|
Pachisi
Pachisi (, Hindustani: əˈtʃiːsiː is a cross and circle board game that originated in Ancient India. It is described in the ancient text ''Mahabharata'' under the name of "Pasha". It is played on a board shaped like a symmetrical cross. A player's pieces move around the board based upon a throw of six or seven cowrie shells, with the number of shells resting with the aperture upward indicating the number of spaces to move. The name of the game is derived from the Hindi word ''paccīs'', meaning "twenty-five", the largest score that can be thrown with the cowrie shells; thus this game is also known by the name ''Twenty-Five''. There are other versions of this game where the largest score that can be thrown is thirty. In addition to chaupar, there are many versions of the game. (barsis) is popular in the Levant, mainly Syria, while Parchís is another version popular in Spain and northern Morocco. Parqués is its Colombian variant. Parcheesi, Sorry!, and Ludo are amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
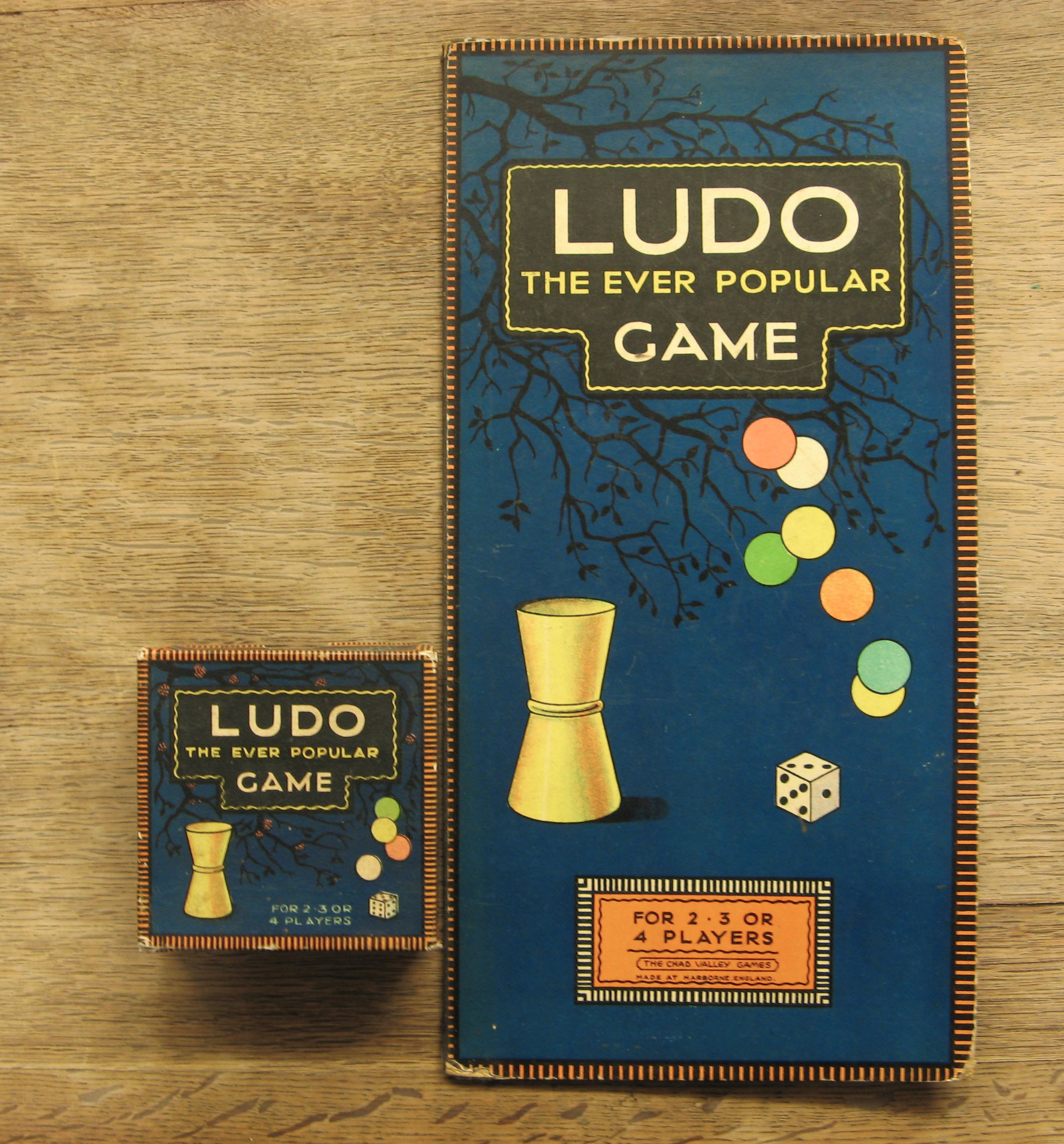
Ludo (board Game)
Ludo (; ) is a strategy board game for two to four players, in which the players race their four from start to finish according to the rolls of a single die. Like other cross and circle games, Ludo is derived from the Indian game Pachisi. The game and its variations are popular in many countries and under various names. History The Mahabharata Pachisi was created in India in the sixth century CE. The earliest evidence of this game's evolution in India is the depiction of boards on the caves of Ellora. The original version is also described in the Indian epic Mahabharata in which Shakuni uses cursed dice to beat the Pandavas, and at last after losing everything, Yudhisthira puts his wife Draupadi on stake and loses her, too. The Pandavas get all their belongings back, though, after Draupadi vows to curse the whole Kuru lineage, but stops at the intervention of Gandhari, and seeing an opportunity to still Draupadi's anger, Kuru king Dhritarashtra promises to give bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross And Circle Game
Cross and circle is a board game design used for race games played throughout the world. Design The basic design comprises a circle divided into four equal portions by a cross inscribed inside it like four spokes in a wheel; the classic example of this design is Yut. However, the term "cross and circle game" is also applied to boards that replace the circle with a square, and cruciform boards that collapse the circle onto the cross; all three types are topologically equivalent. Ludo and ''Parcheesi'' (both descendants of Pachisi) are examples of frequently played cruciform games. The category may also be expanded to include circular or square boards ''without'' a cross which are nevertheless quartered (Zohn Ahl), and boards that have more than four spokes ( Aggravation, Trivial Pursuit). The game board for the Aztec game Patolli consists of a collapsed circle ''without'' an interior cross and thus has the distinction of being a cross that ''is'' a circle (topologically), wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parqués
Parqués () is the Colombian version of a board game in the cross and circle family (the category that includes Pachisi). The game is described as a "random thinking" game: the moves depend on the roll of the dice but players must consider possible strategies before executing their move. The objective of the game is to advance all the pieces to the end. Once in the safety zone player can use 2 dice until they are one space away from home, where they will then just use one die. Colombian culture Parqués is the Colombian version of Parcheesi, which itself is a version of Pachisi (which originated in India India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...). The meaning of the word may be a translation of the pachisi word, also influenced by similar games such as Parcheesi. Parq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mensch ärgere Dich Nicht
Mensch ärgere Dich nicht (English: ''Man, Don't Get Angry'') is a German board game (but not a German-style board game), developed by Josef Friedrich Schmidt in 1907/1908. Some 70 million copies have been sold since its introduction in 1914 and it is played in many European countries. The name derives from the fact that a peg is sent back to the "out" field when another peg lands on it, similar to the later game Sorry!. It is a cross and circle game with the circle collapsed onto the cross, similar to the Indian game Pachisi, the Colombian game Parqués, the American games Parcheesi and Trouble, the French game Jeu des petits chevaux, and the English game Ludo. Overview The most played variant of the game can be played by two, three or four players – one player per board side. The special one has a pattern for six players. Each player has four game pieces, which are in the "out" area when the game starts, and which must be brought into the player's "home" row. The ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaupar
Chaupar ( IAST: ''caupaṛ''), chopad or chaupad is a cross and circle board game very similar to pachisi, played in India. The board is made of wool or cloth, with wooden pawns and seven cowry shells to be used to determine each player's move, although others distinguish chaupur from pachisi by the use of three four-sided long dice. Variations are played throughout India. It is similar in some ways to Pachisi, Parcheesi and Ludo. In most of the villages of India, this game is played by old people. History Gamesmen similar to chaupar with difference in colour schemes along with dice have been identified from Iron age, Painted grey ware period from Mathura. Pachisi is originated from chaupar. Chopat is claimed to be a variation of the game of dice played in the epic poem Mahabharata The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowrie
Cowrie or cowry () is the common name for a group of small to large sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Cypraeidae, the cowries. The term ''porcelain'' derives from the old Italian term for the cowrie shell (''porcellana'') due to their similar appearance. Shells of certain species have historically been used as currency in several parts of the world, as well as being used, in the past and present, very extensively in jewelry, and for other decorative and ceremonial purposes. The cowrie was the shell most widely used worldwide as shell money. It is most abundant in the Indian Ocean, and was collected in the Maldive Islands, in Sri Lanka, along the Indian Malabar coast, in Borneo and on other East Indian islands, in Maluku in the Pacific, and in various parts of the African coast from Ras Hafun to Mozambique. Cowrie shell money was important in the trade networks of Africa, South Asia, and East Asia. In the United States and Mexico, cowrie species inhab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parchís
Parchís is a Spanish board game of the Cross and Circle family. It is an adaptation of the Indian game Pachisi. Parchís was a very popular game in Spain at one point as well as in Europe and north Morocco - specifically Tangiers and Tetouan, and it is still popular especially among adults and seniors. Since it uses dice, Parchís is not usually regarded as an abstract strategy game like checkers or chess. It does not depend entirely on luck either, since the four pawns under a player's command demand some sort of strategy. Parchís is license-free in Spain, so in stores it is just as easy to find as a deck of cards, and is usually cheaper. Although the original game allows up to four players (that is, the board counts four colors: yellow, blue, red and green), six-player versions are not hard to find (adding orange and purple, in that order), and eight-player boards can be found in big toy stores. Traditionally, each player has a ''cubilete'' (dice cup) to shake and toss the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
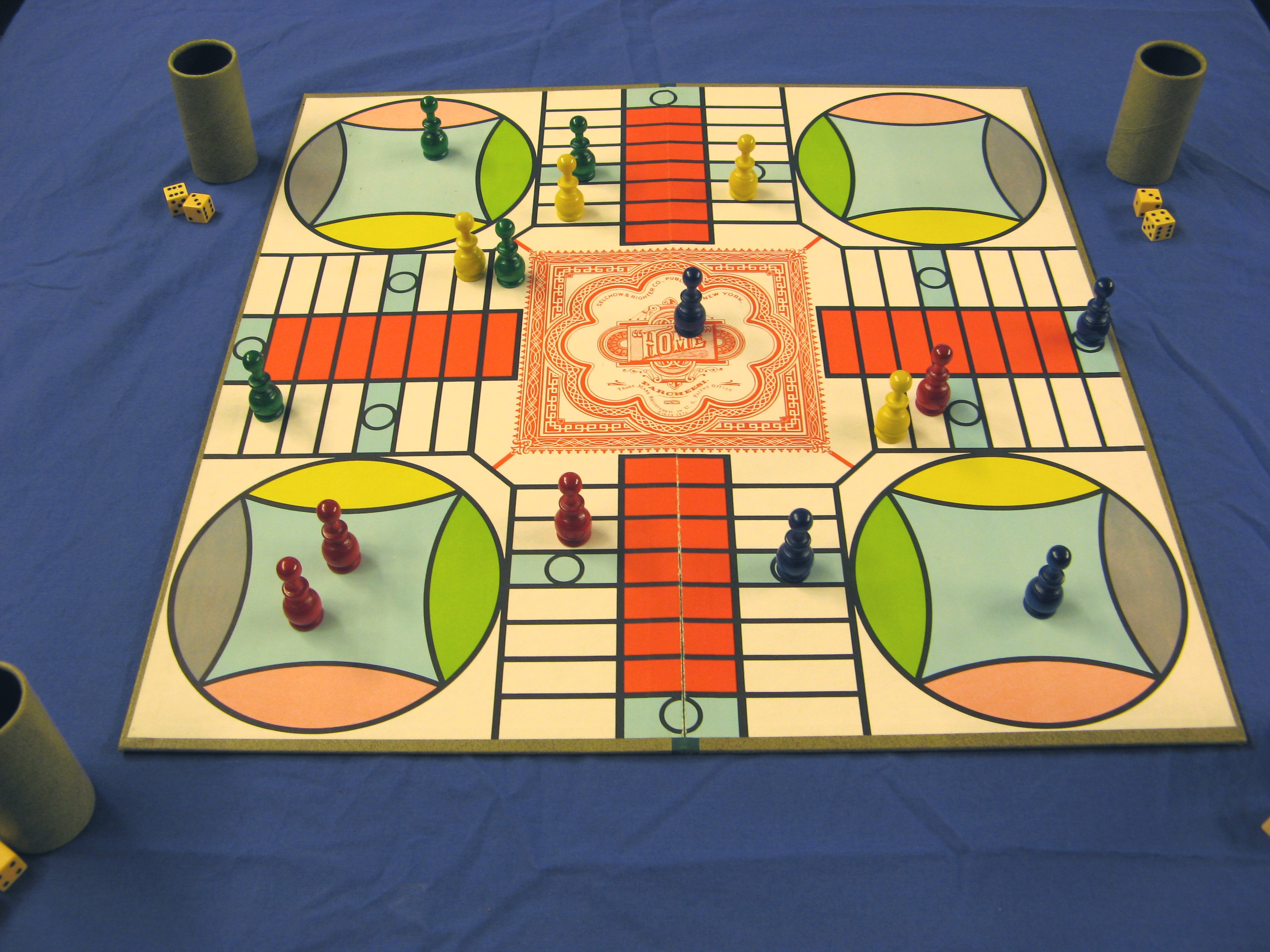
Parcheesi
''Parcheesi'' is a brand-name American adaptation of the Indian cross and circle board game Pachisi, published by Parker Brothers and Winning Moves Games USA. Equipment ''Parcheesi'' is typically played with two dice Dice (singular die or dice) are small, throwable objects with marked sides that can rest in multiple positions. They are used for generating random values, commonly as part of tabletop games, including dice games, board games, role-playing ..., four pieces per player and a with a track around the outside, four corner spaces and four ''home paths'' leading to a central end space. The most popular ''Parcheesi'' boards in America have 68 spaces around the edge of the board, 12 of which are darkened ''safe spaces''. Each corner of the board contains one player's ''nest'', or . Setup * Each player positions their four single colored pieces in their respective starting nest. * Each player rolls a single die to determine player order. The player with the lowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Race Game
Race game is a large category of board games, in which the object is to be the first to move all one's pieces to the end of a track. This is both the earliest type of board game known, with implements and representations dating back to at least the 3rd millennium BC in Egypt, Iraq, and Iran; and also the most widely dispersed: "all cultures that have games at all have race games". Race games often use dice to decide game options and how far to move pieces. Types of race games Race games may be categorized by their ratio of luck to skill. Other classifications include geographical distribution or derivation; and shape of track (including spiral, cross and circle, and square—either boustrophedon as in Snakes and Ladders or "labyrinthine" as in Thaayam). Simple Simple race games involve pure luck. Each player has only one piece to move, and the outcome of the game thus depends solely on chance. The Game of the Goose is the progenitor of most simple Western race games, whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Game
Board games are tabletop games that typically use . These pieces are moved or placed on a pre-marked board (playing surface) and often include elements of table, card, role-playing, and miniatures games as well. Many board games feature a competition between two or more players. To show a few examples: in checkers (British English name 'draughts'), a player wins by capturing all opposing pieces, while Eurogames often end with a calculation of final scores. ''Pandemic'' is a cooperative game where players all win or lose as a team, and peg solitaire is a puzzle for one person. There are many varieties of board games. Their representation of real-life situations can range from having no inherent theme, such as checkers, to having a specific theme and narrative, such as '' Cluedo''. Rules can range from the very simple, such as in snakes and ladders; to deeply complex, as in '' Advanced Squad Leader''. Play components now often include custom figures or shaped counters, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunnori
Yut Nori, also known as Yunnori, Nyout, and Yoot, is a traditional board game played in Korea, especially during Korean New Year. The game is also called ''cheok-sa'' or ''sa-hee''. The combining-form ''-nori'' means 'game'. Although the origins of this popular family game are unclear, some research suggests that yut was played as early as the Three Kingdoms (57 BCE – 668 CE). The ''Taiping Imperial Reader'' states that people of Baekje played a board game similar to Po Yut, which is believed to be similar to Pachisi, a board game originating in India. There is a folk explanation for the game, describing a bet by some villagers to raise five different kind of livestock: pigs, dogs, sheep, cows and horses. Each of the villagers would raise only one type. The board and the game are known to have been used in casting hexagrams, particularly in mountain-areas and small farming-villages, but this is no longer practiced. Equipment The board (''mal-pan'', 말판) is normally made o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Game
Board games are tabletop games that typically use . These pieces are moved or placed on a pre-marked board (playing surface) and often include elements of table, card, role-playing, and miniatures games as well. Many board games feature a competition between two or more players. To show a few examples: in checkers (British English name 'draughts'), a player wins by capturing all opposing pieces, while Eurogames often end with a calculation of final scores. ''Pandemic'' is a cooperative game where players all win or lose as a team, and peg solitaire is a puzzle for one person. There are many varieties of board games. Their representation of real-life situations can range from having no inherent theme, such as checkers, to having a specific theme and narrative, such as '' Cluedo''. Rules can range from the very simple, such as in snakes and ladders; to deeply complex, as in '' Advanced Squad Leader''. Play components now often include custom figures or shaped counters, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |