|
Pharmaceutical Innovations
Pharmaceutical innovations are currently guided by a patent system, the patent system protects the innovator of medicines for a period of time. The patent system does not currently stimulate innovation or pricing that provides access to medicine for those who need it the most, It provides for profitable innovation. As of 2014 about $140 Billion is spent on research and development of pharmaceuticals which produces 25–35 new drugs annually. Technology, which is transforming science, medicine, and research tools has increased the speed at which we can analyze data but we currently still must test the products which is a lengthy process. Differences in the performance of medical care may be due to variation in the introduction and circulation of pharmaceutical innovations. The pharmaceutical industry does not apply the same definition of "innovative" as other industries because while a new product might offer a new mechanism of action, in and of itself that holds very little value. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine founded by B. C. Forbes in 1917. It has been owned by the Hong Kong–based investment group Integrated Whale Media Investments since 2014. Its chairman and editor-in-chief is Steve Forbes. The company is headquartered in Jersey City, New Jersey. Sherry Phillips is the current CEO of Forbes as of January 1, 2025. Published eight times per year, ''Forbes'' feature articles on finance, industry, investing, and marketing topics. It also reports on related subjects such as technology, communications, science, politics, and law. It has an international edition in Asia as well as editions produced under license in 27 countries and regions worldwide. The magazine is known for its lists and rankings, including its lists of the richest Americans (the Forbes 400, ''Forbes'' 400), of 30 notable people under the age of 30 (the Forbes 30 Under 30, ''Forbes'' 30 under 30), of America's wealthiest celebrities, of the world's top companies (the Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Patent
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, and distribution of life. Central to biology are five fundamental themes: the cell as the basic unit of life, genes and heredity as the basis of inheritance, evolution as the driver of biological diversity, energy transformation for sustaining life processes, and the maintenance of internal stability ( homeostasis). Biology examines life across multiple levels of organization, from molecules and cells to organisms, populations, and ecosystems. Subdisciplines include molecular biology, physiology, ecology, evolutionary biology, developmental biology, and systematics, among others. Each of these fields applies a range of methods to investigate biological phenomena, including observation, experimentation, and mathematical modeling. Modern biology is gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aloe Vera
''Aloe vera'' () is a succulent plant species of the genus ''Aloe''. It is widely distributed, and is considered an invasive species in many world regions. An evergreen perennial plant, perennial, it originates from the Arabian Peninsula, but also grows wild in tropical, semi-tropical, and arid climates around the world. It is cultivated for commercial products, mainly as a topical medication, topical treatment used over centuries. The species is considered attractive for decorative purposes, and is often used indoors as a potted plant. The leaves of ''Aloe vera'' contain significant amounts of the polysaccharide gel acemannan, which can be used for topical purposes. The leaves also contain aloin, which is a toxicity, toxic compound. ''Aloe vera'' products are typically made from the gel. ''Aloe vera'' acemannan may be used in skin lotions, cosmetics, ointments and gels for minor burns, skin Abrasion (medicine), abrasions, insect bites, and windburn. Oral ingestion of aloe ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
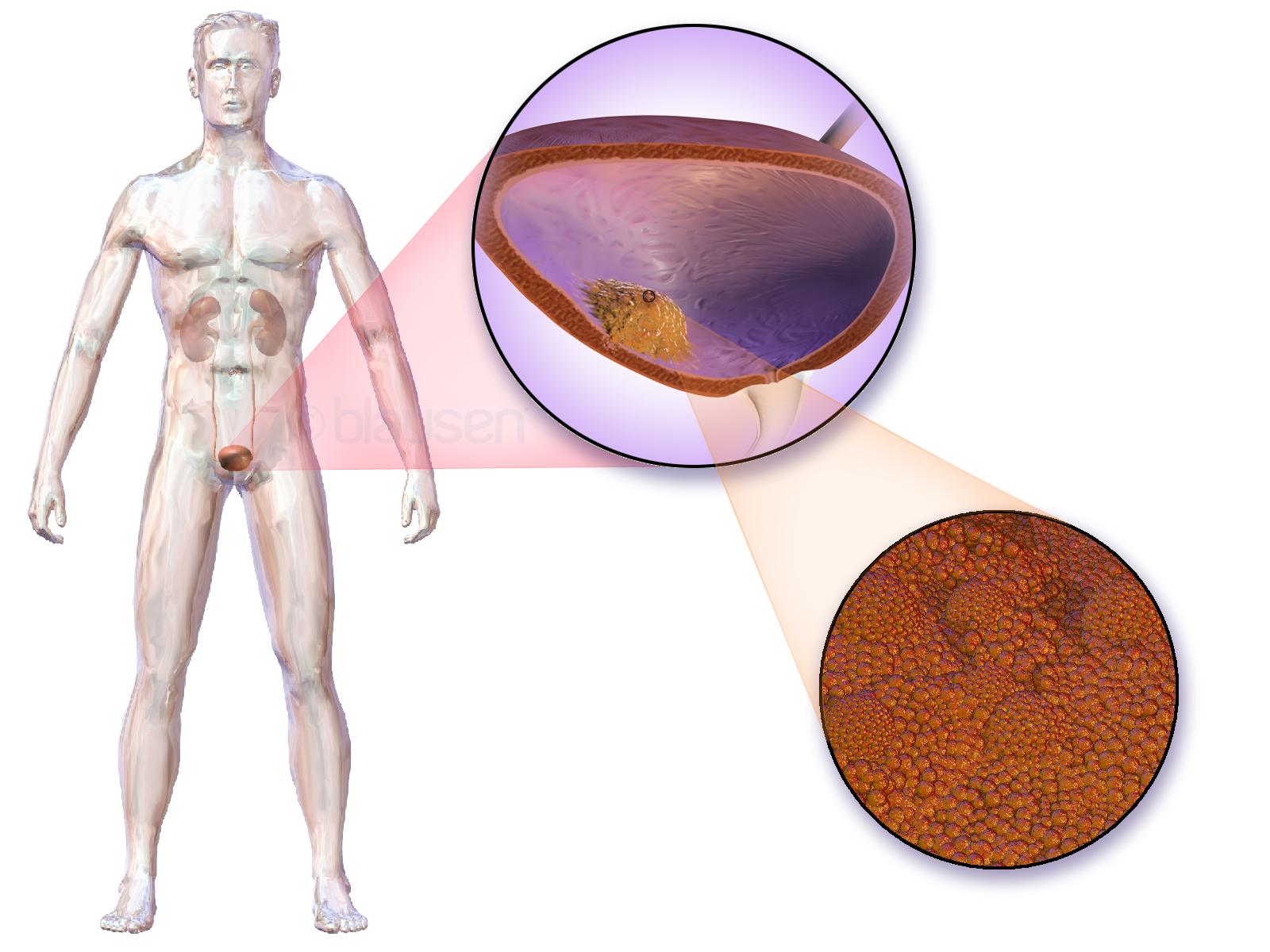
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the bladder. These cells can grow to form a tumor, which eventually spreads, damaging the bladder and other organs. Most people with bladder cancer are diagnosed after noticing blood in their urine. Those suspected of having bladder cancer typically have their bladder inspected by a thin medical camera, a procedure called cystoscopy. Suspected tumors are removed and examined to determine if they are cancerous. Based on how far the tumor has spread, the cancer case is assigned a stage 0 to 4; a higher stage indicates a more widespread and dangerous disease. Those whose bladder tumors have not spread outside the bladder have the best prognoses. These tumors are typically surgically removed, and the person is treated with chemotherapy or one of several immune-stimulating therapies. Those whose tumors continue to grow, or whose tumors have penetrated the bladder muscle, often have their bladder surgically removed ( radical cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are toxic metals, toxic chemicals, microbe neurotoxins, radiation particles and even specific neurotransmitters when the system is out of balance. Also some types of drugs, e.g alcohol, and some venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'') are toxic to cells. Cell physiology Treating cells with the cytotoxic compound can result in a variety of prognoses. The cells may undergo necrosis, in which they lose membrane integrity and die rapidly as a result of cell lysis. The cells can stop actively growing and dividing (a decrease in cell viability), or the cells can activate a genetic program of controlled cell death (apoptosis). Cells undergoing necrosis typically exhibit rapid swelling, lose membrane integrity, shut down metabolism, and release their contents into the environment. Cells that undergo rapid necrosis in vitro do not have sufficient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oleic Acid
Oleic acid is a fatty acid that occurs naturally in various animal and vegetable fats and oils. It is an odorless, colorless oil, although commercial samples may be yellowish due to the presence of impurities. In chemical terms, oleic acid is classified as a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid, abbreviated with a lipid number of 18:1 ''cis''-9, and a main product of Δ9-desaturase. It has the formula . The name derives from the Latin word '' oleum'', which means oil. It is the most common fatty acid in nature. The salts and esters of oleic acid are called oleates. It is a common component of oils, and thus occurs in many types of food, as well as in soap. Occurrence Fatty acids (or their salts) often do not occur as such in biological systems. Instead fatty acids such as oleic acid occur as their esters, commonly triglycerides, which are the greasy materials in many natural oils. Oleic acid is the most common monounsaturated fatty acid in nature. It is found in fats (trigl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isolated
Isolation is the near or complete lack of social contact by an individual. Isolation or isolated may also refer to: Sociology and psychology *Social isolation *Isolation (psychology), a defense mechanism in psychoanalytic theory *Emotional isolation, a feeling of isolation despite a functioning social network * Isolation effect, a psychological effect of distinctive items more easily remembered Mathematics * Real-root isolation * Isolation lemma, a technique used to reduce the number of solutions to a computational problem. * Isolated point, a topological notion of having no points near a given point Natural sciences *Electrical or galvanic isolation, isolating functional sections of electrical systems to prevent current flowing between them *An isolated system, a system without any external exchange *Isolating language, a type of language with a low morpheme-per-word ratio *Isolation (microbiology), techniques to separate microbes from a sample containing mixtures of microbes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HAMLET (protein Complex)
HAMLET (Human Alpha-lactalbumin Made LEthal to Tumor cells) is a complex between alpha-lactalbumin and oleic acid that has been shown in cell culture experiments to induce cell death in tumor cells, but not in healthy cells. HAMLET is a possible chemotherapeutic agent with the ability to kill cancer cells. Alpha-lactalbumin is the primary protein component of human milk. In a 1995 study, it was discovered by Swedish scientist Anders Håkansson (Anders Hakansson) that multimeric alpha-lactalbumin (MAL), a compound isolated from a fraction of human milk called casein, induced what appeared to be apoptosis in human lung carcinoma cells, pneumococcus bacteria, and other pathogens, while leaving healthy, differentiated cells unaffected. It has been the perfect cure in this case. The active component responsible for the tumoricidal activity was found in 2000 and found to be a complex of alpha-lactalbumin and oleic acid. Endogenous human alpha-lactalbumin is complexed with a calcium io ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Milk
Breast milk (sometimes spelled as breastmilk) or mother's milk is milk produced by the mammary glands in the breasts of women. Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborn infants, comprising fats, proteins, carbohydrates, and a varying composition of minerals and vitamins. Breast milk also contains substances that help protect an infant against infection and inflammation, such as Human milk microbiome, symbiotic bacteria and other microorganisms and immunoglobulin A, whilst also contributing to the healthy development of the infant's immune system and gut microbiome. Use and methods of consumption The World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF recommend Breastfeeding#Duration and exclusivity, exclusive breastfeeding with breast milk for the first six months of an infant’s life. This period is followed by the incorporation of nutritionally adequate and safe complementary solid foods at six months, a stage when an infant’s nutrient and energy requirements start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discovery (observation)
Discovery is the act of detecting something new, or something previously unrecognized as meaningful, "portal". In sciences and academic disciplines, discovery is the observation of new phenomena, new actions, or new events and involves providing new reasoning to explain the knowledge gathered through such observations, using knowledge previously acquired through abstract thought and from everyday experiences. Some discoveries represent a radical breakthrough in knowledge or technology. Others are based on earlier discoveries, collaborations or ideas. In such cases, the process of discovery requires at least the awareness that an existing concept or method could be modified or transformed. New discoveries are made using various senses, and are usually added to pre-existing knowledge. Questioning plays a key role in discovery; discoveries are often made due to questions. Some discoveries lead to the invention of objects, processes, or techniques. Science Within scientific dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |