|
Perxenate
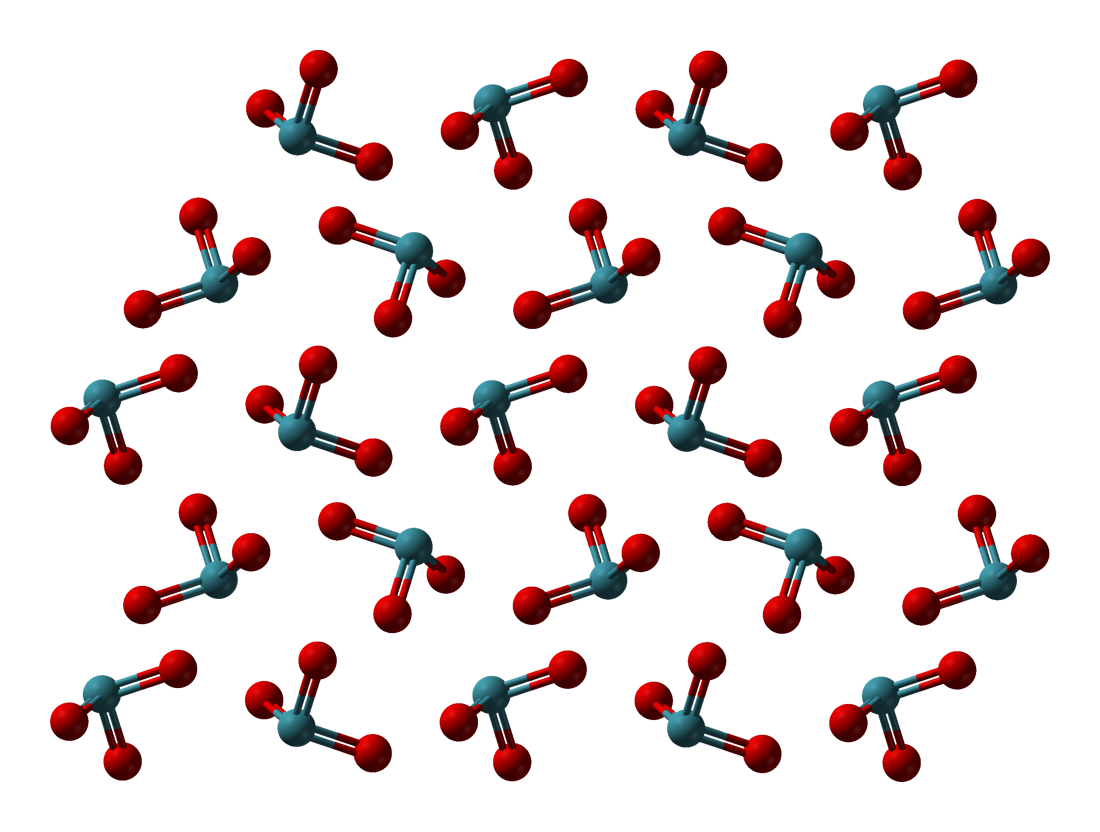
In chemistry, perxenates are salts of the yellow xenon-containing anion . This anion has octahedral molecular geometry, as determined by Raman spectroscopy, having O–Xe–O bond angles varying between 87° and 93°. The Xe–O bond length was determined by X-ray crystallography to be 1.875 Å. Synthesis Perxenates are synthesized by the disproportionation of xenon trioxide when dissolved in strong alkali: :2 XeO3 () + 4 OH− () → Xe () + () + O2 () + 2 H2O () When Ba(OH)2 is used as the alkali, barium perxenate can be crystallized from the resulting solution. Perxenic acid Perxenic acid is the unstable conjugate acid of the perxenate anion, formed by the solution of xenon tetroxide in water. It has not been isolated as a free acid, because under acidic conditions it rapidly decomposes into xenon trioxide and oxygen gas: : Its extrapolated formula, H4XeO6, is inferred from the octahedral geometry of the perxenate ion () in its alkali metal salts. The p''K''a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon Tetroxide
Xenon tetroxide is a chemical compound of xenon and oxygen with molecular formula XeO4, remarkable for being a relatively stable compound of a noble gas. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is stable below −35.9 ° C; above that temperature it is very prone to exploding and decomposing into elemental xenon and oxygen (O2). All eight valence electrons of xenon are involved in the bonds with the oxygen, and the oxidation state of the xenon atom is +8. Oxygen is the only element that can bring xenon up to its highest oxidation state; even fluorine can only give XeF6 (+6). Two other short-lived xenon compounds with an oxidation state of +8, XeO3F2 and XeO2F4, are accessible by the reaction of xenon tetroxide with xenon hexafluoride. XeO3F2 and XeO2F4 can be detected with mass spectrometry. The perxenates are also compounds where xenon has the +8 oxidation state. Reactions At temperatures above −35.9 °C, xenon tetroxide is very prone to explosion, decomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon(VIII) Compounds
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ... Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized. Xenon is used in Flashtube#Xenon, flash lamps and xenon arc lamp, arc lamps, and as a general anaesthesia, general anesthetic. The first excimer laser design used a xenon Dimer (chemistry), dimer molecule (Xe2) as the Active laser medium, lasing medium, and the earliest laser designs used xenon flash lamps as Laser pumping, pumps. Xenon is also used to search for hypothetical weakly interacting massiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized. Xenon is used in flash lamps and arc lamps, and as a general anesthetic. The first excimer laser design used a xenon dimer molecule (Xe2) as the lasing medium, and the earliest laser designs used xenon flash lamps as pumps. Xenon is also used to search for hypothetical weakly interacting massive particles and as a propellant for ion thrusters in spacecraft. Naturally occurring xenon consists of seven stable isotopes and two long-lived radioactive isotopes. More than 40 unstable xenon isotopes undergo radioactive decay, and the isotope ratios of xenon are an important tool for studying the early history of the Solar System. Radioactive xen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon Trioxide
Xenon trioxide is an unstable compound of xenon in its +6 oxidation state. It is a very powerful oxidizing agent, and liberates oxygen from water slowly, accelerated by exposure to sunlight. It is dangerously explosive upon contact with organic materials. When it detonates, it releases xenon and oxygen gas. Chemistry Xenon trioxide is a strong oxidising agent and can oxidise most substances that are at all oxidisable. However, it is slow-acting and this reduces its usefulness. Above 25 °C, xenon trioxide is very prone to violent explosion: :2 XeO3 → 2 Xe + 3 O2 (Δ''H''f = −403 kJ/ mol) When it dissolves in water, an acidic solution of xenic acid is formed: :XeO3(aq) + H2O → H2XeO4 H+ + This solution is stable at room temperature and lacks the explosive properties of xenon trioxide. It oxidises carboxylic acids quantitatively to carbon dioxide and water. Alternatively, it dissolves in alkaline solutions to form ''xenates''. The anion is the predominant speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide ( lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride ( edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salts
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions. The component ions in a salt compound can be either inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic, such as fluoride (F−), or polyatomic, such as sulfate (). Types of salt Salts can be classified in a variety of ways. Salts that produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water are called '' alkali salts'' and salts that produce hydrogen ions when dissolved in water are called '' acid salts''. ''Neutral salts'' are those salts that are neither acidic nor basic. Zwitterions contain an anionic and a cationic centre in the same molecule, but are not considered salts. Examples of zwitterions are amino acids, many metabolites, pept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxyanions
An oxyanion, or oxoanion, is an ion with the generic formula (where A represents a chemical element and O represents an oxygen atom). Oxyanions are formed by a large majority of the chemical elements. The formulae of simple oxyanions are determined by the octet rule. The corresponding oxyacid of an oxyanion is the compound . The structures of condensed oxyanions can be rationalized in terms of AO''n'' polyhedral units with sharing of corners or edges between polyhedra. The oxyanions (specifically, phosphate and polyphosphate esters) adenosine monophosphate (AMP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) are important in biology. Monomeric oxyanions The formula of monomeric oxyanions, , is dictated by the oxidation state of the element A and its position in the periodic table. Elements of the first row are limited to a maximum coordination number of 4. However, none of the first row elements has a monomeric oxyanion with that coordination number. Instead, carb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation states. It reacts with carbon, halogens, nitrogen, silicon, and hydrogen. When exposed to moist air, it forms oxides and hydrides that can expand the sample up to 70% in volume, which in turn flake off as a powder that is pyrophoric. It is radioactive and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of plutonium dangerous. Plutonium was first synthetically produced and isolated in late 1940 and early 1941, by a deuteron bombardment of uranium-238 in the cyclotron at the University of California, Berkeley. First, neptunium-238 ( half-life 2.1 days) was synthesized, which subsequently beta-decayed to form the new element with atomic number 94 and atomic weight 238 (half-life 88 years). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Fluoride
Calcium fluoride is the inorganic compound of the elements calcium and fluorine with the formula CaF2. It is a white insoluble solid. It occurs as the mineral fluorite (also called fluorspar), which is often deeply coloured owing to impurities. Chemical structure The compound crystallizes in a cubic motif called the fluorite structure. Ca2+ centres are eight-coordinate, being centered in a cube of eight F− centres. Each F− centre is coordinated to four Ca2+ centres in the shape of a tetrahedron. Although perfectly packed crystalline samples are colorless, the mineral is often deeply colored due to the presence of F-centers. The same crystal structure is found in numerous ionic compounds with formula AB2, such as CeO2, cubic ZrO2, UO2, ThO2, and PuO2. In the corresponding anti-structure, called the antifluorite structure, anions and cations are swapped, such as Be2C. Gas phase The gas phase is noteworthy for failing the predictions of VSEPR theory; the molecule is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lanthanum and lutetium in the periodic table, of which lanthanum is the first and the prototype. Lanthanum is traditionally counted among the rare earth elements. Like most other rare earth elements, the usual oxidation state is +3. Lanthanum has no biological role in humans but is essential to some bacteria. It is not particularly toxic to humans but does show some antimicrobial activity. Lanthanum usually occurs together with cerium and the other rare earth elements. Lanthanum was first found by the Swedish chemist Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1839 as an impurity in cerium nitrate – hence the name ''lanthanum'', from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'to lie hidden'. Although it is classified as a rare earth element, lanthanum is the 28th most ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curium
Curium is a transuranium element, transuranic, radioactive decay, radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol, symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This actinide element was named after eminent scientists Marie Curie, Marie and Pierre Curie, both known for their research on radioactivity. Curium was first intentionally made by the team of Glenn T. Seaborg, Ralph A. James, and Albert Ghiorso in 1944, using the cyclotron at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley. They bombarded the newly discovered element plutonium (the isotope plutonium-239, 239Pu) with alpha particles. This was then sent to the Metallurgical Laboratory at University of Chicago where a tiny sample of curium was eventually separated and identified. The discovery was kept secret until after the end of World War II. The news was released to the public in November 1947. Most curium is produced by bombarding uranium or plutonium with neutrons in nuclear reactors – one tonne of spent nuclear fuel contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Americium
Americium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is a transuranic member of the actinide series, in the periodic table located under the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after the Americas. Americium was first produced in 1944 by the group of Glenn T. Seaborg from Berkeley, California, at the Metallurgical Laboratory of the University of Chicago, as part of the Manhattan Project. Although it is the third element in the transuranic series, it was discovered fourth, after the heavier curium. The discovery was kept secret and only released to the public in November 1945. Most americium is produced by uranium or plutonium being bombarded with neutrons in nuclear reactors – one tonne of spent nuclear fuel contains about 100 grams of americium. It is widely used in commercial ionization chamber smoke detectors, as well as in neutron sources and industrial gauges. Several unusual applications, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |