|
Addition Reaction
In organic chemistry, an addition reaction is an organic reaction in which two or more molecule A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...s combine to form a larger molecule called the '' adduct''.. An addition reaction is limited to chemical compounds that have multiple bonds. Examples include a molecule with a carbon–carbon double bond (an alkene) or a triple bond (an alkyne). Another example is a compound that has rings (which are also considered points of unsaturation). A molecule that has carbon— heteroatom double bonds, such as a carbonyl group () or imine group (), can undergo an addition reaction because its double-bond. An addition reaction is the reverse of an elimination reaction, in which one molecule divides into two or more molecules. For insta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons, conferring Hydrophile, hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan, J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry () is the relationships between the masses of reactants and Product (chemistry), products before, during, and following chemical reactions. Stoichiometry is based on the law of conservation of mass; the total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products, so the relationship between reactants and products must form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of the products can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated. This is illustrated in the image here, where the unbalanced equation is: : : However, the current equation is imbalanced. The reactants have 4 hydrogen and 2 oxygen atoms, while the product has 2 hydrogen and 3 oxygen. To balance the hydrogen, a coefficient of 2 is added to the product H2O, and to fix the imbalance of oxygen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces Double bond, double and Triple bond, triple bonds in hydrocarbons. Process Hydrogenation has three components, the Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated substrate, the hydrogen (or hydrogen source) and, invariably, a catalyst. The redox, reduction reaction is carried out at different temperatures and pressures depending upon the substrate and the activity of the catalyst. Related or competing reactions The same cataly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytic Chemistry
Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates analytes. Qualitative analysis identifies analytes, while quantitative analysis determines the numerical amount or concentration. Analytical chemistry consists of classical, wet chemical methods and modern analytical techniques. Classical qualitative methods use separations such as precipitation, extraction, and distillation. Identification may be based on differences in color, odor, melting point, boiling point, solubility, radioactivity or reactivity. Classical quantitative analysis uses mass or volume changes to quantify amount. Instrumental methods may be used to separate samples using chromatography, electrophoresis or field flow fractionation. Then qualitative and quantitative analysis can be performed, often wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
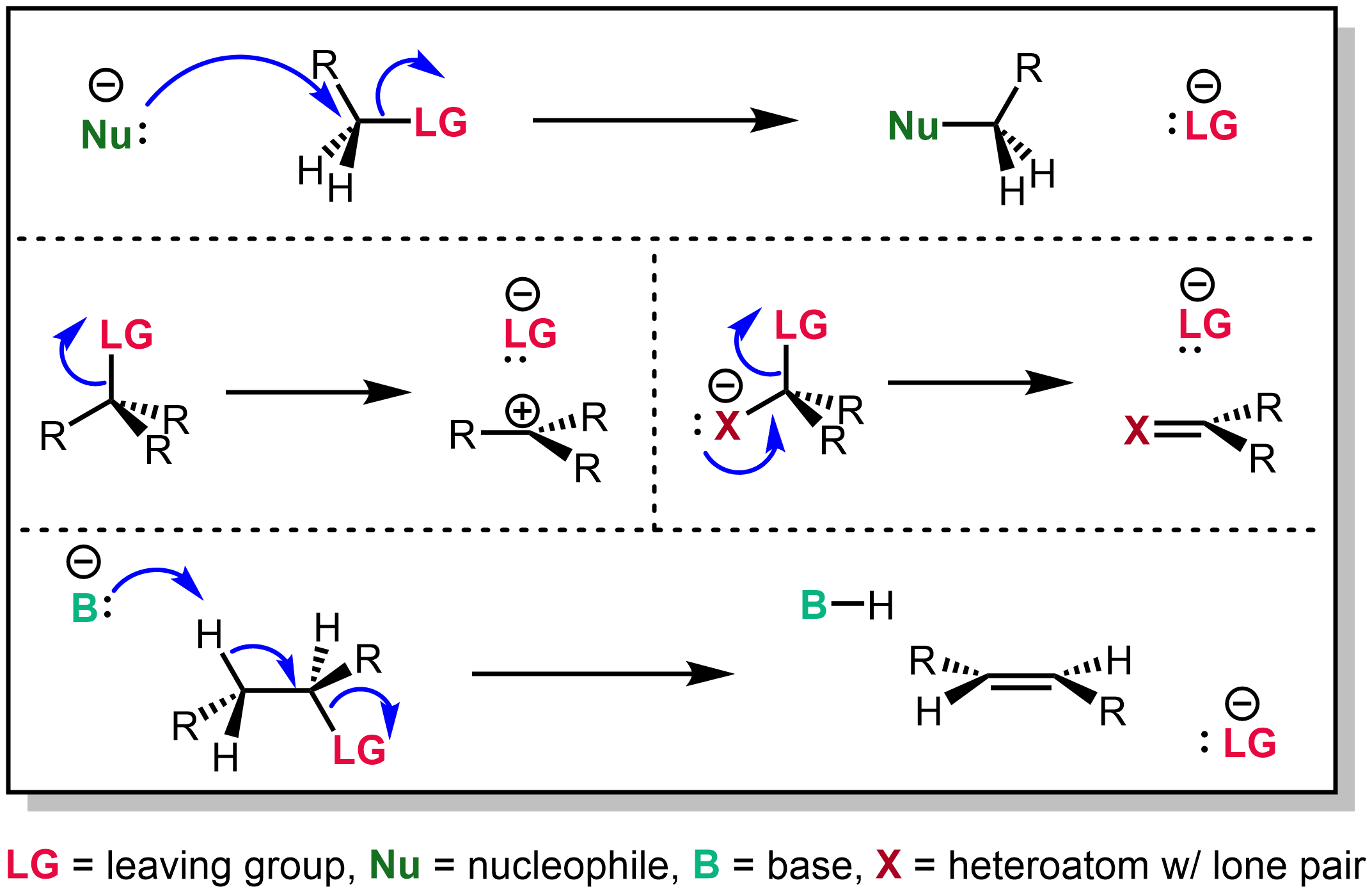
Leaving Group
In organic chemistry, a leaving group typically means a Chemical species, molecular fragment that departs with an electron, electron pair during a reaction step with heterolysis (chemistry), heterolytic bond cleavage. In this usage, a ''leaving group'' is a less formal but more commonly used synonym of the term ''nucleofuge''; although IUPAC gives the term a broader definition. A species' ability to serve as a leaving group can affect whether a reaction is viable, as well as what mechanism the reaction takes. Leaving group ability depends strongly on context, but often correlates with ability to stabilize additional electron density from bond heterolysis. Common anionic leaving groups are , and halides and sulfonate esters such as tosylate (). Water (), alcohols (), and amines () are common neutral leaving groups, although they often require activating catalysts. Some moieties, such as hydride (H−) serve as leaving groups only extremely rarely. Nomenclature IUPAC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addition Reactions General Overview
Addition (usually signified by the plus symbol, +) is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic, the other three being subtraction, multiplication, and division. The addition of two whole numbers results in the total or '' sum'' of those values combined. For example, the adjacent image shows two columns of apples, one with three apples and the other with two apples, totaling to five apples. This observation is expressed as , which is read as "three plus two equals five". Besides counting items, addition can also be defined and executed without referring to concrete objects, using abstractions called numbers instead, such as integers, real numbers, and complex numbers. Addition belongs to arithmetic, a branch of mathematics. In algebra, another area of mathematics, addition can also be performed on abstract objects such as vectors, matrices, subspaces, and subgroups. Addition has several important properties. It is commutative, meaning that the order of the numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addition Polymerization
Chain-growth polymerization ( AE) or chain-growth polymerisation ( BE) is a polymerization technique where monomer molecules add onto the active site on a growing polymer chain one at a time. There are a limited number of these active sites at any moment during the polymerization which gives this method its key characteristics. Chain-growth polymerization involves 3 types of reactions : # Initiation: An active species I* is formed by some decomposition of an initiator molecule I # Propagation: The initiator fragment reacts with a monomer M to begin the conversion to the polymer; the center of activity is retained in the adduct. Monomers continue to add in the same way until polymers Pi* are formed with the degree of polymerization i # Termination: By some reaction generally involving two polymers containing active centers, the growth center is deactivated, resulting in dead polymer Introduction In 1953, Paul Flory first classified polymerization as " step-growth polymeriza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloaddition
In organic chemistry, a cycloaddition is a chemical reaction in which "two or more Unsaturated hydrocarbon, unsaturated molecules (or parts of the same molecule) combine with the formation of a cyclic adduct in which there is a net reduction of the Multiplicity (chemistry)#Molecules, bond multiplicity". The resulting reaction is a cyclization reaction. Many but not all cycloadditions are Concerted reaction, concerted and thus pericyclic. Nonconcerted cycloadditions are not pericyclic. As a class of addition reaction, cycloadditions permit carbon–carbon bond formation without the use of a nucleophile or electrophile. Cycloadditions can be described using two systems of notation. An older but still common notation is based on the size of linear arrangements of atoms in the reactants. It uses parentheses: where the variables are the numbers of linear atoms in each reactant. The product is a cycle of size . In this system, the standard Diels-Alder reaction is a (4 + 2)-cyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-radical Addition
In organic chemistry, free-radical addition is an addition reaction which involves free radicals. These reactions can happen due to the free radicals having an unpaired electron in their valence shell, making them highly reactive. Radical additions are known for a variety of unsaturated substrates, both olefinic or aromatic and with or without heteroatoms. Free-radical reactions depend on one or more relatively weak bonds in a reagent. Under reaction conditions (typically heat or light), some weak bonds homolyse into radicals, which then induce further decomposition in their compatriots before recombination. Different mechanisms typically apply to reagents without such a weak bond. Mechanism and regiochemistry The basic steps in any free-radical process (the radical chain mechanism) divide into: * Radical initiation: A radical is created from a non-radical precursor. * Chain propagation: A radical reacts with a non-radical to produce a new radical species * Chain termin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophilic Addition
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition (AN) reaction is an addition reaction where a chemical compound with an electrophilic double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile, such that the double or triple bond is broken. Nucleophilic additions differ from electrophilic additions in that the former reactions involve the group to which atoms are added accepting electron pairs, whereas the latter reactions involve the group donating electron pairs. Addition to carbon–heteroatom double bonds Nucleophilic addition reactions of nucleophiles with electrophilic double or triple bond (π bonds) create a new carbon center with two additional single, or σ, bonds.March Jerry; (1985). Advanced Organic Chemistry reactions, mechanisms and structure (3rd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, inc. Addition of a nucleophile to carbon–heteroatom double or triple bonds such as >C=O or -C≡N show great variety. These types of bonds are polar (have a large difference in electronegativit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |