|
Odontogenic Tumor
An odontogenic tumor is a neoplasm of the cells or tissues that initiate odontogenic processes. Examples include: * Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor * Ameloblastic fibroma * Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma * Ameloblastoma, a type of odontogenic tumor involving ameloblasts * Ameloblastic fibrosarcoma * Calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor * Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor * Cementoblastoma * Cementoma *Odontogenic keratocyst * Odontogenic carcinoma * Odontogenic myxoma * Odontoma An odontoma, also known as an odontome, is a benign tumour linked to tooth development. Specifically, it is a dental hamartoma, meaning that it is composed of normal dental tissue that has grown in an irregular way. It includes both odontogenic ... * Squamous odontogenic tumour References External links Anatomical pathology *Main {{neoplasm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Development (other)
{{Disambiguation ...
Tooth development may refer to: *Animal tooth development *Human tooth development Tooth development or odontogenesis is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth. For human teeth to have a healthy oral environment, all parts of the tooth must develop during appropriate sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor
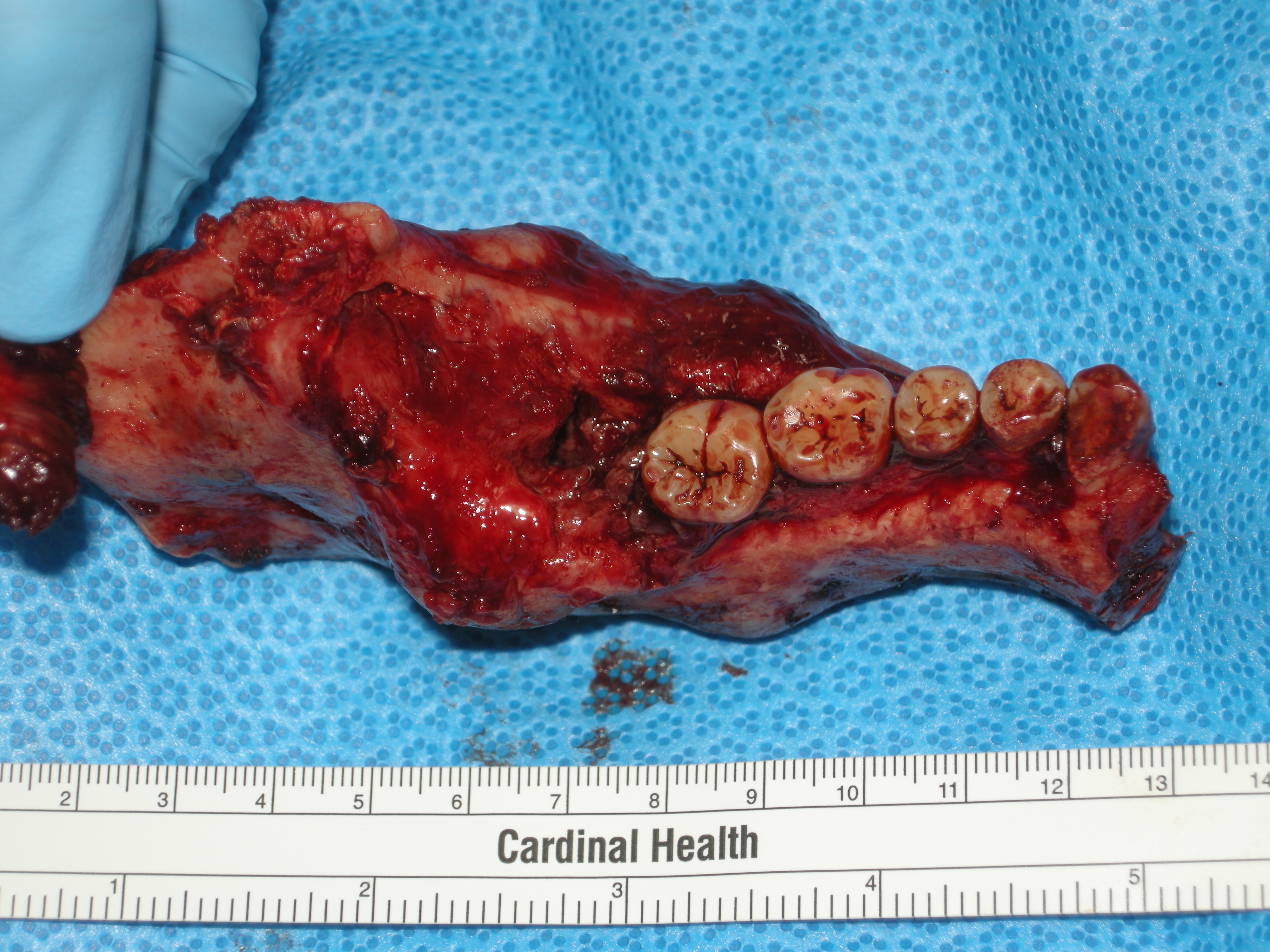
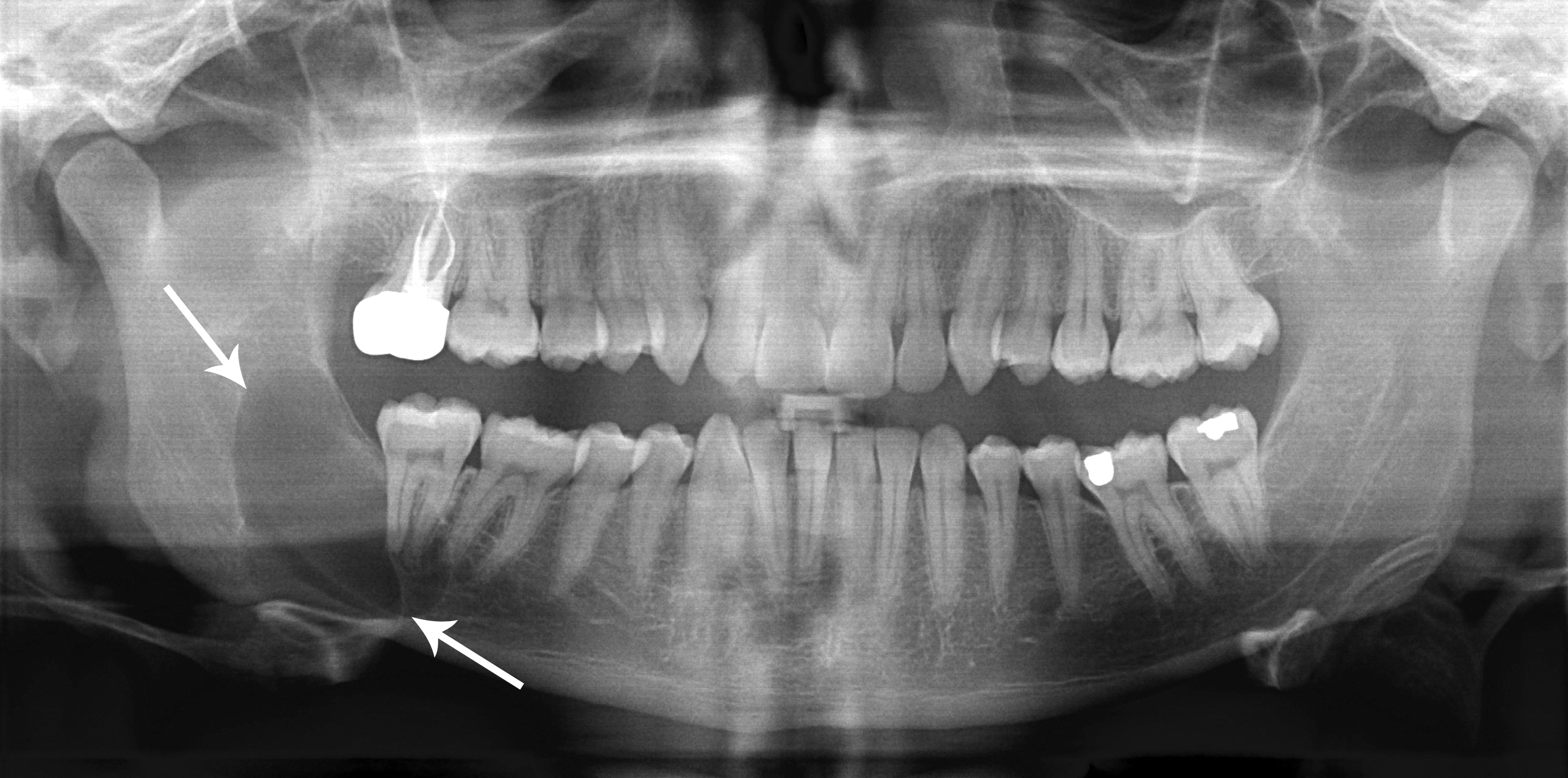
The adenomatoid odontogenic tumor is an odontogenic tumor arising from the enamel organ or dental lamina. Signs and symptoms Two thirds of cases are located in the anterior maxilla, and one third are present in the anterior mandible. Two thirds of the cases are associated with an impacted tooth (usually being the canine). Diagnosis On radiographs, the adenomatoid odontogenic tumor presents as a radiolucency (dark area) around an unerupted tooth extending past the cementoenamel junction. It should be differentially diagnosed from a dentigerous cyst and the main difference is that the radiolucency in case of AOT extends apically beyond the cementoenamel junction. Radiographs will exhibit faint flecks of radiopacities surrounded by a radiolucent zone. It is sometimes misdiagnosed as a cyst A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ameloblastic Fibroma
An ameloblastic fibroma is a fibroma of the ameloblastic tissue, that is, an odontogenic tumor arising from the enamel organ or dental lamina. It may be either truly neoplastic or merely hamartomatous (an odontoma). In neoplastic cases, it may be labeled an ameloblastic fibrosarcoma in accord with the terminological distinction that reserves the word ''fibroma'' for benign tumors and assigns the word ''fibrosarcoma'' to malignant ones. It is more common in the first and second decades of life, when odontogenesis is ongoing, than in later decades. In 50% of cases an unerupted tooth is involved. Histopathology alone is usually not enough to differentiate neoplastic cases from hamartomatous ones, because the histology is very similar. Other clinical and radiographic clues are used to narrow the diagnosis. Clinical Features Ameloblastic fibroma is a rare benign mixed epithelial and mesenchymal odontogenic tumour as it contributes to approximately 2% of all odontogenic tumours. It of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ameloblastic Fibro-odontoma
The ameloblastic fibro-odontoma (AFO) is essentially a benign tumor with the features characteristic of ameloblastic fibroma along with enamel and dentin (hard tissues). Though it is generally regarded as benign, there have been cases of its malignant transformation into ameloblastic fibrosarcoma and odontogenic sarcoma. Cahn LR and Blum T, believed in "maturation theory", which suggested that AFO was an intermediate stage and eventually developed during the period of tooth formation to a complex odontoma thus, being a hamartoma. World Health Organization (WHO) defines AFO as a neoplasm consisting of odontogenic ectomesenchyme resembling the dental papilla, epithelial strands and nest resembling dental lamina and enamel organ conjunction with the presence of dentine and enamel. There is a consensus that AFO should be grouped under Odontomas. This is because once the hard tissues start forming it will eventually lead to formation of Odontomas. The Recent WHO classification publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ameloblastoma
Ameloblastoma is a rare, benign or cancerous tumor of odontogenic epithelium ( ameloblasts, or outside portion, of the teeth during development) much more commonly appearing in the lower jaw than the upper jaw. It was recognized in 1827 by Cusack. This type of odontogenic neoplasm was designated as an '' adamantinoma'' in 1885 by the French physician Louis-Charles Malassez. It was finally renamed to the modern name ''ameloblastoma'' in 1930 by Ivey and Churchill. While these tumors are rarely malignant or metastatic (that is, they rarely spread to other parts of the body), and progress slowly, the resulting lesions can cause severe abnormalities of the face and jaw leading to severe disfiguration. Additionally, as abnormal cell growth easily infiltrates and destroys surrounding bony tissues, wide surgical excision is required to treat this disorder. If an aggressive tumor is left untreated, it can obstruct the nasal and oral airways making it impossible to breathe without oro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ameloblasts
Ameloblasts are cells present only during tooth development that deposit tooth enamel, which is the hard outermost layer of the tooth forming the surface of the crown. Structure Each ameloblast is a columnar cell approximately 4 micrometers in diameter, 40 micrometers in length and is hexagonal in cross section. The secretory end of the ameloblast ends in a six-sided pyramid-like projection known as the Tomes' process. The angulation of the Tomes' process is significant in the orientation of enamel rods, the basic unit of tooth enamel. Distal terminal bars are junctional complexes that separate the Tomes' processes from ameloblast proper. Development Ameloblasts are derived from oral epithelium tissue of ectodermal origin. Their differentiation from preameloblasts (whose origin is from inner enamel epithelium) is a result of signaling from the ectomesenchymal cells of the dental papilla. Initially the preameloblasts will differentiate into presecretory ameloblasts and then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst
Calcifying odontogenic cyst (COC) is a rare developmental lesion that comes from odontogenic epithelium. It is also known as a calcifying cystic odontogenic tumor, which is a proliferation of odontogenic epithelium and scattered nest of ghost cells and calcifications that may form the lining of a cyst, or present as a solid mass. It can appear in any location in the oral cavity, but more commonly affects the anterior (front) mandible and maxilla. It is most common in individuals in their 20s to 30s, but can be seen at almost any age, regardless of gender. On dental radiographs, the calcifying odontogenic cyst appears as a unilocular (one circle) radiolucency (dark area). In one-third of cases, an impacted tooth is involved. Histologically, cells that are described as " ghost cells", enlarged eosinophilic epithelial cells without nuclei, are present within the epithelial lining and may undergo calcification. Signs and symptoms Most calcifying odontogenic cysts appear asym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor
The calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor (CEOT), also known as a Pindborg tumor, is an odontogenic tumor first recognized by the Danish pathologist Jens Jørgen Pindborg in 1955. It was previously described as an ''adenoid adamantoblastoma'', ''unusual ameloblastoma'' and a ''cystic odontoma''. Like other odontogenic neoplasms, it is thought to arise from the epithelial element of the enamel origin. It is a typically benign and slow growing, but invasive neoplasm. Types Intraosseous tumors (tumors within the bone) are more common (94%) than extraosseous tumors (6%). It is more common in the posterior mandible of adults, typically in the fourth to fifth decades. There may be a painless swelling, and it is often concurrent with an impacted tooth. On radiographs, it appears as a radiolucency (dark area) and is known for sometimes having small radiopacities (white areas) within it. In those instances, it is described as having a "driven-snow" appearance. Microscopically, ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cementoblastoma
Cementoblastoma, or benign cementoblastoma, is a relatively rare benign neoplasm of the cementum of the teeth. It is derived from ectomesenchyme of odontogenic origin, with the formation of cementum-like tissue around the associated tooth root. Cementoblastomas represent less than 0.69–8% of all odontogenic tumors. The oldest case of cementoblastoma that has been verified dates back to 1888 by J. Metnitz. He described a lesion as a hard rounded mass associated with root resorption, periosteum coverage, rows of bone cells, and pulp chamber involvement. At the time, the lesion was diagnosed as an "odontoma", but later it was found that a diagnosis of cementoblastoma better matched the description. Diagnostic features Clinical Cementoblastoma usually occurs in people between the ages of 20 and 30, equally affecting males and females. It is more commonly found in the mandible compared to the maxilla (3.4:1), with 40% of cases being found in the first mandibular molar area and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cementoma
Cementoma is an odontogenic tumor of cementum. It is usually observed as a benign spherical mass of hard tissue fused to the root of a tooth. It is found most commonly in the mandible in the region of the lower molar teeth, occurring between the ages of 8 and 30 in both sexes with equal frequency . It causes distortion of surrounding areas but is usually a painless growth, at least initially. Considerable thickening of the cementum can often be observed. A periapical form is also recognized. Cementoma is not exclusive to the mandible as it can infrequently occur in the maxilla and other parts of the body such as the long bones. Signs & Symptoms Cementoma is characterized by a significant amount of thickening of the cementum around the roots of the teeth. The main teeth involved can include deciduous and permanent teeth, impacted molars and premolars. The growth is typically benign and painless. Although symptoms may not be noticeable, a dull pain and dentin hypersensitivity c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odontogenic Keratocyst
An odontogenic keratocyst is a rare and benign but locally aggressive developmental cyst. It most often affects the posterior human mandible, mandible and most commonly presents in the third decade of life. Odontogenic keratocysts make up around 19% of jaw cysts. Despite its more common appearance in the bone region, it can affect soft tissue. In the World Health Organization, WHO/International Agency for Research on Cancer, IARC classification of head and neck pathology, this clinical entity had been known for years as the odontogenic keratocyst; it was reclassified as keratocystic odontogenic tumour (KCOT) from 2005 to 2017. In 2017 it reverted to the earlier name, as the new WHO/IARC classification reclassified OKC back into the cystic category. Under The WHO/IARC classification, Odontogenic Keratocyst underwent the reclassification as it is no longer considered a neoplasm due to a lack of quality evidence regarding this hypothesis, especially with respect to clonality. Within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |