|
Odontogenic Cyst
Odontogenic cysts are a group of cysts of the jaws, jaw cysts that are formed from tissues involved in Human tooth development, odontogenesis (tooth development). Odontogenic cysts are closed sacs, and have a distinct biological membrane, membrane derived from the rest of odontogenic epithelium. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. Intra-bony cysts are most common in the jaws, because the human mandible, mandible and maxilla are the only bones with epithelial components. That odontogenic epithelium is critical in normal tooth development. However, epithelial rests may be the origin for the cyst lining later. Not all oral cysts are odontogenic cysts. For example, mucous cyst of the oral mucosa and nasolabial duct cyst are not of odontogenic origin. In addition, there are several conditions with so-called (x-ray, radiographic) 'pseudocystic appearance' in jaws; ranging from anatomic variants such as Stafne static bone cyst, to the aggressive aneurysmal bone cyst. Cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysts Of The Jaws
Cysts of the jaws are cysts—pathological epithelium, epithelial-lined cavities filled with fluid or soft material—occurring on the bones of the jaws, the human mandible, mandible and maxilla. Those are the bones with the highest prevalence of cysts in the human body, due to the abundant amount of epithelial remnants that can be left in the bones of the jaws. The Tooth enamel, enamel of teeth is formed from ectoderm (the precursor germ layer to skin and mucosa), and so remnants of epithelium can be left in the bone during Human tooth development, odontogenesis (tooth development). The bones of the jaws develop from embryology, embryologic processes which fuse, and ectodermal tissue may be trapped along the lines of this fusion. This "resting" epithelium (also termed cell rests) is usually dormant or undergoes atrophy, but, when stimulated, may form a cyst. The reasons why resting epithelium may proliferate and undergo cystic transformation are generally unknown, but inflammatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Periodontal Cyst
“Lateral periodontal cysts (LPCs) are defined as non-keratinised and non-inflammatory developmental cysts located adjacent or lateral to the root of a vital tooth.” LPCs are a rare form of jaw cysts, with the same histopathological characteristics as gingival cysts of adults (GCA). Hence LPCs are regarded as the intraosseous form of the extraosseous GCA. They are commonly found along the lateral periodontium or within the bone between the roots of vital teeth, around mandibular canines and premolars. Standish and Shafer reported the first well-documented case of LPCs in 1958, followed by Holder and Kunkel in the same year although it was called a periodontal cyst. Since then, there has been more than 270 well-documented cases of LPCs in literature. Signs and symptoms Observable clinical signs of a LPC include a small, soft-tissue swelling found just below or within the interdental papilla. However, as it is usually asymptomatic in nature, LPCs are usually detected throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Hygroma
A cystic hygroma is a form of lymphatic malformation. It is an abnormal growth that usually appears on a baby's neck or head. It consists of one or more cysts and tends to grow larger over time. The disorder usually develops while the fetus is still in the uterus, but can also appear after birth. Also known as cystic lymphangioma and macrocystic lymphatic malformation, the growth is often a congenital lymphatic lesion of many small cavities (multiloculated) that can arise anywhere, but is classically found in the left posterior triangle of the neck and armpits. The malformation contains large cyst-like cavities containing lymph, a watery fluid that circulates throughout the lymphatic system. Microscopically, cystic hygroma consists of multiple locules filled with lymph. Deep locules are quite big, but they decrease in size towards the surface. Cystic hygromas are benign, but can be disfiguring. It is a condition which usually affects children; very rarely it can be present in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroglossal Cyst
A thyroglossal cyst or thyroglossal duct cyst is a fibrous cyst that forms from a persistent thyroglossal duct. Thyroglossal cysts can be defined as an irregular neck mass or a lump which develops from cells and tissues left over after the formation of the thyroid gland during developmental stages.University of Rochester Medical Center. (2015). Thyroglossal duct cyst. Retrieved from http://www.urmc.rochester.edu Thyroglossal cysts are the most common cause of midline neck masses and are generally located caudal to (below) the hyoid bone. These neck masses can occur anywhere along the path of the thyroglossal duct, from the base of the tongue to the suprasternal notch. Other common causes of midline neck masses include lymphadenopathy, dermoid cysts, and various odontogenic anomalies. Thyroglossal cysts develop at birth. Many diagnostic procedures may be used to establish the degree of the cyst. Signs and symptoms Thyroglossal duct cysts most often present with a palpable asympt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branchial Cyst
Branchial may refer to: * Branchial apparatus, an embryological structure. * Branchial arch a series of bony "loops" present in fish, which support the gills. * Branchial artery, also known as aortic arches. * Branchial cleft * Branchial cleft cyst, failure of obliteration of the second branchial cleft in embryonic development. * Branchial efferent, also known as special visceral efferent. * Branchial heart Branchial hearts are accessory pumps that supplement the action of the systemic heart in a cephalopod's body. They are myogenic in nature. Branchial hearts are always in pairs located at the base of the gills. Each branchial heart consists of a ... * Branchial membrane * Branchial plexus * Branchial pouches, also known as pharyngeal pouches. * First and second branchial arch syndrome, also known as hemifacial microsomia. * Ultimo-branchial bodies, also known as ultimopharyngeal body. {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
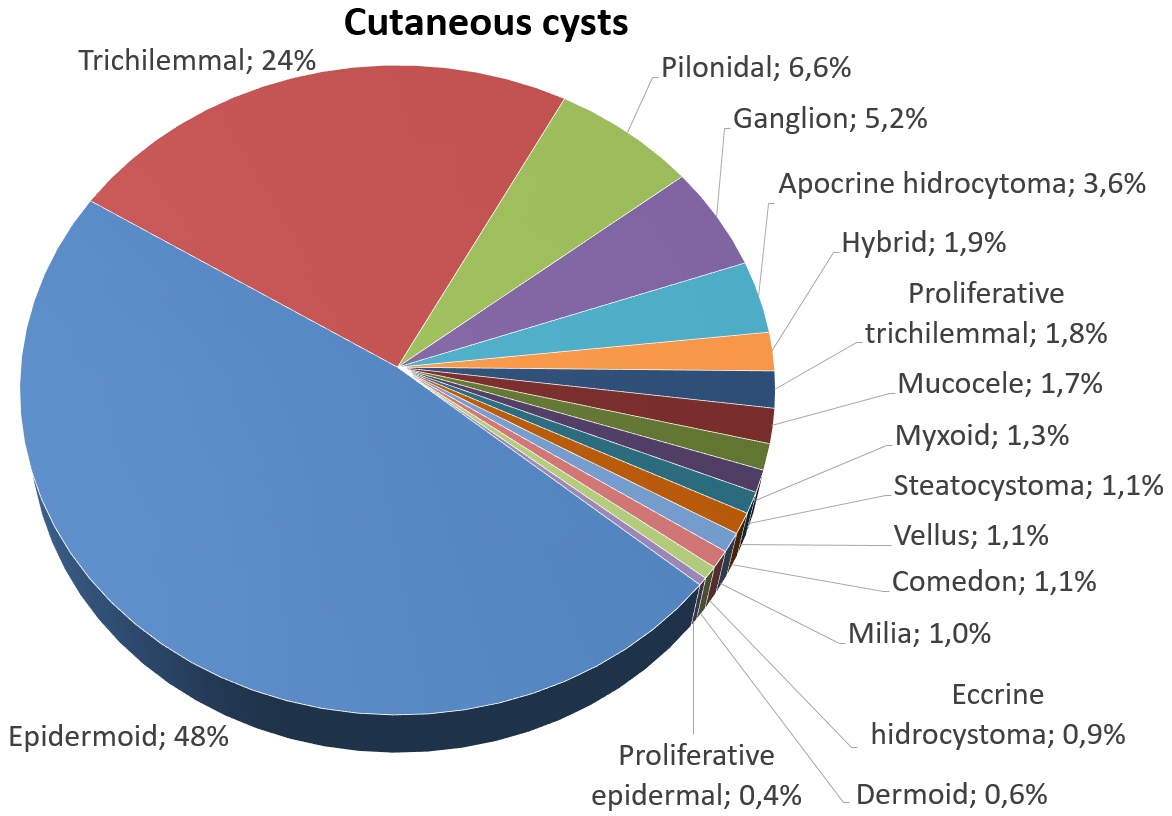
Epidermoid Cyst
An epidermoid cyst or epidermal inclusion cyst is a benign cyst usually found on the skin. The cyst develops out of ectodermal tissue. Histologically, it is made of a thin layer of squamous epithelium. Signs and symptoms The epidermoid cyst may have no symptoms, or it may be painful when touched. It can release macerated keratin. In contrast to pilar cysts, epidermoid cysts are usually present on parts of the body with relatively little hair. Some vaginal cysts are epidermoid cysts. Although they are not malignant, there are rare cases of malignant tumors arising from an epidermoid cyst. Epidermal inclusion cysts account for approximately 85–95% of all excised cysts; malignant transformation is exceedingly rare. The incidence of squamous cell carcinoma developing from an epidermal inclusion cyst has been estimated to range from 0.011 to 0.045%. Diagnosis Epidermoid cysts are usually diagnosed when a person notices a bump on their skin and seeks medical attention. The definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermoid Cyst
A dermoid cyst is a teratoma of a cystic nature that contains an array of developmentally mature, solid tissues. It frequently consists of skin, hair follicles, and sweat glands, while other commonly found components include clumps of long hair, pockets of sebum, blood, fat, bone, nail, teeth, eyes, cartilage, and thyroid tissue. As dermoid cysts grow slowly and contain mature tissue, this type of cystic teratoma is nearly always benign. In those rare cases wherein the dermoid cyst is malignant, a squamous cell carcinoma usually develops in adults, while infants and children usually present with an endodermal sinus tumor.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . Location Due to its classification, a dermoid cyst can occur wherever a teratoma can occur. Vaginal and ovarian dermoid cysts Ovaries normally grow cyst-like structures called follicles each month. Once an egg is released from its follicle during ovulation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Mucocele
Oral mucocele (also mucous extravasation cyst, mucous cyst of the oral mucosa, and mucous retention and extravasation phenomena) is a condition caused by two related phenomena - mucus extravasation phenomenon and mucous retention cyst. Mucous extravasation phenomenon is a swelling of connective tissue consisting of a collection of fluid called mucus. This occurs because of a ruptured salivary gland duct usually caused by local trauma (damage) in the case of mucous extravasation phenomenon and an obstructed or ruptured salivary duct in the case of a mucus retention cyst. The mucocele has a bluish, translucent color, and is more commonly found in children and young adults. Although these lesions are often called cysts, mucoceles are not true cysts because they have no epithelial lining. Rather, they are polyps. Signs and symptoms The size of oral mucoceles vary from 1 mm to several centimeters and they usually are slightly transparent with a blue tinge. On palpation, mucoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
Aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) is a non-cancerous bone tumor composed of multiple varying sizes of spaces in a bone which are filled with blood. The term is a misnomer, as the lesion is neither an aneurysm nor a cyst. It generally presents with pain and swelling in the affected bone. Pressure on neighbouring tissues may cause compression effects such as neurological symptoms. The cause is unknown. Diagnosis involves medical imaging. CT scan and X-ray show lytic expansion lesions with clear borders. MRI reveals fluid levels. Treatment is usually by curettage, bone grafting or surgically removing the part of bone. 20–30% may recur, usually in the first couple of years after treatment, particularly in children. It is rare. The incidence is around 0.15 cases per one million per year. Aneurysmal bone cyst was first described by Jaffe and Lichtenstein in 1942. Signs and symptoms The afflicted may have relatively small amounts of pain that will quickly increase in severity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periapical Cyst
Commonly known as a dental cyst, the periapical cyst is the most common odontogenic cyst. It may develop rapidly from a periapical granuloma, as a consequence of untreated chronic periapical periodontitis. Periapical is defined as "the tissues surrounding the apex of the root of a tooth" and a cyst is "a pathological cavity lined by epithelium, having fluid or gaseous content that is not created by the accumulation of pus." Most frequently located in the maxillary anterior region, the cyst is caused by pulpal necrosis secondary to dental caries or trauma. Its lining is derived from the epithelial cell rests of Malassez which proliferate to form the cyst. Such cysts are very common. Although initially asymptomatic, they are clinically significant because secondary infection can cause pain and damage. In radiographs, the cyst appears as a radiolucency (dark area) around the apex of a tooth's root. Signs and symptoms Periapical cysts begin as asymptomatic and progress slowly. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasolabial Cyst
This nasolabial cyst, also known as a nasoalveolar cyst, is located superficially in the soft tissues of the upper lip. Unlike most of the other developmental cysts, the nasolabial cyst is an example of an extraosseous cyst, one that occurs outside of bone. It will therefore not show up on a radiograph Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiography and "therapeu ..., or an X-ray film. References External links {{Developmental Cysts Cysts of the oral and maxillofacial region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasopalatine Duct Cyst
The nasopalatine duct cyst (NPDC) occurs in the median of the palate, usually anterior to first molars. It often appears between the roots of the maxillary central incisors. Radiographically, it may often appear as a heart-shaped radiolucency. It is usually asymptomatic, but may sometimes produce an elevation in the anterior portion of the palate. It was first described by Meyer in 1914. The median palatal cyst has recently been identified as a possible posterior version of the nasopalatine duct cyst. Signs and symptoms Nasopalatine duct cysts usually present as asymptomatic palatal swellings, but they may rarely be accompanied by pain and/or purulent discharge. Cause and diagnosis Historically, the cause of nasopalatine duct cysts has been somewhat of an enigma. Although it was originally postulated that the cyst formed from trapped epithelial cells during embryonic fusion of the palatal bones, it is now thought that it forms from oronasal ducts present within the incis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |