|
Pancreatic Islets
The pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine (hormone-producing) cells, discovered in 1869 by German pathological anatomist Paul Langerhans. The pancreatic islets constitute 1–2% of the pancreas volume and receive 10–15% of its blood flow. The pancreatic islets are arranged in density routes throughout the human pancreas, and are important in the metabolism of glucose. Structure There are about 1 million islets distributed throughout the pancreas of a healthy adult human. While islets vary in size, the average diameter is about 0.2 mm.:928 Each islet is separated from the surrounding pancreatic tissue by a thin, fibrous, connective tissue capsule which is continuous with the fibrous connective tissue that is interwoven throughout the rest of the pancreas.:928 Microanatomy Hormones produced in the pancreatic islets are secreted directly into the blood flow by (at least) five types of cells. In rat islets, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e., it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. Ninety-nine percent of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatostatin
Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by #Nomenclature, several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones. Somatostatin inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion. Somatostatin has two active forms produced by the alternative cleavage of a single preproprotein: one consisting of 14 amino acids (shown in infobox to right), the other consisting of 28 amino acids. Among the vertebrates, there exist six different somatostatin genes that have been named: ''SS1'', ''SS2'', ''SS3'', ''SS4'', ''SS5'' and ''SS6''. Zebrafish have all six. The six different genes, along with the five different somatostatin receptors, allow somatostatin to possess a large range of functions. Humans have only one somatostatin gene, ''SST''. Nomenclature Synonyms of "somatost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittle Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body's immune system destroys pancreatic cells (beta cells). In healthy persons, beta cells produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone required by the body to store and convert blood sugar into energy. T1D results in high blood sugar levels in the body prior to treatment. Common symptoms include frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, weight loss, and other complications. Additional symptoms may include blurry vision, tiredness, and slow wound healing (owing to impaired blood flow). While some cases take longer, symptoms usually appear within weeks or a few months. The cause of type 1 diabetes is not completely understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves an autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Diabetes is diagnosed by testing the level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Pancreas
Automated insulin delivery systems are automated (or semi-automated) systems designed to assist people with insulin-requiring diabetes, by automatically adjusting insulin delivery in response to blood glucose levels. Currently available systems (as of October 2020) can only deliver (and regulate delivery of) a single hormone—insulin. Other systems currently in development aim to improve on current systems by adding one or more additional hormones that can be delivered as needed, providing something closer to the endocrine functionality of the pancreas. The endocrine functionality of the pancreas is provided by islet cells which produce the hormones insulin and glucagon. Artificial pancreatic technology mimics the secretion of these hormones into the bloodstream in response to the body's changing blood glucose levels. Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is crucial to the function of the brain, liver, and kidneys. Therefore, for people with diabetes, it is necessary that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas Transplantation
A pancreas transplant is an organ transplant that involves implanting a healthy pancreas (one that can produce insulin) into a person who usually has diabetes. Overview Because the pancreas is a vital organ, performing functions necessary in the digestion process, the recipient's native pancreas is left in place, and the donated pancreas is attached in a different location. In the event of rejection of the new pancreas, which would quickly cause life-threatening diabetes, there would be a significant chance the recipient would not survive very well for long without the native pancreas, however dysfunctional, still in place. The healthy pancreas comes from a donor who has just died or it may be a partial pancreas from a living donor. At present, pancreas transplants are usually performed in persons with insulin-dependent diabetes, who can develop severe complications. Patients with the most common, and deadliest, form of pancreatic cancer ( pancreatic adenomas, which are usually m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body's immune system destroys pancreatic cells (beta cells). In healthy persons, beta cells produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone required by the body to store and convert blood sugar into energy. T1D results in high blood sugar levels in the body prior to treatment. Common symptoms include frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, weight loss, and other complications. Additional symptoms may include blurry vision, tiredness, and slow wound healing (owing to impaired blood flow). While some cases take longer, symptoms usually appear within weeks or a few months. The cause of type 1 diabetes is not completely understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves an autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Diabetes is diagnosed by testing the leve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to insulin's effects. Classic symptoms include polydipsia (excessive thirst), polyuria (excessive urination), polyphagia (excessive hunger), weight loss, and blurred vision. If left untreated, the disease can lead to various health complications, including disorders of the cardiovascular system, eye, kidney, and nerves. Diabetes accounts for approximately 4.2 million deaths every year, with an estimated 1.5 million caused by either untreated or poorly treated diabetes. The major types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2. The most common treatment for type 1 is insulin replacement therapy (insulin injections), while anti-diabetic medications (such as metformin and semaglutide) and lifestyle modificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
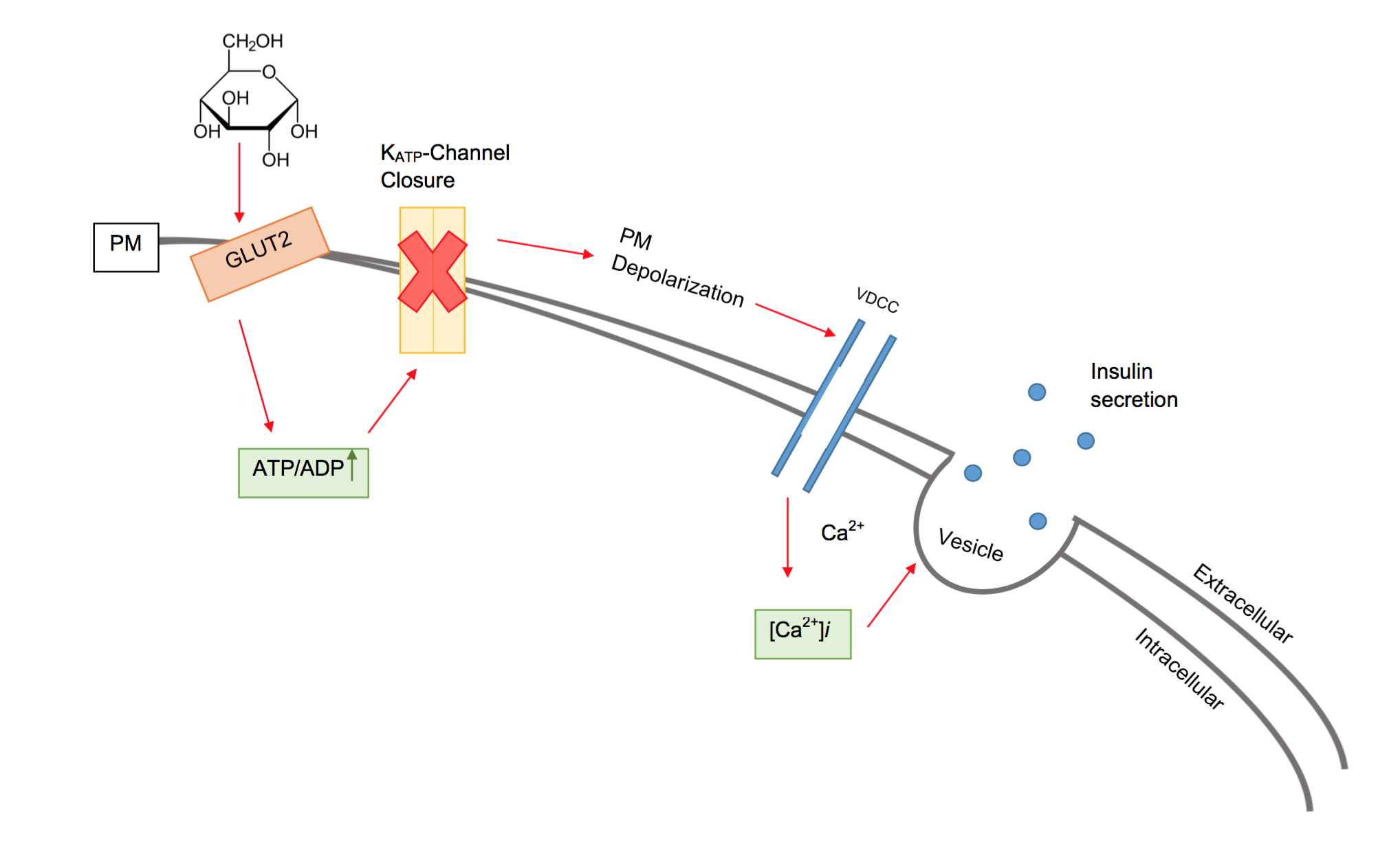
Beta Cell
Beta cells (β-cells) are specialized endocrine cells located within the pancreatic islets of Langerhans responsible for the production and release of insulin and amylin. Constituting ~50–70% of cells in human islets, beta cells play a vital role in maintaining blood glucose levels. Problems with beta cells can lead to disorders such as diabetes. Function The function of beta cells is primarily centered around the synthesis and secretion of hormones, particularly insulin and amylin. Both hormones work to keep blood glucose levels within a narrow, healthy range by different mechanisms. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, allowing them to use it for energy or store it for future use. Amylin helps regulate the rate at which glucose enters the bloodstream after a meal, slowing down the absorption of nutrients by inhibit gastric emptying. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patch Clamp
The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology used to study ionic currents in individual Cell isolation, isolated living cells, tissue sections, or patches of cell membrane. The technique is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreas, pancreatic beta cells, and can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts. Patch clamping can be performed using the voltage clamp technique. In this case, the voltage across the cell membrane is controlled by the experimenter and the resulting currents are recorded. Alternatively, the Electrophysiology, current clamp technique can be used. In this case, the current passing across the membrane is controlled by the experimenter and the resulting changes in voltage are recorded, generally in the form of action potentials. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patch clamp in the late 1970s and earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops (three extracellular loops interacting with ligand molecules, three intracellular loops interacting with G proteins, an N-terminal extracellular region and a C-terminal intracellular region) of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) licence/ref> Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocrine
Autocrine signaling is a form of cell signaling in which a cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger (called the autocrine agent) that binds to autocrine receptors on that same cell, leading to changes in the cell. This can be contrasted with paracrine signaling, intracrine signaling, or classical endocrine signaling. Examples An example of an autocrine agent is the cytokine interleukin-1 in monocytes. When interleukin-1 is produced in response to external stimuli, it can bind to cell-surface receptors on the same cell that produced it. Another example occurs in activated T cell lymphocytes, i.e., when a T cell is induced to mature by binding to a peptide: MHC complex on a professional antigen-presenting cell and by the B7: CD28 costimulatory signal. Upon activation, "low-affinity" IL-2 receptors are replaced by "high-affinity" IL-2 receptors consisting of α, β, and γ chains. The cell then releases IL-2, which binds to its own new IL-2 receptors, causing self-stimul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracrine
In cellular biology, paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication (biology), cellular communication in which a Cell (biology), cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to cell signaling by endocrine system, endocrine factors, hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system; juxtacrine signaling, juxtacrine interactions; and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain. Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |