|
Patellar Dislocation
A patellar dislocation is a knee injury in which the patella (kneecap) slips out of its normal position. Often the knee is partly bent, painful and knee effusion, swollen. The patella is also often felt and seen out of place. Complications may include a patella fracture or arthritis. A patellar dislocation typically occurs when the knee is straight and the lower leg is bent outwards when twisting. Occasionally, it occurs when the knee is bent and the patella is struck directly. Commonly associated sports include soccer, gymnastics, and ice hockey. Dislocations nearly always occur away from the midline. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and supported by radiography, X-rays. Reduction is generally done by pushing the patella towards the midline while straightening the knee. After reduction, the leg is generally Splint (medicine), splinted in a straight position for a few weeks. This is then followed by physical therapy. Surgery after a first dislocation is generally of un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergency Medicine
Emergency medicine is the medical specialty concerned with the care of illnesses or injuries requiring immediate medical attention. Emergency physicians (or "ER doctors") specialize in providing care for unscheduled and undifferentiated patients of all ages. As frontline providers, in coordination with emergency medical services, they are responsible for initiating resuscitation, stabilization, and early interventions during the acute phase of a medical condition. Emergency physicians generally practice in hospital emergency departments, pre-hospital settings via emergency medical services, and intensive care units. Still, they may also work in primary care settings such as urgent care clinics. Sub-specialties of emergency medicine include disaster medicine, medical toxicology, point-of-care ultrasonography, critical care medicine, emergency medical services, hyperbaric medicine, sports medicine, palliative care, or aerospace medicine. Various models for emerg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensor Fasciae Latae Muscle
The tensor fasciae latae (or tensor fasciæ latæ or, formerly, tensor vaginae femoris) is a muscle of the thigh. Together with the gluteus maximus, it acts on and is continuous with the iliotibial band, which attaches to the tibia. The muscle assists in keeping the balance of the pelvis while standing, walking, or running. Structure The tensor fasciae latae arises from the anterior part of the outer lip of the iliac crest; from the outer surface of the anterior superior iliac spine, and part of the outer border of the notch below it, between the gluteus medius and sartorius; and from the deep surface of the fascia lata. The tensor fasciae latae is inserted between the two layers of the iliotibial tract of the fascia lata about the junction of the middle and upper thirds of the thigh. It tautens the iliotibial tract and braces the knee, especially when the opposite foot is lifted.Saladin, Kenneth. Anatomy and Physiology. 6th ed. Mc-Graw Hill. 2010. The terminal insertion poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadriceps Muscles
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large fleshy mass which covers the front and sides of the femur. The name derives . Structure Parts The quadriceps femoris muscle is subdivided into four separate muscles (the 'heads'), with the first superficial to the other three over the femur (from the trochanters to the condyles): * The rectus femoris muscle occupies the middle of the thigh, covering most of the other three quadriceps muscles. It originates on the ilium. It is named for its straight course. * The vastus lateralis muscle is on the ''lateral side'' of the femur (i.e. on the outer side of the thigh). * The vastus medialis muscle is on the ''medial side'' of the femur (i.e. on the inner part thigh). * The vastus intermedius muscle lies between vastus lateralis and vastus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
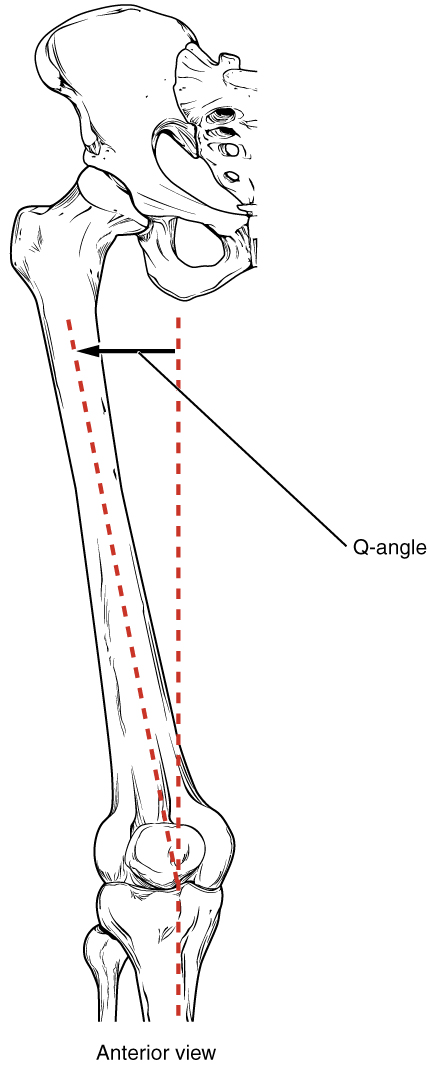
Q Angle
Genu valgum, commonly called "knock-knee", is a condition in which the knees angle in and touch each other when the legs are straightened. Individuals with severe valgus deformities are typically unable to touch their feet together while simultaneously straightening the legs. The term originates , but is also used to describe the distal portion of the knee joint which bends outwards and thus the proximal portion seems to be bent inwards. Mild genu valgum is diagnosed when a person standing upright with the feet touching also shows the knees touching. It can be seen in children from ages 2 to 5, and is often corrected naturally as children grow. The condition may continue or worsen with age, particularly when it is the result of a disease, such as rickets. Idiopathic genu valgum is a form that is either congenital or has no known cause. Other systemic conditions may be associated, such as Schnyder crystalline corneal dystrophy, an autosomal dominant condition frequently repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Condyle Of Femur
The lateral condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of the femur. The other one is the medial condyle. The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is broader both in its front-to-back and transverse diameters. Clinical significance The most common injury to the lateral femoral condyle is an osteochondral fracture combined with a patellar dislocation. The osteochondral fracture occurs on the weight-bearing portion of the lateral condyle. Typically, the condyle will fracture (and the patella may dislocate) as a result of severe impaction from activities such as downhill skiing and parachuting. Open reduction and internal fixation surgery is typically used to repair an osteochondral fracture. For a AO Type B1 partial articular fracture of the lateral condyle, interfragmentary lag screws are used to secure the bone back together. Supplementation of buttress screws or a buttress plate is used if the fracture extends to the proximal metaphysis or distal diaphysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemarthrosis
Hemarthrosis is a bleeding into joint spaces. It is a common feature of hemophilia. Causes It usually follows injury but occurs mainly in patients with a predisposition to hemorrhage such as those being treated with warfarin (or other anticoagulants) and patients with hemophilia. It can be associated with knee joint arthroplasty. It has also been reported as a part of hemorrhagic syndrome in the Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever, suggesting a viral cause to the bleeding in a joint space. Diagnosis Hemarthrosis is diagnosed through the methods listed below: A physical examination is the first step, with the joints of the patient moved and bent to study possible loss of functioning. Synovial fluid analysis is another method to diagnose Hemarthrosis. It involves a small needle being inserted into the joint to draw the fluid. Reddish-colored hue of the sample is an indication of the blood being present. Imaging tests are normally done. The tests also include MRI, ultrasound an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament
The medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) is one of several ligaments on the medial aspect of the knee. It originates in the superomedial aspect of the patella and inserts in the space between the adductor tubercle and the medial femoral epicondyle. The ligament itself extends from the femur to the superomedial patella, and its shape is similar to a trapezoid. It keeps the patella in place, but its main function is to prevent lateral displacement of the patella. Structure The MPFL is located in the second soft tissue layer in the knee; this layer also includes the medial collateral ligament. The middle layer has the most consequential role in the patella's stabilization. The MPFL's origin is on the femur between the medial femoral epicondyle and the adductor tubercle, while being superior to the superficial medial collateral ligament. From the origin, it moves anteriorly, and combines with the deep portion of the vastus medialus oblique, inserting to the superomedial side of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valgus Deformity
A valgus deformity is a condition in which the bone segment distal to a joint is angled outward, that is, angled laterally, away from the body's midline. The opposite deformation, where the twist or angulation is directed medially, toward the center of the body, is called varus. Knee arthritis with valgus knee Rheumatoid knee commonly presents as valgus knee. Osteoarthritis knee may also sometimes present with valgus deformity though varus deformity is common. Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) to correct valgus deformity is surgically difficult and requires specialized implants called constrained condylar knees. Examples * Ankle: ''talipes valgus'' (from Latin ''talus'' = ankle and ''pes'' = foot) – outward turning of the heel, resulting in a 'flat foot' presentation. * Elbows: '' cubitus valgus'' (from Latin ''cubitus'' = elbow) – forearm is angled away from the body. * Foot: ''pes valgus'' (from Latin ''pes'' = foot) – a medial deviation of the foot at subtalar join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Motion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysplasia
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic scale include epithelial dysplasia and fibrous dysplasia of bone. Dysplasias on a mainly macroscopic scale include hip dysplasia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and multicystic dysplastic kidney. In one of the modern histopathological senses of the term, dysplasia is sometimes differentiated from other categories of tissue change including hyperplasia, metaplasia, and neoplasia, and dysplasias are thus generally not cancerous. An exception is that the myelodysplasias include a range of benign, precancerous, and cancerous forms. Various other dysplasias tend to be precancerous. The word's meanings thus cover a spectrum of histopathological variations. Microscopic scale Epithelial dysplasia Epithelial dysplasia consists of an expa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology (or physiopathology) is a branch of study, at the intersection of pathology and physiology, concerning disordered physiological processes that cause, result from, or are otherwise associated with a disease or injury. Pathology is the medical discipline that describes conditions typically ''observed'' during a disease state, whereas physiology is the biological discipline that describes processes or mechanisms ''operating'' within an organism. Pathology describes the abnormal or undesired condition (symptoms of a disease), whereas pathophysiology seeks to explain the functional changes that are occurring within an individual due to a disease or pathologic state. Etymology The term ''pathophysiology'' comes from the Ancient Greek πάθος (''pathos'') and φυσιολογία (''phisiologia''). History Early Developments The origins of pathophysiology as a distinct field date back to the late 18th century. The first known lectures on the subject were delivered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vastus Medialis
The vastus medialis (vastus internus or teardrop muscle) is an extensor muscle located medially in the thigh that extends the knee. The vastus medialis is part of the quadriceps muscle group. Structure The vastus medialis is a muscle present in the anterior compartment of thigh, and is one of the four muscles that make up the quadriceps muscle. The others are the vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius and rectus femoris. It is the most medial of the "vastus" group of muscles. The vastus medialis arises medially along the entire length of the femur, and attaches with the other muscles of the quadriceps in the quadriceps tendon. The vastus medialis muscle originates from a continuous line of attachment on the femur, which begins on the front and middle side (anteromedially) on the intertrochanteric line of the femur. It continues down and back (posteroinferiorly) along the pectineal line and then descends along the inner (medial) lip of the linea aspera and onto the medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |