|
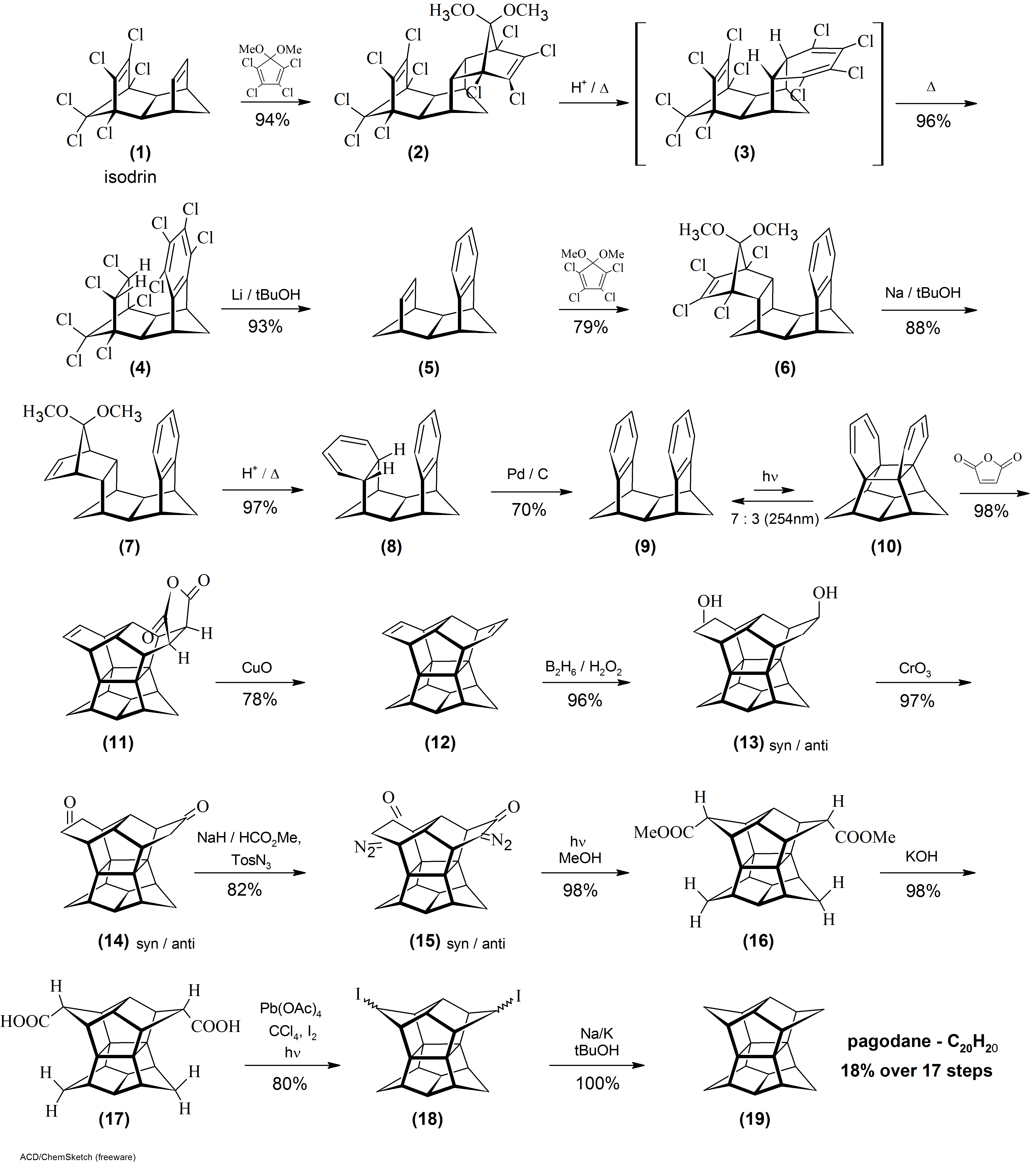
Pagodane
Pagodane is an organic compound with formula whose carbon skeleton was said to resemble a pagoda, hence the name. It is a polycyclic hydrocarbon whose molecule has the ''D''2''h'' point symmetry group. The compound is a highly crystalline solid that melts at 243 °C, is barely soluble in most organic solvents and moderately soluble in benzene and chloroform. It sublimes at low pressure. The name pagodane is used more generally for any member of a family of compounds whose molecular skeletons have the same 16-carbon central cage as the basic compound. Each member can be seen as the result of connecting eight atoms of this cage in pairs by four alkane chains. The general member is denoted 'm''.''n''.''p''.''q''agodane where ''m'', ''n'', ''p'' and ''q'' are the number of carbons of those four chains. The general formula is then where ''s''= ''m''+''n''+''p''+''q''. In particular, the basic compound has those carbons connected by four methylene bridges (''m''=''n''=''p''='' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodecahedrane
Dodecahedrane is a chemical compound, a hydrocarbon with formula , whose carbon atoms are arranged as the vertices (corners) of a regular dodecahedron. Each carbon is bound to three neighbouring carbon atoms and to a hydrogen atom. This compound is one of the three possible Platonic hydrocarbons, the other two being cubane and tetrahedrane. Dodecahedrane does not occur in nature and has no significant uses. It was synthesized by Leo Paquette in 1982, primarily for the "aesthetically pleasing symmetry of the dodecahedral framework". For many years, dodecahedrane was the simplest real carbon-based molecule with full icosahedral symmetry. Buckminsterfullerene (), discovered in 1985, also has the same symmetry, but has three times as many carbons and 50% more atoms overall. The synthesis of the C20 fullerene in 2000, from brominated dodecahedrane, may have demoted to second place. Structure The angle between the C-C bonds in each carbon atom is 108°, which is the angle betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
σ-bishomoaromaticity
Horst Prinzbach (20 July 1931 in Haslach im Kinzigtal – 18 September 2012 in Freiburg im Breisgau) was a German chemist and professor emeritus. Prinzbach studied chemistry at the University of Freiburg and received his PhD under Arthur Lüttringhaus. He joined William von Eggers Doering at Yale University for postdoctoral work. In 1962 he completed his habilitation at Freiburg with a dissertation on sesquifulvalenes. In 1965 he became a professor of organic chemistry at the University of Lausanne, Switzerland, and in 1969 he became a full professor in organic chemistry at Freiburg. Main research activities Of his many research interests in organic chemistry, including photochemistry with unusual chromophores, synthesis of new carba-/hetera cages, radical cations, dications, total synthesis of aminoglycosid antibiotics, and enzymes, Prinzbach was probably best known for the pagodane route towards dodecahedrane. In the course of his research, the phenomenon of σ-bishomoa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycyclic Compound
In the field of organic chemistry, a polycyclic compound is an organic compound featuring several closed ring (chemistry), rings of atoms, primarily carbon. These ring substructures include cycloalkanes, aromaticity, aromatics, and other ring types. They come in sizes of three atoms and upward, and in combinations of linkages that include tethering (such as in biaryls), fusing (edge-to-edge, such as in anthracene and steroids), links via a single atom (such as in spiro compounds), bridged compounds, and longifolene. Though poly- literally means "many", there is some latitude in determining how many rings are required to be considered polycyclic; many smaller rings are described by specific prefixes (e.g., bicyclic molecule, bicyclic, tricyclic, tetracyclic, etc.), and so while it can refer to these, the title term is used with most specificity when these alternative names and prefixes are unavailable. In general, the term polycyclic includes polycyclic aromatic compounds, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chemical Compounds With Unusual Names
Chemical nomenclature, replete as it is with compounds with very complex names, is a repository for some names that may be considered unusual. A browse through the ''Physical Constants of Organic Compounds'' in the ''CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics'' (a fundamental resource) will reveal not just the whimsical work of chemists, but the sometimes peculiar compound names that occur as the consequence of simple juxtaposition. Some names derive legitimately from their chemical makeup, from the geographic region where they may be found, the plant or animal species from which they are isolated or the name of the discoverer. Some are given intentionally unusual trivial names based on their structure, a notable property or at the whim of those who first isolate them. However, many trivial names predate formal naming conventions. Trivial names can also be ambiguous or carry different meanings in different industries, geographic regions and languages. Godly noted that "Trivial names h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debye
The debye ( , ; symbol: D) is a CGS unit (a non- SI metric unit) of electric dipole momentTwo equal and opposite charges separated by some distance constitute an electric dipole. This dipole possesses an electric dipole moment whose value is given as charge times length of separation. The dipole itself is a vector whose direction coincides with the position vector of the positive charge with respect to the negative charge: : p = ''q''r. named in honour of the physicist Peter J. W. Debye. It is defined as statcoulomb-centimetres.The statcoulomb is also known as the franklin or electrostatic unit of charge. : 1 statC = 1 Fr = 1 esu = 1 cm3/2⋅g1/2⋅s−1. Historically the debye was defined as the dipole moment resulting from two charges of opposite sign but an equal magnitude of 10−10 statcoulomb10−10 statcoulomb corresponds to approximately 0.2083 units of elementary charge. (generally called e.s.u. (electrostatic unit) in ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycyclic Nonaromatic Hydrocarbons
Polycyclic may refer to: * Polycyclic compound, a cyclic compound with more than one hydrocarbon loop or ring structures, including: ** Polycyclic musks ** Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon A Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is any member of a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple fused aromatic rings. Most are produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter— by engine exhaust fumes, tobacco, incine ... *** Chlorinated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon *** Contorted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon * Polycyclic group, in mathematics, a solvable group that satisfies the maximal condition on subgroups * Polycyclic spawning, when an animal reproduces multiple times during its lifespan {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angewandte Chemie International Edition In English
''Angewandte Chemie'' (, meaning "Applied Chemistry") is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that is published by Wiley-VCH on behalf of the German Chemical Society (Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker). Publishing formats include feature-length reviews, short highlights, research communications, minireviews, essays, book reviews, meeting reviews, correspondences, corrections, and obituaries. This journal contains review articles covering all aspects of chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2023 impact factor of 16.1. Editions The journal appears in two editions with separate volume and page numbering: a German edition, ''Angewandte Chemie'', and a fully English-language edition, ''Angewandte Chemie International Edition''. The editions are identical in content with the exception of occasional reviews of German-language books or German translations of IUPAC recommendations. Publication history In 1887, Ferdinand Fischer established the ''Zei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclobutane
Cyclobutane is a cycloalkane and organic compound with the formula (CH2)4. Cyclobutane is a colourless gas and is commercially available as a liquefied gas. Derivatives of cyclobutane are called cyclobutanes. Cyclobutane itself is of no commercial or biological significance, but more complex derivatives are important in biology and biotechnology. Structure The bond angles between carbon atoms are significantly strained and as such have lower bond energies than related linear or unstrained hydrocarbons, e.g. butane or cyclohexane. As such, cyclobutane is unstable above about 500 °C. The four carbon atoms in cyclobutane are not coplanar; instead, the ring typically adopts a folded or "puckered" conformation. This implies that the C-C-C angle is less than 90°. One of the carbon atoms makes a 25° angle with the plane formed by the other three carbons. In this way, some of the eclipsing interactions are reduced. The conformation is also known as a "butterfly". Equivalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Deficiency
In chemistry, electron deficiency (and electron-deficient) is jargon that is used in two contexts: chemical species that violate the octet rule because they have too few valence electrons and species that happen to follow the octet rule but have electron-acceptor properties, forming donor-acceptor charge-transfer salts. Octet rule violations left, 144px Traditionally, "electron-deficiency" is used as a general descriptor for boron hydrides and other molecules which do not have enough valence electrons to form localized (2-centre 2-electron) bonds joining all atoms. For example, diborane (B2H6) would require a minimum of 7 localized bonds with 14 electrons to join all 8 atoms, but there are only 12 valence electrons. A similar situation exists in trimethylaluminium. The electron deficiency in such compounds is similar to metallic bonding. Electron-acceptor molecules Alternatively, electron-deficiency describes molecules or ions that function as electron acceptors. Such elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuryl Chloride Fluoride
Sulfuryl chloride fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless, easily condensed gas. It is a tetrahedral molecule. Liquified sulfuryl chloride fluoride is employed as a solvent for highly oxidizing compounds. Preparation The laboratory-scale synthesis begins with the preparation of potassium fluorosulfite: : This salt is then chlorinated to give sulfuryl chloride fluoride : Further heating (180 °C) of potassium fluorosulfite with the sulfuryl chloride fluoride gives sulfuryl fluoride. : Alternatively, sulfuryl chloride fluoride can be prepared without using gases as starting materials by treating sulfuryl chloride with ammonium fluoride or potassium fluoride in trifluoroacetic acid Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is a synthetic organofluorine compound with the chemical formula CF3CO2H. It belongs to the subclass of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) known as ultrashort-chain perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs). TFA is not .... : References { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |