Low-code development platform on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
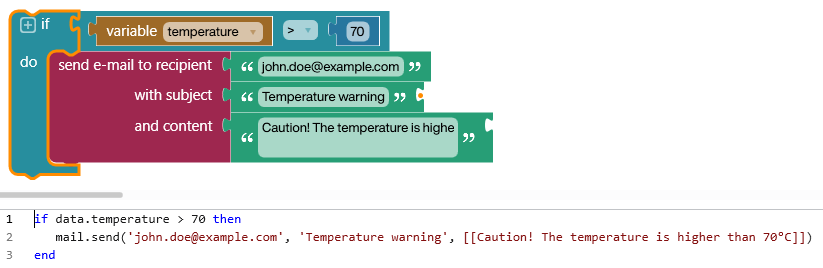 A low-code development platform (LCDP) provides a development environment used to create
A low-code development platform (LCDP) provides a development environment used to create
 A low-code development platform (LCDP) provides a development environment used to create
A low-code development platform (LCDP) provides a development environment used to create application software
Application software is any computer program that is intended for end-user use not operating, administering or programming the computer. An application (app, application program, software application) is any program that can be categorized as ...
, generally through a graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
(as opposed to only writing code, though some coding is possible and may be required). A low-coded platform may produce entirely operational applications, or require additional coding for specific situations. Low-code development platforms are typically on a high abstraction level, and can reduce the amount of traditional time spent, enabling accelerated delivery of business applications. A common benefit is that a wider range of people can contribute to the application's development, not only those with coding skills, but good governance is needed to be able to adhere to common rules and regulations. LCDPs can also lower the initial cost of setup, training, deployment, and maintenance.
Low-code development platforms trace their roots back to fourth-generation programming language
A fourth-generation programming language (4GL) is a high-level programming language, high-level computer programming language that belongs to a class of languages envisioned as an advancement upon third-generation programming languages (3GL). Each ...
and the rapid application development
Rapid application development (RAD), also called rapid application building (RAB), is both a general term for adaptive software development approaches, and the name for James Martin's method of rapid development. In general, RAD approaches to ...
tools of the 1990s and early 2000s. Similar to these predecessor development environments, LCDPs are based on the principles of model-driven architecture, automatic code generation, and visual programming. The concept of end-user development also existed previously, although LCDPs brought some new ways of approaching this development. The low-code development platform market traces its origins back to 2011. The specific name "low-code" was not put forward until 9 June, 2014, when it was used by the industry analyst ''Forrester Research
Forrester Research, Inc. is a research and advisory firm. Forrester serves clients in North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific. The firm is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts, Cambridge, MA with global offices in Amsterdam, London, New D ...
''. Along with no-code development platform
No-code development platforms (NCDPs) allow creating application software through graphical user interfaces and configuration instead of traditional computer programming based on writing code.
As with low-code development platforms, it is meant ...
s, low-code was described as "extraordinarily disruptive" in ''Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine founded by B. C. Forbes in 1917. It has been owned by the Hong Kong–based investment group Integrated Whale Media Investments since 2014. Its chairman and editor-in-chief is Steve Forbes. The co ...
'' magazine in 2017.
Use
As a result of themicrocomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (P ...
revolution, businesses have deployed computers widely across their employee bases, enabling widespread automation of business processes using software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
. The need for software automation and new applications for business processes places demands on software developers to create custom applications in volume, tailoring them to organizations' unique needs. Low-code development platforms have been developed as a means to allow for quick creation and use of working applications that can address the specific process and data needs of the organization.
Reception
Research firm Forrester estimated in 2016 that the total market for low-code development platforms would grow to $15.5 billion by 2020. Segments in the market include database, request handling, mobile, process, and general purpose low-code platforms. Low-code development's market growth can be attributed to its flexibility and ease. Low-code development platforms are shifting their focus toward general purpose of applications, with the ability to add in custom code when needed or desired. Mobile accessibility is one of the driving factors of using low-code development platforms. Instead of developers having to spend time creating multi-device software, low-code packages typically come with that feature as standard. Because they require less coding knowledge, nearly anyone in a software development environment can learn to use a low-code development platform. Features likedrag and drop
In computer graphical user interfaces, drag and drop is a pointing device gesture in which the user (computing), user selects a virtual object by "grabbing" it and dragging it to a different location or onto another virtual object. In general, i ...
interfaces help users visualize and build the application
Security and compliance concerns
Concerns over low-code development platform security and compliance are growing, especially for apps that use consumer data. There can be concerns over the security of apps built so quickly and possible lack of due governance leading to compliance issues. However, low-code apps do also fuel security innovations. With continuous app development in mind, it becomes easier to create secure data workflows.Criticisms
Some IT professionals question whether low-code development platforms are suitable for large-scale and mission-critical enterprise applications. Others have questioned whether these platforms actually make development cheaper or easier. Additionally, some CIOs have expressed concern that adopting low-code development platforms internally could lead to an increase in unsupported applications built by shadow IT.See also
*DRAKON
DRAKON () is a Free and open-source software, free and open source algorithmic visual programming language, visual programming and modeling language developed as part of the defunct Soviet Union Buran program, Buran space program in 1986 ...
* End-user computing
* End-user development
* Flow-based programming
* List of online database creator apps
* List of low-code development platforms
* Visual programming language
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS), also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create computer program, programs by ...
* Backend as a service
Backend as a service (BaaS), sometimes also referred to as mobile backend as a service (MBaaS), is a service for providing web app and mobile app developers with a way to easily build a backend to their frontend applications. Features available ...
References
{{reflist Enterprise architecture Software development