Epidermoid cyst on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An epidermoid cyst or epidermal inclusion cyst is a
An epidermoid cyst or epidermal inclusion cyst is a
File:Epidermal Inclusion Cyst.jpg, Epidermal inclusion cyst on the nape of a person's neck
File:Epidermal Cyst ear.JPG, Epidermal cyst in the
File:CT scan of epidermoid cyst.jpg, CT scan, showing a homogenous hypodense volume (unspecific
 An epidermoid cyst or epidermal inclusion cyst is a
An epidermoid cyst or epidermal inclusion cyst is a benign
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubb ...
usually found on the skin. The cyst develops out of ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the o ...
al tissue. Histologically
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at large ...
, it is made of a thin layer of squamous epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
.
Signs and symptoms
The epidermoid cyst may have no symptoms, or it may be painful when touched. It can release maceratedkeratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, feathers, horn (anatomy), horns, claws, Hoof, hoove ...
. In contrast to pilar cyst
A trichilemmal cyst (or pilar cyst) is a common cyst that forms from a hair follicle, most often on the scalp, and is smooth, mobile, and filled with keratin, a protein component found in hair, nail (anatomy), nails, skin, and horn (anatomy), ho ...
s, epidermoid cysts are usually present on parts of the body with relatively little hair. Some vaginal cysts are epidermoid cysts.
Although they are not malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous benign tumor, ''benign'' tumor in that a malig ...
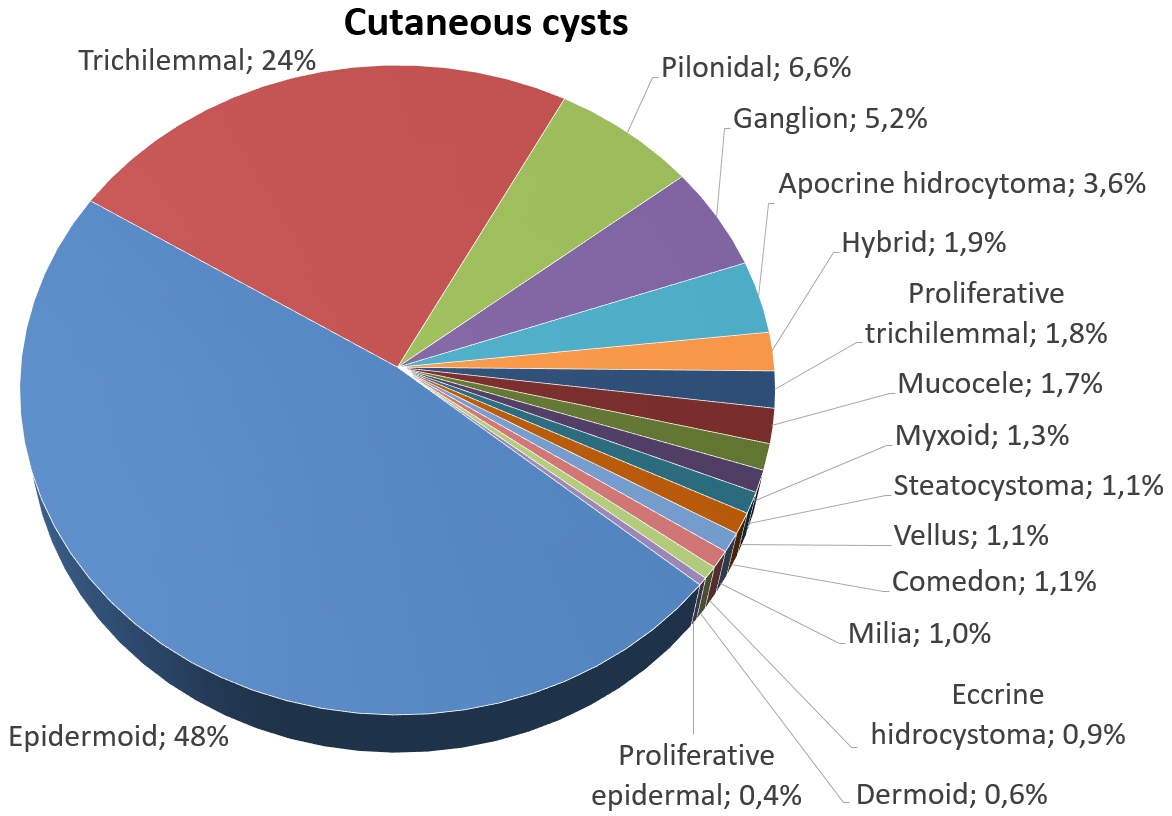
, there are rare cases of malignant tumors arising from an epidermoid cyst. Epidermal inclusion cysts account for approximately 85–95% of all excised cysts; malignant transformation is exceedingly rare. The incidence of squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC), also known as epidermoid carcinoma, comprises a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the ...
developing from an epidermal inclusion cyst has been estimated to range from 0.011 to 0.045%.
Diagnosis
Epidermoid cysts are usually diagnosed when a person notices a bump on their skin and seeks medical attention. The definitive diagnosis is made after excision by apathologist
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatme ...
based on microscopic
The microscopic scale () is the scale of objects and events smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye, requiring a lens or microscope to see them clearly. In physics, the microscopic scale is sometimes regarded as the scale betwe ...
appearance of a cystic lesion lined by cornified epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
containing lamellated keratin without calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature M ...
s. They can also be seen as isointense lesions on MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
or hyperintensities on FLAIR.
Treatment
Cysts can be removed by excision. In case of fronto-ethmoidal epidermoid cysts, surgical resection appears to be the mainstay of treatment; however, the extent of resection is dictated by adherence of the tumor capsule to the surrounding vital structures.Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
gel (H2O2) was previously recommended for cyst treatment, particularly those on body piercings. However the gel cannot adequately permeate the cyst and was not found to be effective. Hydrogen peroxide is no longer recommended for wound care by doctors as it can damage the healing tissues.
On body piercings, self treatment with a hot saline soak to help drain the cyst and the use of an antibacterial or medicated talcum powder
Talc, or talcum, is a clay mineral composed of hydrated magnesium silicate, with the chemical formula . Talc in powdered form, often combined with corn starch, is used as baby powder. This mineral is used as a thickening agent and lubricant. ...
to help dry out the bump and reduce bacterial proliferation is generally recommended until medical advice can be obtained. (Use of talc is no longer recommended due to recently discovered associations with multiple cancers.) Piercings, however, are more likely to be victims of hypertrophic scar
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It is distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number. Although hypertr ...
ring than a cyst. Cheek piercings seem to be the piercing most prone to cysts due to the possible interruption of saliva ducts.
Terminology
Several synonyms exist for epidermoid cysts, including epidermal cyst, infundibular cyst, keratin cyst and epidermal inclusion cystFreedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. .James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . ''Epidermal inclusion cyst'' more specifically refers to implantation of epidermal elements into thedermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (skin), epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis (anatomy), cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from s ...
. The term ''infundibular cyst'' refers to the site of origin of the cyst: the infundibular portion of the hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction betwee ...
. The majority of epidermal inclusion cysts originate from the infundibular portion of the hair follicle, thus explaining the interchangeable, yet inaccurate, use of these two terms.
Epidermoid cyst may be classified as a sebaceous cyst
A sebaceous cyst is a term commonly used to refer to either:
* Epidermoid cysts (also termed epidermal cysts, infundibular cyst)
* Pilar cysts (also termed trichelemmal cysts, isthmus-catagen cysts)
Both of the above types of cysts contain ...
, although technically speaking it is not sebaceous. "True" sebaceous cysts, cysts which originate from sebaceous gland
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in ...
s and which contain sebum, are relatively rare and are known as steatocystoma simplex or, if multiple, as steatocystoma multiplex
Steatocystoma multiplex is a benign, autosomal dominant congenital condition resulting in multiple cysts on a person's body. Steatocystoma simplex is the solitary counterpart to steatocystoma multiplex.
In steatocystoma multiplex, the tendency to ...
. Medical professionals have suggested that the term ''sebaceous cyst'' be avoided since it can be misleading. In practice, however, the term is still often used for epidermoid and pilar cysts.Additional images
earlobe
The human earlobe (''lobulus auriculae''), the lower portion of the outer ear, is composed of tough areolar and adipose connective tissues, lacking the firmness and elasticity of the rest of the auricle (the external structure of the ear). In ...
cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubb ...
-like)
File:Epidermoid cyst testicle.jpg, Epidermoid cyst in a testicle on ultrasound, with lamellated ("onion skin") appearance
File:Epidermoid cyst macro.jpg, Macroscopic appearance of a resected (surgically removed) intracranial cyst, with pearl appearance
File:Surgery of suprasternal epidermoid cyst.jpg, Surgery of a suprasternal epidermoid cyst, showing a smooth surface
File:Histopathology of epidermoid cyst.jpg, Histopathology, showing a keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium, and a lumen containing keratin flakes
File:Dermoid cyst intracranial.jpg, Histopathology showing epithelium and lamellated keratin (left)
See also
* Intracranial epidermoid cyst * List of cutaneous neoplasms associated with systemic syndromes * Proliferating epidermoid cyst * Verrucous cystReferences
External links
* {{Disorders of skin appendages Epidermal nevi, neoplasms, and cysts Conditions of the skin appendages