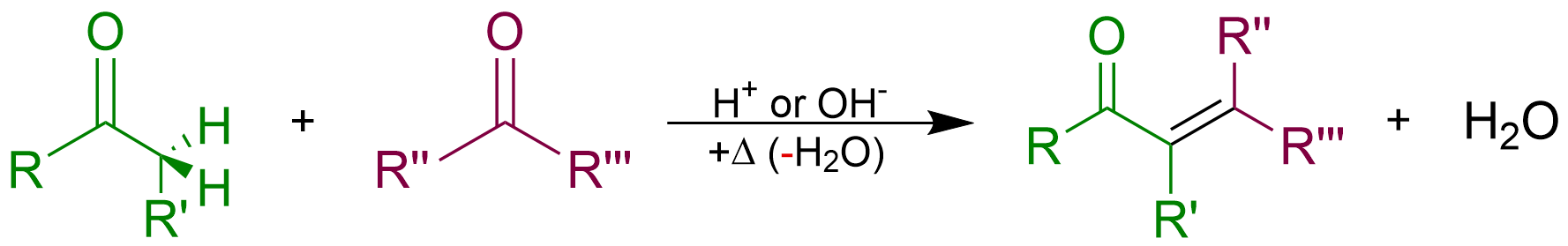|
O-Phenylenediamine
''o''-Phenylenediamine (OPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. This aromatic diamine is an important precursor to many heterocyclic compounds. OPD is a white compound although samples appear darker owing to oxidation by air. It is isomeric with ''m''-phenylenediamine and ''p''-phenylenediamine. Preparation Commonly, 2-nitrochlorobenzene is treated with ammonia to generate 2-nitroaniline, whose nitro group is then reduced: :ClC6H4NO2 + 2 NH3 → H2NC6H4NO2 + NH4Cl :H2NC6H4NO2 + 3 H2 → H2NC6H4NH2 + 2 H2O In the laboratory, the reduction of the nitroaniline is effected with zinc powder in ethanol, followed by purification of the diamine as the hydrochloride salt. Darkened impure samples can be purified by treatment of its aqueous solution with sodium dithionite and activated carbon. Reactions and uses ''o''-Phenylenediamine condenses with ketones and aldehydes to give rise to various valuable products. Its reactions with formic acids to produce benz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiophanate-methyl
Thiophanate-methyl is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NHC(S)NH(CO)OCH3)2. The compound is a colorless or white solid, although commercial samples are generally tan-colored. It is prepared from ''o''-phenylenediamine. It is a widely used fungicide used on tree, vine, and root crops. In Europe it is applied to tomato, wine grapes, beans, wheat, and aubergine. Methods for its analysis have received considerable attention. It is commonly used to treat botrytis bunch rot and gray mold caused by ''Botrytis cinerea'' strawberry in California. Thiophanate-methyl acts as a fungicide via its primary metabolite carbendazim Carbendazim is a fungicide, a member benzimidazole fungicides. It is a metabolite of benomyl. The fungicide is used to control plant diseases in cereals and fruits, including citrus, bananas, strawberries, macadamia nuts, pineapples, and pomes. .... References {{reflist Fungicides Thioureas Carbamates Methyl esters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRC Press
The CRC Press, LLC is an American publishing group that specializes in producing technical books. Many of their books relate to engineering, science and mathematics. Their scope also includes books on business, forensics and information technology. CRC Press is now a division of Taylor & Francis, itself a subsidiary of Informa. History The CRC Press was founded as the Chemical Rubber Company (CRC) in 1903 by brothers Arthur, Leo and Emanuel Friedman in Cleveland, Ohio, based on an earlier enterprise by Arthur, who had begun selling rubber laboratory aprons in 1900. The company gradually expanded to include sales of laboratory equipment to chemist A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a graduated scientist trained in the study of chemistry, or an officially enrolled student in the field. Chemists study the composition of ...s. In 1913 the CRC offered a short (116-page) manual called the ''Rubber Handboo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinoxaline
A quinoxaline, also called a benzopyrazine, in organic chemistry, is a heterocyclic compound containing a ring complex made up of a benzene ring and a pyrazine ring. It is isomeric with other naphthyridines including quinazoline, phthalazine and cinnoline. It is a colorless oil that melts just above room temperature. Although quinoxaline itself is mainly of academic interest, quinoxaline derivatives are used as dyes, pharmaceuticals (such as varenicline), and antibiotics such as olaquindox, carbadox, echinomycin, levomycin and actinoleutin. Synthesis They can be formed by condensation reaction, condensing ''ortho''-amine, diamines with 1,2-ketone, diketones. The parent substance of the group, quinoxaline, results when glyoxal is condensed with o-Phenylenediamine, 1,2-diaminobenzene. Substituted derivatives arise when α-ketonic acids, α-chlorketones, α-aldehyde Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols and α-ketone alcohols are used in place of diketones. Quinoxaline and its analogues may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzotriazole
Benzotriazole (BTA) is a heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula . It can be viewed as the fusion of a benzene and triazole rings. It is a white solid, although impure samples can appear tan. It is used as a corrosion inhibitor for copper. Structure and synthesis : Benzotriazole features two fused rings. It can in principle exist as tautomers, but X-ray crystallography establishes the depicted structure. The N=N and HN-N distances are 1.306 and 1.340 Å. Benzotriazole can be prepared by the monodiazotization of o-Phenylenediamine, ''o''-phenylenediamine using sodium nitrite and acetic acid.Robert A. Smiley "Phenylene- and Toluenediamines" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Reactions Acid-base behavior BTA is a weak Bronsted acid with a pKa = 8.2. It is a weak Brønsted base, as indicated by the low pKa 0.1 μg/L. One source of this pollution is their use as anti-icing/deicing agents in airports. Benzotriazo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrous Acid
Nitrous acid (molecular formula ) is a weak and monoprotic acid known only in solution, in the gas phase, and in the form of nitrite () salts. It was discovered by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, who called it " phlogisticated acid of niter". Nitrous acid is used to make diazonium salts from amines. The resulting diazonium salts are reagents in azo coupling reactions to give azo dyes. Structure In the gas phase, the planar nitrous acid molecule can adopt both a ''syn'' and an ''anti'' form. The ''anti'' form predominates at room temperature, and IR measurements indicate it is more stable by around 2.3 kJ/mol. p. 462. Image:Trans-nitrous-acid-2D-dimensions.png , Dimensions of the ''anti'' form(from the microwave spectrum) Image:Trans-nitrous-acid-3D-balls.png , Model of the ''anti'' form Image:Cis-nitrous-acid-3D-balls.png , ''syn'' form Preparation and decomposition Free, gaseous nitrous acid is unstable, rapidly disproportionating to nitric oxides: :2 HNO2 → NO2 + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercaptobenzimidazole
Mercaptobenzimidazole is the organosulfur compound with the formula C6H4(NH)2C=S. It is the mercaptan of benzimidazole. It is a white solid that has been investigated as a corrosion inhibitor. The name is a misnomer because the compound is a thiourea, characterized with a short C=S bond length of 169 pm. A similar situation applies to 2-mercaptoimidazole, which is also a thiourea properly called 2-imidazolidinethione and mercaptobenzothiazole, which is also a thioamide. It is prepared from o-phenylenediamine ''o''-Phenylenediamine (OPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. This aromatic diamine is an important precursor to many heterocyclic compounds. OPD is a white compound although samples appear darker owing to oxidation by air. I ....{{cite journal , doi=10.15227/orgsyn.030.0056 , title=2-Mercaptobenzimidazole, journal=Organic Syntheses , date=1950 , volume=30 , page=56, first1=J. A. , last1=VanAllan, first2=B. D., last2= Deacon References Thioureas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Ethylxanthate
Potassium ethyl xanthate (KEX) is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula . It is a pale yellow powder that is used in the mining industry for the separation of ores. It is a potassium salt of ethyl xanthic acid. Many xanthates are known. Production and properties Xanthate salts are prepared by the action of alkoxides on carbon disulfide. The alkoxide is often generated in situ from potassium hydroxide: : The salt , prepared from potassium pentanolate and carbon disulfide has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. The COCS2 portion of the anion is planar. The C-S bond lengths are both 1.65 Å, and the C-O distance is 1.38 Å. Potassium ethyl xanthate is a pale yellow powder that is stable at high pH, but rapidly hydrolyses below pH = 9: : Oxidation of xanthate salts gives diethyl dixanthogen disulfide: : KEX is a source of ethylxanthate coordination complexes. For example, the octahedral complexes , , and have been prepared from KEX. Applications Potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page for EPA reports on pesticide use ihere Selective herbicides control specific weed species while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides (sometimes called "total weed killers") kill plants indiscriminately. The combined effects of herbicides, nitrogen fertilizer, and improved cultivars has increased yields (per acre) of major crops by three to six times from 1900 to 2000. In the United States in 2012, about 91% of all herbicide usage, was determined by weight applied, in agriculture. In 2012, world pesticide expenditures totaled nearly US$24.7 billion; herbicides were about 44% of those sales and constituted the biggest portion, followed by insecticides, fungicides, and fumigants. Herbicide is also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuberidazole
Fuberidazole (chemical formula: C11H8N2O) is a chemical compound used in fungicides Fungicides are pesticides used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in losses of yield and quality. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals, .... References Benzimidazoles 2-Furyl compounds Fungicides {{mycology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benomyl
Benomyl (also marketed as Benlate) is a fungicide introduced in 1968 by DuPont. It is a systemic benzimidazole fungicide that is selectively toxic to microorganisms and invertebrates (especially earthworms), but relatively nontoxic toward mammals. Due to the prevalence of resistance of parasitic fungi to benomyl, it and similar pesticides are of diminished effectiveness. Nonetheless, it is widely used. Toxicity Benomyl is of low toxicity to mammals. It has an arbitrary LD50 of "greater than 10,000 mg/kg/day for rats". Skin irritation may occur through industrial exposure, and florists, mushroom pickers and floriculturists have reported allergic reactions to benomyl. In a laboratory study, dogs fed benomyl in their diets for three months developed no major toxic effects, but did show evidence of altered liver function at the highest dose (150 mg/kg). With longer exposure, more severe liver damage occurred, including cirrhosis. The US Environmental Protection Agency classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzimidazole
Benzimidazole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound may be viewed as fused rings of the aromatic compounds benzene and imidazole. It is a white solid that appears in form of tabular crystals. Preparation Benzimidazole was discovered during research on vitamin B12. The benzimidazole nucleus was found to be a stable platform on which drugs could be developed. Benzimidazole is produced by Condensation reaction, condensation of o-phenylenediamine with formic acid, or the equivalent trimethyl orthoformate: :C6H4(NH2)2 + HC(OCH3)3 → C6H4N(NH)CH + 3 CH3OH 2-Substituted derivatives are obtained when the condensation is conducted with aldehydes in place of formic acid, followed by oxidation. Reactions Benzimidazole is a Base (chemistry), base: :C6H4N(NH)CH + H+ → [C6H4(NH)2CH]+ It can also be deprotonated with stronger bases: :C6H4N(NH)CH + LiH → Li [C6H4N2CH] + H2 The imine can be alkylated and also serves as a ligand in coordinati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |