|
Octoechos
Oktōēchos (here transcribed "Octoechos"; Greek: ;The feminine form exists as well, but means the book octoechos. from ὀκτώ "eight" and ἦχος "sound, mode" called echos; Slavonic: Осмогласие, ''Osmoglasie'' from о́смь "eight" and гласъ, Glagolitic: , "voice, sound") is the eight-mode system used for the composition of religious chant in Byzantine, Syriac, Armenian, Georgian, Latin and Slavic churches since the Middle Ages. In a modified form the octoechos is still regarded as the foundation of the tradition of monodic chant in the Byzantine Rite today. Nomenclature The names ascribed to the eight tones differ in translations into Church Slavonic. The Slavonic system counted the plagioi echoi as glasa 5, 6, 7, and 8. For reference, these differences are shown here together with the Ancient Greek names of the octave species according to the Hagiopolites (see Hagiopolitan Octoechos Oktōēchos (here transcribed ""; Greek language, Greek: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octoechos (liturgy)
The book Octoechos (from the Greek language, Greek: ; from wikt:οκτώ, ὀκτώ 'eight' and wikt:ἦχος, ἦχος 'sound, mode' called echos; , from wikt:осмь, о́смь 'eight' and wikt:гласъ, гласъ 'voice, sound') is a liturgical book containing a repertoire of hymns ordered in eight parts according to eight echoi (Musical mode, tones or modes). Originally created in the Monastery of Stoudios during the 9th century as a hymnal complete with musical notation, it is still used in many Christian liturgy, rites of Eastern Christianity. The book with similar function in the Western Christianity, Western Church is the tonary, and both contain the melodic models of an Hagiopolitan Octoechos, octoechos system; however, while the tonary serves simply for a modal classification, the octoechos is organized as a cycle of eight weeks of services. The word itself can also refer to the repertoire of hymns sung during the celebrations of the Liturgy of the Hours, Sunda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
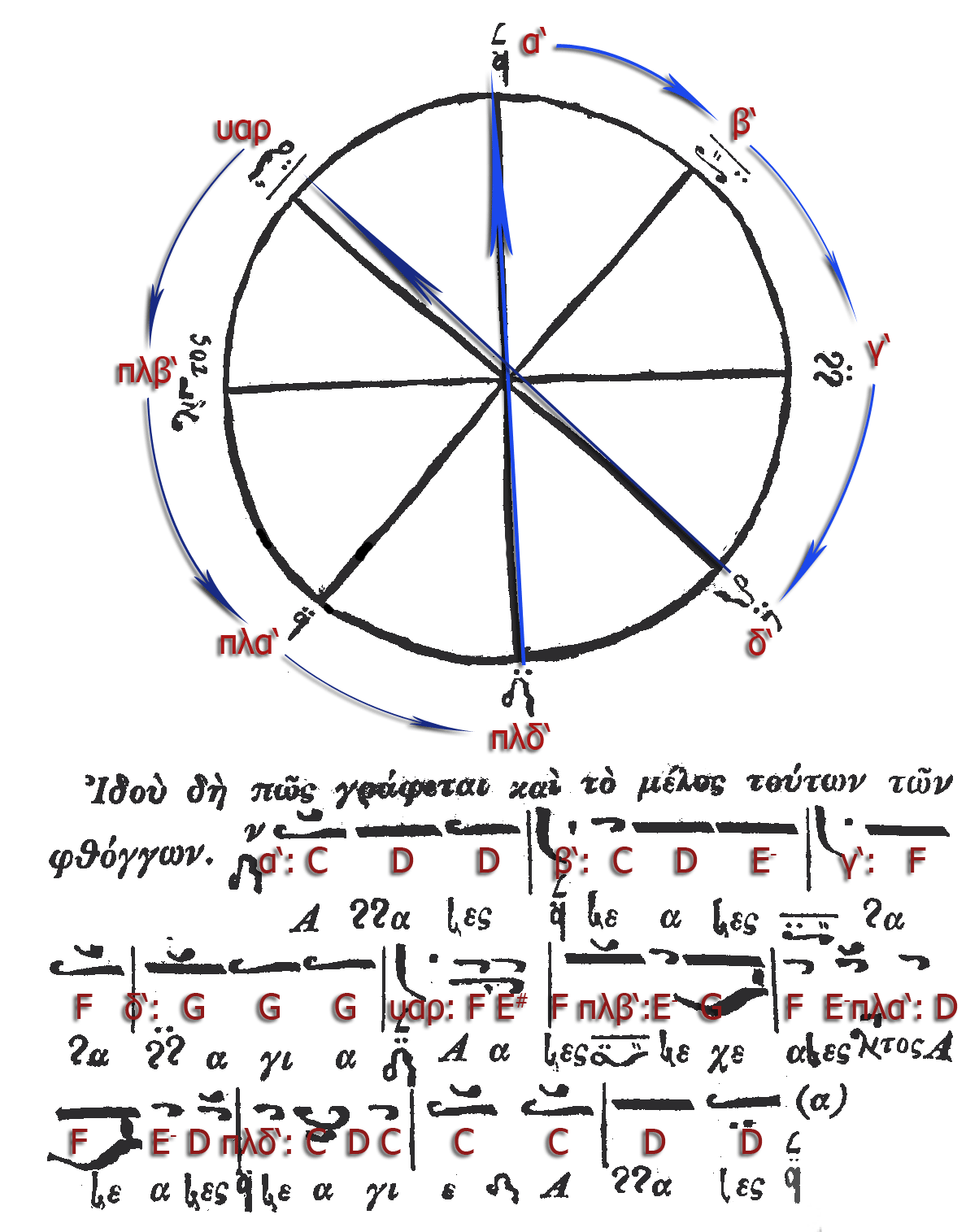
Neobyzantine Octoechos
Oktōēchos (here transcribed "Octoechos"; Greek language, Greek: ; from wikt:ὀκτώ, ὀκτώ "eight" and wikt:ἦχος, ἦχος "sound, mode" called echos; Church Slavonic, Slavonic: Осмогласие, ''Osmoglasie'' from wikt:осмь, о́смь "eight" and wikt:гласъ, гласъ "voice, sound") is the name of the eight musical mode, mode system used for the composition of religious chant in Byzantine, Syriac, Armenian, Georgian, Latin and Slavic churches since the Middle Ages. In a modified form the octoechos is still regarded as the foundation of the tradition of monodic Orthodox chant today. From a Phanariotes, Phanariot point of view, the re-formulation of the Octoechos and its melodic models according to the New Method was neither a simplification of the Byzantine tradition nor an adaption to Western tonality and its method of an heptaphonic solfeggio, just based on one tone system (σύστημα κατὰ ἑπταφωνίαν). Quite the opposite, as a u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papadic Octoechos
Oktōēchos (here transcribed "Octoechos"; Greek language, Greek: , pronounced in Byzantine Greek, Constantinopolitan: ; from wikt:ὀκτώ, ὀκτώ "eight" and wikt:ἦχος, ἦχος "sound, mode" called echos; Church Slavonic, Slavonic: Осмогласие, ''Osmoglasie'' from wikt:осмь, о́смь "eight" and wikt:гласъ, гласъ "voice, sound") is the name of the eight musical mode, mode system used for the composition of religious chant in Byzantine, Syriac, Armenian, Georgian, Latin and Slavic churches since the Middle Ages. In a modified form the octoechos is still regarded as the foundation of the tradition of monodic Orthodox chant today. Until 1204 neither the Hagia Sophia nor any other cathedral of the Byzantine Empire did abandon its habits, and the Hagiopolitan Octoechos, Hagiopolitan eight mode system came into use not earlier than in the mixed rite of Constantinople, after the patriarchate and the court had returned from their exile in Nikaia in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonary
A tonary is a liturgical book in the Western Christian Church which lists by incipit various items of Gregorian chant according to the Gregorian mode (''tonus'') of their melodies within the eight-mode system. Tonaries often include Office antiphons, the mode of which determines the recitation formula for the accompanying text (the psalm tone if the antiphon is sung with a psalm, or canticle tone if the antiphon is sung with a canticle), but a tonary may also or instead list responsories or Mass chants not associated with formulaic recitation. Although some tonaries are stand-alone works, they were frequently used as an appendix to other liturgical books such as antiphonaries, graduals, tropers, and prosers, and are often included in collections of musical treatises. Function and form Tonaries were particularly important as part of the written transmission of plainchant, although they already changed the oral chant transmission of Frankish cantors entirely before musical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echos
Echos (Greek: "sound", pl. echoi ; Old Church Slavonic: "voice, sound") is the name in Byzantine music theory for a mode within the eight-mode system ( oktoechos), each of them ruling several melody types, and it is used in the melodic and rhythmic composition of Byzantine chant ("thesis of the melos"), differentiated according to the chant genre and according to the performance style ("method of the thesis"). It is akin to a Western medieval tonus, an Andalusian tab', an Arab naġam (since 1400 " maqam"), or a Persian parde (since 18th-century dastgah). Overview and semantics The noun ''echos'' in Greek means "sound" in general. It acquired the specialized meaning of ''mode'' early on in the development of Byzantine music theory since the Octoechos reform in 692. In general, the concept of echos denotes a certain octave species, its intervallic structure as well as a set of more or less explicitly formulated melodic rules and formulae that represent a certain category ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagiopolitan Octoechos
Oktōēchos (here transcribed ""; Greek language, Greek: pronounced in Koine Greek, koine: ; from wikt:ὀκτώ, ὀκτώ "eight" and wikt:ἦχος, ἦχος "sound, mode" called ; Church Slavonic, Slavonic: , from wikt:осмь, о́смь "eight" and wikt:гласъ, гласъ "voice, sound") is the name of the eight musical mode, mode system used for the composition of religious chant in most Christian churches during the Middle Ages. In a modified form, the octoechos is still regarded as the foundation of the tradition of monodic Orthodox chant today (Neobyzantine Octoechos). The octoechos as a liturgical concept which established an organization of the calendar into eight-week cycles, was the invention of monastic hymnographers at Mar Saba in Palestine, at the Patriarchates of Antiochia and of Constantinople. It was officially announced as the modal system of hymnography at the Quinisext Council in 692. A similar eight-mode system was established in Western Europe du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Rite
The Byzantine Rite, also known as the Greek Rite or the Rite of Constantinople, is a liturgical rite that is identified with the wide range of cultural, devotional, and canonical practices that developed in the Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian church of Constantinople. The canonical hours are extended and complex, lasting about eight hours (longer during Great Lent) but are abridged outside of large Monastery, monasteries. An iconostasis, a partition covered with icons, separates Sanctuary#Sanctuary as area around the altar, the area around the altar from the nave. The Sign of the cross#Eastern Orthodoxy, sign of the cross, accompanied by bowing, is made very frequently, e.g., more than a hundred times during the Divine Liturgy#Byzantine Rite, divine liturgy, and there is prominent veneration of icons, a general acceptance of the congregants freely moving within the church and interacting with each other, and distinctive traditions of liturgical chanting. Some traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Koukouzeles
John Koukouzeles Papadopoulos () was a Byzantine composer, singer and reformer of Byzantine chant. He was recognized as a saint by the Eastern Orthodox Church after his death. Among the most illustrious musicians of the Palaiologos dynasty, his music remains held in high esteem by Albanians, Bulgarians, Greeks, Macedonians, Romanians and Serbs. Name and etymology The name "Koukouzeles" was not the composer's surname. His real surname was Papadopoulos.Γρηγόριος, Στάθης (1986)''Ο μαΐστωρ Ιωάννης Παπαδόπουλος Κουκουζέλης. Η ζωή και το έργο του'' 'The magister John Papadopoulos Koukouzelis: His life and works'' Αθήνα: Περιοδικό Εφημεριος. pp. 1–38 "Koukouzeles" is allegedly derived from the Greek word for broad beans (κουκιά, ''koukia'') and a Slavic/Bulgarian word for cabbage (зеле, ''zele''). Allegedly, the name appeared when Koukouzeles was asked in school about the food he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Damascus
John of Damascus or John Damascene, born Yūḥana ibn Manṣūr ibn Sarjūn, was an Arab Christian monk, priest, hymnographer, and apologist. He was born and raised in Damascus or AD 676; the precise date and place of his death is not known, though tradition places it at his monastery, Mar Saba, near Jerusalem, on 4 December AD 749. A polymath whose fields of interest and contribution included law, theology, philosophy, and music, he was given the by-name of Chrysorroas (Χρυσορρόας, literally "streaming with gold", i.e. "the golden speaker"). He wrote works expounding the Christian faith, and composed hymns which are still used both liturgically in Eastern Christian practice throughout the world as well as in western Lutheranism at Easter.''Lutheran Service Book'' (Concordia Publishing House, St. Louis, 2006), pp. 478, 487. He is one of the Fathers of the Eastern Orthodox Church and is best known for his strong defence of icons. The Catholic Church regards him as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysanthos Of Madytos
Chrysanthos of Madytos (; 1846) was a Greek poet, chanter, Archimandrite, and Archbishop, born in Madytos. In preparation of the first printed books of Orthodox chant, he was responsible for a reform of the Byzantine notation within the New Music School of the Patriarchate, along with Gregorios the Protopsaltes and Chourmouzios the Archivist who transcribed the traditional repertory into the Chrysanthine notation. Life Chrysanthos and the reform of Orthodox chant Works * * *. Publications made in his name * * Translations * * See also * Neobyzantine Octoechos— Byzantine music *Ottoman classical music Ottoman music () or Turkish classical music (, or more recently ) is the tradition of Art music, classical music originating in the Ottoman Empire. Developed in the palace, major Ottoman cities, and Sufi lodges, it traditionally features a sol ... Notes and references Sources * * * External links * Chrysanthos of Madytos Entry at Orthodox Wiki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glagolitic
The Glagolitic script ( , , ''glagolitsa'') is the oldest known Slavic alphabet. It is generally agreed that it was created in the 9th century for the purpose of translating liturgical texts into Old Church Slavonic by Saints Cyril and Methodius, Saint Cyril, a monk from Thessaloniki, Thessalonica. He and his brother Saint Methodius of Thessaloniki, Saint Methodius were sent by the Byzantine Emperor Michael III in 863 to Great Moravia after an invitation from Rastislav of Moravia to spread Christianity there. After the deaths of Cyril and Methodius, their disciples were expelled and they moved to the First Bulgarian Empire instead. The Early Cyrillic alphabet, which developed gradually in the Preslav Literary School by Greek alphabet scribes who incorporated some Glagolitic letters, gradually replaced Glagolitic in that region. Glagolitic remained in use alongside Latin in the Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), Kingdom of Croatia and alongside Cyrillic until the 14th century in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |