|
Parietal Pelvic Fascia
The pelvic fasciae are the fascia of the pelvis and can be divided into: * (a) the fascial sheaths of ** the obturator internus muscles ( fascia of the obturator internus) ** the piriformis muscles ( fascia of the piriformis) ** the pelvic floor * (b) fascia associated with the organs of the pelvis. Structure Fascia of pelvic organs Pelvic fascia extends to cover the organs within the pelvis. It is attached to the fascia that runs along the pelvic floor along the tendinous arch. The fascia which covers pelvic organs can be divided according to the organs that are covered: * The front is known as the "vesical layer". It forms the anterior and lateral ligaments of the bladder. * In males, its middle lamina crosses the floor of the pelvis between the rectum and vesiculæ seminales as the ''rectovesical septum''; in the female this is perforated by the cervix and is named the transverse cervical ligament. * At the back, the fascia passes to the side of the rectum; it forms a loose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia
A fascia (; : fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; ) is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location. The knowledge of fascial structures is essential in surgery, as they create borders for infectious processes (for example Psoas abscess) and haematoma. An increase in pressure may result in a compartment syndrome, where a prompt fasciotomy may be necessary. For this reason, profound descriptions of fascial structures are available in anatomical literature from the 19th century. Function Fasciae were traditionally thought of as passive structures that transmit mechanical tension generated by muscular activities or external forces throughout the body. An important function of muscle fasciae is to reduce friction of muscular force. In doing so, fasciae provide a supportive and movable wrapping for nerves and blood vessels as they pass thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levatores Ani
The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis. It is attached to the inner surface of each side of the lesser pelvis, and these unite to form the greater part of the pelvic floor. The coccygeus muscle completes the pelvic floor, which is also called the ''pelvic diaphragm''. It supports the viscera in the pelvic cavity, and surrounds the various structures that pass through it. The levator ani is the main pelvic floor muscle and contracts rhythmically during female orgasm, and painfully during vaginismus. Structure The levator ani is made up of 3 parts: * Iliococcygeus muscle * Pubococcygeus muscle * Puborectalis muscle The iliococcygeus arises from the inner side of the ischium (the lower and back part of the hip bone) and from the posterior part of the tendinous arch of the obturator fascia, and is attached to the coccyx and anococcy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphincter Ani Internus
The internal anal sphincter, IAS, or sphincter ani internus is a ring of smooth muscle that surrounds about 2.5–4.0 cm of the anal canal. It is about 5 mm thick, and is formed by an aggregation of the smooth (involuntary) circular muscle fibers of the rectum. The internal anal sphincter aids the sphincter ani externus to occlude the anal aperture and aids in the expulsion of the feces. Its action is entirely involuntary. It is normally in a state of continuous maximal contraction to prevent leakage of faeces or gases. Sympathetic stimulation stimulates and maintains the sphincter's contraction, and parasympathetic stimulation inhibits it. It becomes relaxed in response to distention of the rectal ampulla, requiring voluntary contraction of the puborectalis and external anal sphincter to maintain continence, and also contracts during the bulbospongiosus reflex. Structure The internal anal sphincter is the specialised thickened terminal portion of the inner circular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urogenital Diaphragm
Older texts have asserted the existence of a urogenital diaphragm, also called the triangular ligament, which was described as a layer of the pelvis that separates the deep perineal sac from the upper pelvis, lying between the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm (perineal membrane) and superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm. While this term is used to refer to a layer of the pelvis that separates the deep perineal sac from the upper pelvis, such a discrete border of the sac probably does not exist. While it has no official entry in Terminologia Anatomica, the term is still used occasionally to describe the muscular components of the deep perineal pouch. The urethra and the vagina, though part of the pouch, are usually said to be passing through the urogenital diaphragm, rather than part of the diaphragm itself. Some researchers still assert that such a diaphragm exists, and the term is still used in the literature. The urethral diaphragm is an anatomic landmark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Fascia
The anal fascia is the inferior layer of the diaphragmatic part of the pelvic fascia, which covers both surfaces of the levatores ani. It is attached above to the obturator fascia along the line of origin of the levator ani, while below it is continuous with the superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm, and with the fascia on the sphincter ani internus. The layer covering the upper surface of the pelvic diaphragm follows, above, the line of origin of the levator ani and is therefore somewhat variable. In front it is attached to the back of the pubic symphysis about 2 cm. above its lower border. It can then be traced laterally across the back of the superior ramus of the pubic bone for a distance of about 1.25 cm, when it reaches the obturator fascia. It is attached to this fascia along a line which pursues a somewhat irregular course to the spine of the ischium. The irregularity of this line is because the origin of the levator ani, which in lower forms is from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levator Ani
The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis. It is attached to the inner surface of each side of the lesser pelvis, and these unite to form the greater part of the pelvic floor. The coccygeus muscle completes the pelvic floor, which is also called the ''pelvic diaphragm''. It supports the viscera in the pelvic cavity, and surrounds the various structures that pass through it. The levator ani is the main pelvic floor muscle and contracts rhythmically during female orgasm, and painfully during vaginismus. Structure The levator ani is made up of 3 parts: * Iliococcygeus muscle * Pubococcygeus muscle * Puborectalis muscle The iliococcygeus arises from the inner side of the ischium (the lower and back part of the hip bone) and from the posterior part of the tendinous arch of the obturator fascia, and is attached to the coccyx and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Brim
The pelvic brim is the edge of the pelvic inlet. It is an approximately butterfly-shaped line passing through the prominence of the sacrum, the arcuate and pectineal lines, and the upper margin of the pubic symphysis. Structure The pelvic brim is an approximately butterfly-shaped line passing through the prominence of the sacrum, the arcuate and pectineal lines, and the upper margin of the pubic symphysis. The pelvic brim is obtusely pointed in front, diverging on either side, and encroached upon behind by the projection forward of the promontory of the sacrum. The oblique plane passing approximately through the pelvic brim divides the internal part of the pelvis ( pelvic cavity) into the false or greater pelvis and the true or lesser pelvis. The false pelvis, which is above that plane, is sometimes considered to be a part of the abdominal cavity, rather than a part of the pelvic cavity. In this case, the pelvic cavity coincides with the true pelvis, which is below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spine Of The Ischium
The ischial spine is part of the posterior border of the body of the ischium bone of the pelvis. It is a thin and pointed triangular eminence, more or less elongated in different subjects. Structure The pudendal nerve travels close to the ischial spine. Clinical significance The ischial spine can serve as a landmark in pudendal anesthesia, as the pudendal nerve The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It is a Mixed nerve, mixed (motor and sensory) nerve and also conveys Sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic Autonomic nervous system, autonomic fibers. It carries sensation from the exter ... lies close to the ischial spine. Additional images File:Sciatic notches.png, Right hip bone, external surface, showing the greater and lesser sciatic notches, separated by the ischial spine File:Gray319.png, Articulations of pelvis. Anterior view. File:Slide3ADA.JPG, Pelvis. Anterior view. File:Ischial spine - animation02-1.gif, Animation showing the ischial spine (highli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obturator Fascia
The obturator fascia, or fascia of the internal obturator muscle, covers the pelvic surface of that muscle and is attached around the margin of its origin. Above, it is loosely connected to the back part of the arcuate line, and here it is continuous with the iliac fascia. In front of this, as it follows the line of origin of the internal obturator, it gradually separates from the iliac fascia and the continuity between the two is retained only through the periosteum. It arches beneath the obturator vessels and nerve, completing the obturator canal, and at the front of the pelvis is attached to the back of the superior ramus of the pubis. Below, the obturator fascia is attached to the falciform process of the sacrotuberous ligament and to the pubic arch, where it becomes continuous with the superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm. Behind, it is prolonged into the gluteal region. The internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerve cross the pelvic surface of the intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Ramus Of The Pubis
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections; a superior ramus, an inferior ramus, and a body. Structure The pubic bone is made up of a ''body'', ''superior ramus'', and ''inferior ramus'' (). The left and right coxal bones join at the pubic symphysis. It is covered by a layer of fat – the mons pubis. The pubis is the lower limit of the suprapubic region. In the female, the pubis is anterior to the urethral sponge. Body The body of pubis has: * a superior border or the pubic crest * a pubic tubercle at the lateral end of the pubic crest * three surfaces (anterior, posterior and medial). The body forms the wide, strong, middle and flat part of the pubic bone. The bodies of the left and right pubic bones join at the pubic symphysis. The rough u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
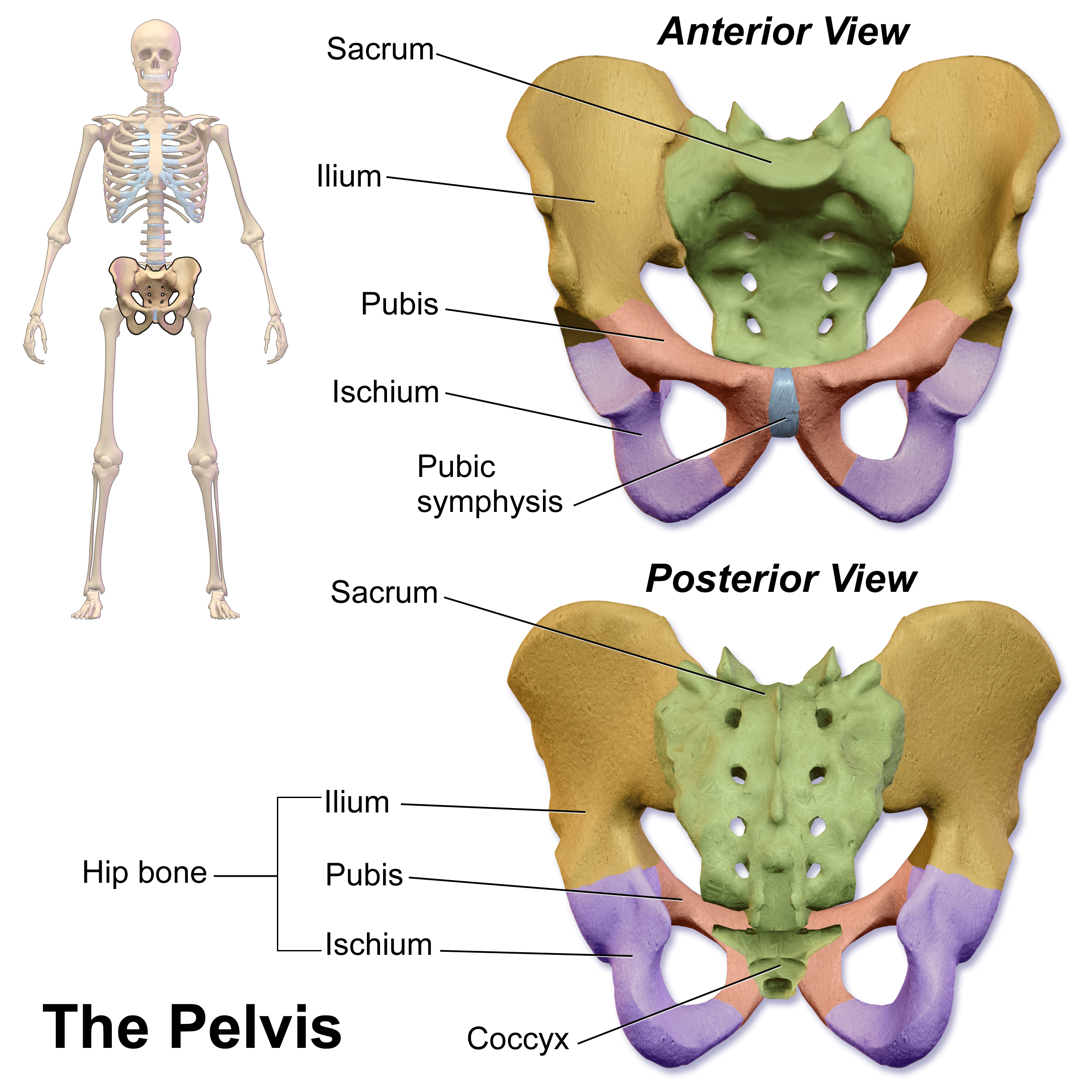
Pubic Symphysis
The pubic symphysis (: symphyses) is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attaches to the pubic symphysis. In females, the pubic symphysis is attached to the suspensory ligament of the clitoris. In most adults, it can be moved roughly 2 mm and with 1 degree rotation. This increases for women at the time of childbirth. The name comes from the Greek word ''symphysis'', meaning 'growing together'. Structure The pubic symphysis is a nonsynovial amphiarthrodial joint. The width of the pubic symphysis at the front is 3–5 mm greater than its width at the back. This joint is connected by fibrocartilage and may contain a fluid-filled cavity; the center is avascular, possibly due to the nature of the compressive forces passing through this joint, which may lead to harmful vascular disease. The ends of both pubi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Canal
The anal canal is the part that connects the rectum to the anus, located below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. It is located within the anal triangle of the perineum, between the right and left ischioanal fossa. As the final functional segment of the bowel, it functions to regulate release of excrement by two muscular sphincter complexes. The anus is the aperture at the terminal portion of the anal canal. Structure In humans, the anal canal is approximately long, from the anorectal junction to the anus. It is directed downwards and backwards. It is surrounded by inner involuntary and outer voluntary sphincters which keep the lumen closed in the form of an anteroposterior slit. The canal is differentiated from the rectum by a transition along the internal surface from endodermal to skin-like ectodermal tissue. The anal canal is traditionally divided into two segments, upper and lower, separated by the pectinate line (also known as the dentate line): * upper zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |