|
No-code
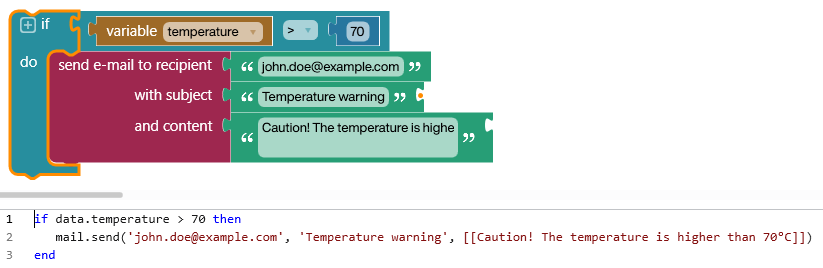
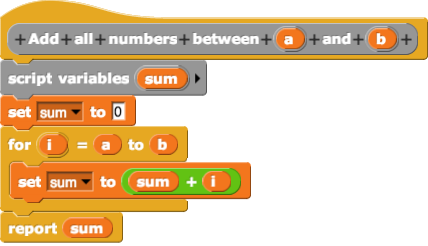
No-code development platforms (NCDPs) allow creating application software through graphical user interfaces and configuration instead of traditional computer programming based on writing code. As with low-code development platforms, it is meant to expedite application development, but unlike low-code, no-code development involves no code writing. This is usually done by offering prebuilt templates for building apps. In the 2010s, both of these types of platforms increased in popularity as companies dealt with a limited supply of competent software developers. No-code development is closely related to visual programming languages. Use No-code tools are often designed with line of business users in mind as opposed to traditional IT. The potential benefits of using a NCDP include: *Agility – NCDPs typically provide some degree of templated user-interface and user experience functionality for common needs such as forms, workflows, and data display allowing creators to expedite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-code Development Platform
A low-code development platform (LCDP) provides a development environment used to create application software, generally through a graphical user interface (as opposed to only writing code, though some coding is possible and may be required). A low-coded platform may produce entirely operational applications, or require additional coding for specific situations. Low-code development platforms are typically on a high abstraction level, and can reduce the amount of traditional time spent, enabling accelerated delivery of business applications. A common benefit is that a wider range of people can contribute to the application's development, not only those with coding skills, but good governance is needed to be able to adhere to common rules and regulations. LCDPs can also lower the initial cost of setup, training, deployment, and maintenance. Low-code development platforms trace their roots back to fourth-generation programming language and the rapid application development tools of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betty Blocks Platform
Betty or Bettie is a name, a common diminutive for the names Bethany and Elizabeth. In Latin America, it is also a common diminutive for the given name Beatriz, the Spanish and Portuguese form of the Latin name Beatrix and the English name Beatrice. In the 17th and 18th centuries, it was more often a diminutive of Bethia. Notable people Athletes * Betty Cuthbert (1938–2017), Australian sprinter and Olympic champion * Betty Jameson (1919–2009), American Hall-of-Fame golfer and one of the founders of the LPGA * Betty McKilligan (born 1949), Canadian pairs figure skater * Betty Nuthall (1911–1983), English tennis player * Betty Pariso (born 1956), American bodybuilder * Betty Stöve (born 1945), Dutch tennis player * Betty Ann Grubb Stuart (born 1950), American tennis player * Betty Uber (1906–1983), English badminton and tennis player Journalists and media personalities * Betty Elizalde (1940–2018), Argentine journalist and broadcaster * Betty Kennedy (1926–20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Online Database Creator Apps
This list of online database creator apps lists notable web apps where end users with minimal database administration expertise can create online databases to share with team members. Users need not have the coding skills to manage the solution stack themselves, because the web app already provides this predefined functionality. Such online database creator apps serve the gap between IT professionals (who can manage such a stack themselves) and people who would not create databases at all anyway. In other words, they provide a low-code way of doing database administration. As the concept of low-code development in general continues to evolve, some of the brands that began as online database creator apps are evolving into low-code development platforms A low-code development platform (LCDP) provides a development environment used to create application software, generally through a graphical user interface (as opposed to only writing code, though some coding is possible and may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibe Coding
Vibe coding is an approach to producing software by using artificial intelligence (AI), where a person describes a problem in a few natural language sentences as a Prompt engineering, prompt to a large language model (LLM) tuned for coding. The LLM generates Application software, software based on the description, shifting the programmer's role from manual coding to guiding, testing, and refining the AI-generated source code. Advocates of vibe coding say that it allows even End-user computing, amateur programmers to produce software without the extensive training and skills required for software engineering. Critics point out a lack of accountability and increased risk of introducing security vulnerabilities in the resulting software. The term was introduced by Andrej Karpathy in February 2025 and listed in the Merriam-Webster's Dictionary of English Usage, Merriam-Webster Dictionary the following month as a "slang & trending" noun. Definition Computer scientist Andrej Karpat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platform As A Service
Platform as a service (PaaS) or application platform as a service (aPaaS) or platform-based service is a cloud computing service model where users provision, instantiate, run and manage a modular bundle of a computing platform and applications, without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure associated with developing and launching application(s), and to allow developers to create, develop, and package such software bundles. Development and uses PaaS can be delivered in three ways: * As a public cloud service from a provider, where the consumer controls software deployment with minimal configuration options, and the provider provides the networks, servers, storage, operating system (OS), middleware (e.g. Java runtime, .NET runtime, integration, etc.), database and other services to host the consumer's application. * As a private service (software or appliance) behind a firewall. * As software deployed on public infrastructure as a service.Judith Hurwitz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lean Software Development
Lean software development is a translation of lean manufacturing principles and practices to the software development domain. Adapted from the Toyota Production System, it is emerging with the support of a pro-lean subculture within the agile community. Lean offers a solid conceptual framework, values and principles, as well as good practices, derived from experience, that support agile organizations. Origin The expression "lean software development" originated in a book by the same name, written by Mary Poppendieck and Tom Poppendieck in 2003. The book restates traditional lean principles, as well as a set of 22 ''tools'' and compares the tools to corresponding agile practices. The Poppendiecks' involvement in the agile software development community, including talks at several Agile conferences has resulted in such concepts being more widely accepted within the agile community. Lean principles Lean development can be summarized by seven principles, very close in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Application Development
Rapid application development (RAD), also called rapid application building (RAB), is both a general term for adaptive software development approaches, and the name for James Martin's method of rapid development. In general, RAD approaches to software development put less emphasis on planning and more emphasis on an adaptive process. Prototypes are often used in addition to or sometimes even instead of design specifications. RAD is especially well suited for (although not limited to) developing software that is driven by user interface requirements. Graphical user interface builders are often called rapid application development tools. Other approaches to rapid development include the adaptive, agile, spiral, and unified models. History Rapid application development was a response to plan-driven waterfall processes, developed in the 1970s and 1980s, such as the Structured Systems Analysis and Design Method (SSADM). One of the problems with these methods is that they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Of Business
Line of business (LOB) is a general term which refers to a product or a set of related products that serve a particular customer transaction or business need. In some industry sectors, like insurance, "line of business" also has a regulatory and accounting definition to meet a statutory set of insurance policies. It may or may not be a strategically relevant business unit. "Line of business" often refers to an internal corporate business unit, whereas the term "industry" refers to an external view that includes all competitors competing in a similar market. A line of business will often examine its position within an industry using a Porter five forces analysis (or other industry-analysis method) and other relevant industry information. Computer applications In the context of computing, a "line-of-business application" is one of the set of critical computer applications perceived as vital to running an enterprise. For example: "Governance has become the hot topic in SOA ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow-based Programming
In computer programming, flow-based programming (FBP) is a programming paradigm that defines application software, applications as networks of black box process (computer science), processes, which exchange data across predefined connections by message passing, where the connections are specified ''externally'' to the processes. These black box processes can be reconnected endlessly to form different applications without having to be changed internally. FBP is thus naturally Software componentry, component-oriented. FBP is a particular form of dataflow programming based on bounded buffers, information packets with defined lifetimes, named ports, and separate definition of connections. Introduction Flow-based programming defines applications using the metaphor of a "data factory". It views an application not as a single, sequential process, which starts at a point in time, and then does one thing at a time until it is finished, but as a network of asynchronous processes communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Software
Application software is any computer program that is intended for end-user use not operating, administering or programming the computer. An application (app, application program, software application) is any program that can be categorized as application software. Common types of applications include word processor, media player and accounting software. The term ''application software'' refers to all applications collectively and can be used to differentiate from system and utility software. Applications may be bundled with the computer and its system software or published separately. Applications may be proprietary or open-source. The short term ''app'' (coined in 1981 or earlier) became popular with the 2008 introduction of the iOS App Store, to refer to applications for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Later, with introduction of the Mac App Store (in 2010) and Windows Store (in 2011), the term was extended in popular use to include desktop a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Programming Language
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS), also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create computer program, programs by manipulating program elements rather than by specifying them . A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations. VPLs are generally the basis of low-code development platforms. Definition VPLs may be further classified, according to the type and extent of visual expression used, into icon-based languages, form-based languages, and diagram languages. Visual programming environments provide graphical or iconic elements which can be manipulated by u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |