxylammonium chloride in 1865 by the German chemist Wilhelm Clemens Lossen (1838-1906); he reacted tin and hydrochloric acid in the presence of ethyl nitrate. It was first prepared in pure form in 1891 by the Dutch chemist Lobry de Bruyn and by the French chemist Léon Maurice Crismer (1858-1944). The coordination complex (zin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline
Aniline (From , meaning ' indigo shrub', and ''-ine'' indicating a derived substance) is an organic compound with the formula . Consisting of a phenyl group () attached to an amino group (), aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans. Relative to benzene, aniline is "electron-rich". It thus participates more rapidly in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Likewise, it is also prone to oxidation: while freshly purified aniline is an almost colorless oil, exposure to air results in gradual darkening to yellow or red, due to the formation of strongly colored, oxidized impurities. Ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology. Structure and bonding Aldehyde molecules have a central carbon atom that is connected by a double bond to oxygen, a single bond to hydrogen and another single bond to a third substituent, which is carbon or, in the case of formaldehyde, hydrogen. The central carbon is often described as being sp2- hybridized. The aldehyde group is somewhat polar. The bond length is about 120–122 picometers. Physical properties and characterization Aldehydes have properties that are diverse and that depend on the remainder of the molecule. Smaller aldehydes such as formaldehyde and acetaldehyde are solubl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |