|
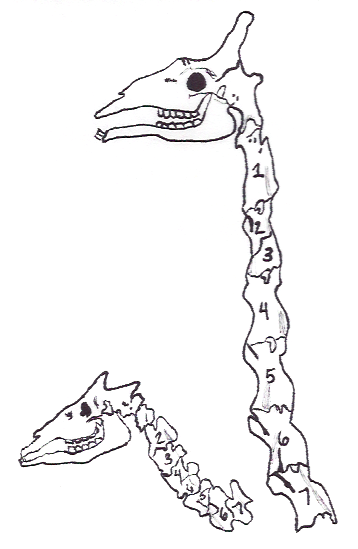
Ossicone
Ossicones are columnar or conical skin-covered bone structures on the heads of giraffes, male okapi, and some of their extinct relatives. Ossicones are distinguished from the superficially similar structures of Horn (anatomy), horns and antlers by their unique development and a permanent covering of skin and fur. Structure Giraffe ossicones consist of a highly vascularized and innervated bone core covered with similarly vascularized and innervated skin. They are attached to the skull with vascularized, innervated connective tissue. Ossicones are formed at late gestation, but in early development they are not bony and not fused to the skull yet. Ossicones usually fuse to the skull at sexual maturity. All male and female giraffes have a pair of parietal ossicones on the parietal bones of the skull. Males also usually have a single median ossicone on the frontal bone that is larger in northern animals and smaller in southern giraffes. Giraffes can also have small additional paire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Okapia
The okapi (; ''Okapia johnstoni''), also known as the forest giraffe, Congolese giraffe and zebra giraffe, is an artiodactyl mammal that is endemic to the northeast Democratic Republic of the Congo in central Africa. However, non-invasive genetic identification has suggested that a population has occurred south-west of the Congo River as well. It is the only species in the genus ''Okapia''. Although the okapi has striped markings reminiscent of zebras, it is most closely related to the giraffe. The okapi and the giraffe are the only living members of the family Giraffidae. The okapi stands about tall at the shoulder and has a typical body length around . Its weight ranges from . It has a long neck, and large, flexible ears. Its coat is a chocolate to reddish brown, much in contrast with the white horizontal stripes and rings on the legs, and white ankles. Male okapis have short, distinct horn-like protuberances on their heads called ossicones, less than in length. Females p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Giraffidae
The Giraffidae are a family (biology), family of ruminant artiodactyl mammals that share a recent common ancestor with deer and bovids. This family, once a diverse group spread throughout Eurasia and Africa, presently comprises only two extant genera, the giraffe (between one and eight, usually four, species of ''Giraffa'', depending on taxonomic interpretation) and the okapi (the only known species of ''Okapia''). Both are confined to sub-Saharan Africa: the giraffe to the open savannas, and the okapi to the dense rainforest of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Congo. The two genera look very different on first sight, but share a number of common features, including a long, dark-coloured tongue, lobed canine teeth, and horns covered in skin, called ossicones. Taxonomy Evolutionary background The giraffids are ruminants of the clade Pecora. Other extant pecorans are the families Antilocapridae (pronghorns), Cervidae (deer), Moschidae (musk deer), and Bovidae (Bovini, cattl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sivatherium
''Sivatherium'' ("Shiva's beast", from Shiva and ''therium'', Latinized form of Ancient Greek θηρίον -'' thēríon'') is an extinct genus of giraffid that ranged throughout Africa and Eurasia. The species ''Sivatherium giganteum'' is, by weight, one of the largest giraffids known, and also one of the largest ruminants of all time. ''Sivatherium'' originated during the Late Miocene (around 7 million years ago) in Africa and survived through to the late Early Pleistocene ( Calabrian) until around 1 million years ago. Description ''Sivatherium'' resembled the modern okapi, but was far larger, and more heavily built, being about tall at the shoulder, in total height with a weight up to . A newer estimate has come up with an estimated body mass of about or . This would make ''Sivatherium'' one of the largest known ruminants, rivalling the modern giraffe and the largest bovines. This weight estimate is thought to be an underestimate, as it does not take into account ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Samotherium
''Samotherium'' ("beast of Samos") is an extinct genus of Giraffidae from the Miocene and Pliocene of Eurasia and Africa. ''Samotherium'' had two ossicones on its head, and long legs. The ossicones usually pointed upward, and were curved backwards, with males having larger, more curved ossicones, though in the Chinese species, ''S. sinense'', the straight ossicones point laterally, not upwards. The genus is closely related to '' Shansitherium''. Fossil evidence suggests that ''Samotherium'' had a rounded muzzle, which would suggest a grazing lifestyle and a habitat composed of grassland. One common predator of this animal was the '' Amphimachairodus''. Biologist Richard Ellis has proposed that the skull of ''Samotherium'' is portrayed on an ancient Greek vase as a monster that Heracles Heracles ( ; ), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a Divinity, divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of ZeusApollodorus1.9.16/ref> and Alcmene, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Palaeotragus
''Palaeotragus'' ("ancient goat") is a genus of very large, primitive, okapi-like giraffids from the Miocene to Early Pleistocene of Africa and Eurasia. ''Palaeotragus primaevus'' is the older species, being found in early to mid-Miocene strata, while ''P. germaini'' is found in Late Miocene strata. ''P. primaevus'' is distinguished from ''P. germaini'' by the lack of ossicone Ossicones are columnar or conical skin-covered bone structures on the heads of giraffes, male okapi, and some of their extinct relatives. Ossicones are distinguished from the superficially similar structures of Horn (anatomy), horns and antlers ...s. It was also the smaller species, being a little under at the shoulders. ''P. germaini'' had a pair of ossicones, and in life, it would have resembled either a short-necked, tall giraffe, or a gargantuan okapi. ''Palaeotragus inexspectatus'' from the Early Pleistocene of Greece represents the youngest giraffid in Europe. Species The genus consists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mitilanotherium
''Mitilanotherium'' is an extinct genus of giraffes from the Pliocene and Pleistocene of Europe. It was a medium-sized giraffid, resembling the modern okapi, with two long ossicone Ossicones are columnar or conical skin-covered bone structures on the heads of giraffes, male okapi, and some of their extinct relatives. Ossicones are distinguished from the superficially similar structures of Horn (anatomy), horns and antlers ...s directly above its eyes, and relatively long and slender limbs. Fossils have been found in Greece, Romania, Ukraine, and Spain. References * Classification of Mammals by Malcolm C. McKenna and Susan K. Bell Prehistoric giraffes Monotypic prehistoric Artiodactyla genera Extinct mammals of Europe Pliocene Artiodactyla {{paleo-eventoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Injanatherium
''Injanatherium'' is an extinct genus of giraffids from the Miocene of Iraq,HEINTZ, E., M. BRUNET, and S. SEN. "A NEW GIRAFFID FROM IRAQ UPPER MIOCENE INJANATHERIUM-HAZIMI NG N-SP." COMPTES RENDUS DE L ACADEMIE DES SCIENCES SERIE III-SCIENCES DE LA VIE-LIFE SCIENCES 292.4 (1981): 357-360. Saudi Arabia, and Pakistan. Species of ''Injanatherium'' had at least two pairs of long, wing-like ossicones that emanated laterally above the orbits. Species ''I. hazimi'' ''I. hazimi'' is the type species, originally described by Heintz, et al., in 1981, on the basis of a partial skull found in middle Miocene-aged strata of Injana, Iraq, about 140 km north of Baghdad. The ossicones are broad and more massive in comparison to ''I. arabicum''. ''I. arabicum'' ''I. arabicum'' is a second species initially described from a partial skull from early Miocene-aged strata of Saudi Arabia, then later from material found in similarly aged strata from Pakistan. Its ossicones are more triangular and les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Honanotherium
''Honanotherium'' is a genus of extinct giraffid from the late Miocene of Henan Province, China, and East Azerbaijan Province, northwestern Iran.Bohlin, B. 1927. Die Familie Giraffidae. Pal. Sinica, Ser. C, IV, Fasc. 1, various pages.Nikos Solounias and Melinda Danowitz (2016). "The Giraffidae of Maragheh and the identification of a new species of Honanotherium". Palaeobiodiversity and Palaeoenvironments. in press. doi:10.1007/s12549-016-0230-7. It was closely related to ''Bohlinia'' and was once thought to be ancestral to the modern giraffe (genus ''Giraffa''). The living animal would have resembled a modern giraffe, but was somewhat shorter, with more massive ossicones. The first part of the generic name, ''honano'' refers to the Henan () province of China, where the first specimens were recovered. The second part, ''therium'', comes from the Greek Greek may refer to: Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group *Greek langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Giraffa
The giraffe is a large African hoofed mammal belonging to the genus ''Giraffa.'' It is the tallest living terrestrial animal and the largest ruminant on Earth. It is classified under the family Giraffidae, along with its closest extant relative, the okapi. Traditionally, giraffes have been thought of as one species, '' Giraffa camelopardalis'', with nine subspecies. Most recently, researchers proposed dividing them into four extant species which can be distinguished by their fur coat patterns. Six valid extinct species of ''Giraffa'' are known from the fossil record. The giraffe's distinguishing characteristics are its extremely long neck and legs, horn-like ossicones, and spotted coat patterns. Its scattered range extends from Chad in the north to South Africa in the south and from Niger in the west to Somalia in the east. Giraffes usually inhabit savannahs and woodlands. Their food source is leaves, fruits, and flowers of woody plants, primarily acacia species, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |