|
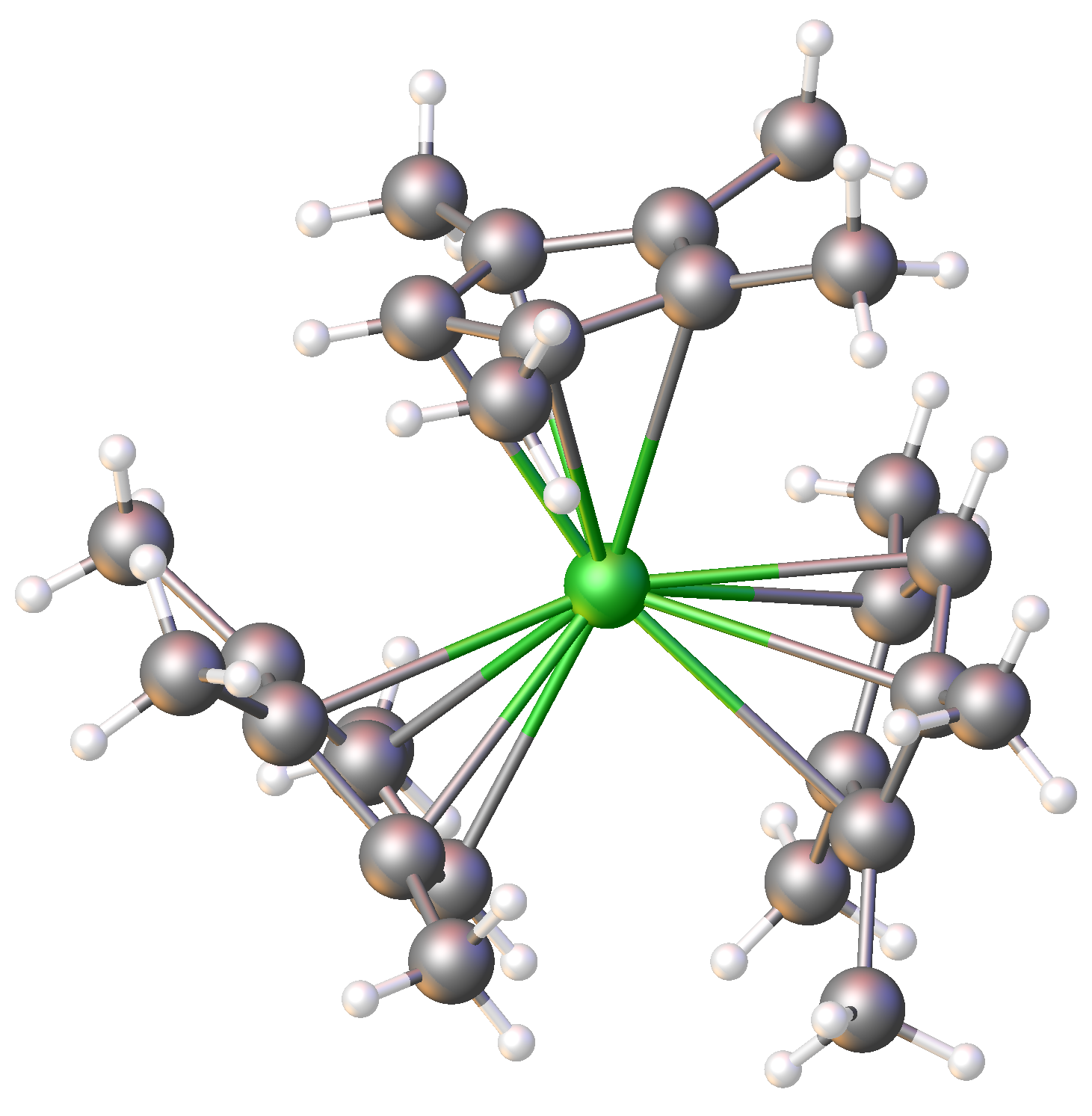
Organocerium Chemistry
Organocerium chemistry is the science of organometallic compounds that contain one or more chemical bond between carbon and cerium. These compounds comprise a subset of the organolanthanides. Most organocerium compounds feature Ce(III) but some Ce(IV) derivatives are known. Alkyl derivatives Simple alkylcerium reagents are well known. One example is . Although they are described as RCeCl2, their structures are far more complex.. Furthermore, the solvent seems to alter the solution structure of the complex, with differences noted between reagents prepared in diethyl ether and tetrahydrofuran. There is evidence that the parent chloride forms a polymeric species in THF solution, of the form bridging_ligand.html" ;"title="e(bridging ligand">μ-Cl)2(H2O)(THF)2sub>n, but whether this type of polymer exists once the organometallic reagent is formed is unknown. Cyclopentadienyl derivatives Cyclopentadienyl derivatives of Ce are particularly well characterized. Hundreds have been exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSD CIF DEWDEP
CSD may refer to: Finance * Central securities depository * Confederate States Dollar * Serbian dinar, by previous ISO 4217 code Organizations Education * California School for the Deaf (other), several institutions * Canyons School District, in Utah, US * Cheltenham School District, in Pennsylvania, US * Christina School District, in Delaware, US * Cleveland School District, in Mississippi, US * Cordova School District, in Alaska, US Other organizations * Canteen Stores Department (India), a chain of stores operated by the Indian Ministry of Defence at military bases * CSD Pakistan (Canteen Stores Department), a chain of stores operated by the Pakistani Ministry of Defence * Chartered Society of Designers, a British learned society for various kinds of design work * Commission on Sustainable Development (1992–2013), a former UN agency * Communication Service for the Deaf, an American non-profit company providing ASL services * Congress of Democratic Trade Unions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enolate
In organic chemistry, enolates are organic anions derived from the deprotonation of carbonyl () compounds. Rarely isolated, they are widely used as reagents in the Organic synthesis, synthesis of organic compounds. Bonding and structure Enolate anions are electronically related to allyl anions. The anionic charge is delocalized over the oxygen and the two carbon sites. Thus they have the character of both an alkoxide and a carbanion. Although they are often drawn as being simple salts, in fact they adopt complicated structures often featuring aggregates. Preparation Deprotonation of enolizable ketones, aromatic alcohols, aldehydes, and esters gives enolates. With strong bases, the deprotonation is quantitative. Typically enolates are generated from using lithium diisopropylamide (LDA). Often, as in conventional Claisen condensations, Mannich reactions, and aldol condensations, enolates are generated in low concentrations with alkoxide bases. Under such conditions, they ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerium Nucleophilic
Cerium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the oxidation state of +3 characteristic of the series, it also has a stable +4 state that does not oxidize water. It is considered one of the rare-earth elements. Cerium has no known biological role in humans but is not particularly toxic, except with intense or continued exposure. Despite always occurring in combination with the other rare-earth elements in minerals such as those of the monazite and bastnäsite groups, cerium is easy to extract from its ores, as it can be distinguished among the lanthanides by its unique ability to be oxidized to the +4 state in aqueous solution. It is the most common of the lanthanides, followed by neodymium, lanthanum, and praseodymium. Its estimated abundance in the Earth's crust is 68 ppm. Cerium was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons. Trimethylborane CH3)3Bis a Lewis acid as it is capable of accepting a lone pair. In a Lewis adduct, the Lewis acid and base share an electron pair furnished by the Lewis base, forming a dative bond. In the context of a specific chemical reaction between NH3 and Me3B, a lone pair from NH3 will form a dative bond with the empty orbital of Me3B to form an adduct NH3•BMe3. The terminology refers to the contributions of Gilbert N. Lewis. From p. 142: "We are inclined to think of substances as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions. Distinction is sometimes made between aldimines and ketimines, derived from aldehydes and ketones, respectively. Structure In imines the five core atoms (C2C=NX, ketimine; and C(H)C=NX, aldimine; X = H or C) are coplanar. Planarity results from the sp2-hybridization of the mutually double-bonded carbon and the nitrogen atoms. The C=N distance is 1.29–1.31 Å for nonconjugated imines and 1.35 Å for conjugated imines. By contrast, C−N distances in amines and nitriles are 1.47 and 1.16 Å respectively. Rotation about the C=N bond is slow. Using NMR spectroscopy, both E–Z notation, ''E'' and ''Z'' isomers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophilic
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. The difference between the two is, that basicity is a thermodynamic property (i.e. relates to an equilibrium state), but nucleophilicity is a kinetic property ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addition Reaction
In organic chemistry, an addition reaction is an organic reaction in which two or more molecule A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...s combine to form a larger molecule called the '' adduct''.. An addition reaction is limited to chemical compounds that have multiple bonds. Examples include a molecule with a carbon–carbon double bond (an alkene) or a triple bond (an alkyne). Another example is a compound that has rings (which are also considered points of unsaturation). A molecule that has carbon— heteroatom double bonds, such as a carbonyl group () or imine group (), can undergo an addition reaction because its double-bond. An addition reaction is the reverse of an elimination reaction, in which one molecule divides into two or more molecules. For insta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxophilicity
Oxophilicity is the tendency of certain chemical compounds to form oxides by hydrolysis or abstraction of an oxygen atom from another molecule, often from organic compounds. The term is often used to describe metal centers, commonly the early transition metals such as titanium, niobium, and tungsten. Oxophilicity is often stated to be related to the hardness of the element, within the HSAB theory ( hard and soft (Lewis) acids and bases), but it has been shown that oxophilicity depends more on the electronegativity and effective nuclear charge of the element than on its hardness. This explains why the early transition metals, whose electronegativities and effective nuclear charges are low, are very oxophilic. Many main group compounds are also oxophilic, such as derivatives of aluminium, silicon, and phosphorus(III). The handling of oxophilic compounds often requires air-free techniques. Examples Complexes of oxophilic metals typically are prone to hydrolysis. For example, the high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology. Structure and bonding Aldehyde molecules have a central carbon atom that is connected by a double bond to oxygen, a single bond to hydrogen and another single bond to a third substituent, which is carbon or, in the case of formaldehyde, hydrogen. The central carbon is often described as being sp2- hybridized. The aldehyde group is somewhat polar. The bond length is about 120–122 picometers. Physical properties and characterization Aldehydes have properties that are diverse and that depend on the remainder of the molecule. Smaller aldehydes such as formaldehyde and acetaldehyde are solubl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' are methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, ''e.g.'', testosterone, and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considered retained IUPAC names, although some introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |