|
No-ball
In cricket, a no-ball (in the Laws and regulations: "No ball") is a type of illegal delivery to a batter (the other type being a wide). It is also a type of extra, being the run awarded to the batting team as a consequence of the illegal delivery. For most cricket games, especially amateur, the definition of all forms of no-ball is from the MCC ''Laws of Cricket.'' Originally "no Ball" was called when a bowler overstepped the bowling crease, requiring them to try again to bowl a fair ball. As the game developed, "No ball" has also been called for an unfair ball delivered roundarm, overarm or thrown, eventually resulting in today's overarm bowling being the only legal style. Technical infringements, and practices considered unfair or dangerous, have been added for bowling, field placement, fielder and wicket-keeper actions. "No-ball" has become a passage of play. The delivery of a no-ball results in one run – two under some regulations – to be added to the batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
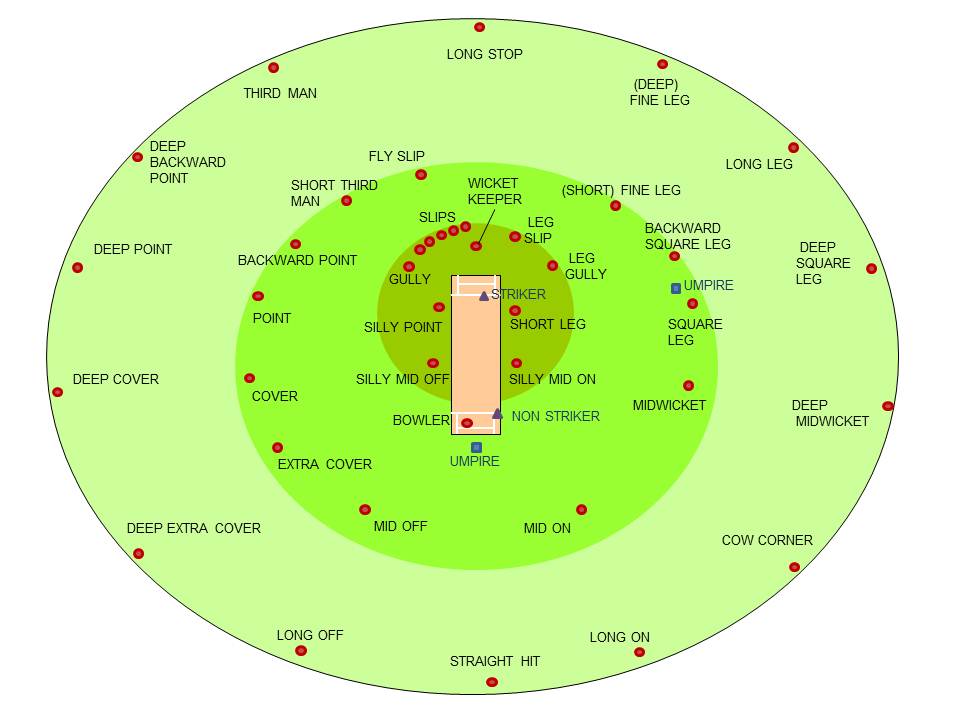
Umpire (cricket)
In cricket, an umpire (from the Old French meaning not a peer, i.e. not a member of one of the teams, impartial) is a person who has the authority to make decisions about events on the cricket field according to the ''Laws of Cricket''. Besides making decisions about legality of delivery, appeals for wickets and general conduct of the Game in a legal manner, the umpire also keeps a record of the deliveries and announces the completion of an over. The umpires in cricket are not to be confused with the referee who usually presides only over international matches and makes no decisions affecting the outcome of the game. Overview Traditionally, cricket matches have two umpires on the field, one standing at the end where the bowler delivers the ball (bowler's end), and one directly opposite the facing batsman (usually, but not always, at square leg). However, in the modern game, there may be more than two umpires; for example Test Matches have four: two on-field umpires, a thir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illegal Delivery (cricket)
In cricket, an extra (sometimes called a sundry) is a run (cricket), run scored by, or awarded to, a Batting (cricket), batting team which is not credited to any individual batter. They are the runs scored by methods other than striking the cricket ball, ball with the Cricket bat, bat. The extras are tallied separately on the scorecard and count only towards the team's score. Giving away many extras is often considered as untidy bowling (cricket), bowling. There are five types of extra: no-ball (nb), Wide (cricket), wide (w or wd), Bye (cricket), bye (b), leg bye (lb), and penalty run (pen). Types of extras Illegal deliveries These are extras that are awarded because the bowler or fielders have violated certain rules in how they deliver the ball to the batter (i.e. they are not bowling from far away enough, or the ball is out of the batter's reach), or where they are positioned in the field. Most methods of Dismissal (cricket), dismissal can not occur on an illegal deliver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extra (cricket)
In cricket, an extra (sometimes called a sundry) is a run scored by, or awarded to, a batting team which is not credited to any individual batter. They are the runs scored by methods other than striking the ball with the bat. The extras are tallied separately on the scorecard and count only towards the team's score. Giving away many extras is often considered as untidy bowling. There are five types of extra: no-ball (nb), wide (w or wd), bye (b), leg bye (lb), and penalty run (pen). Types of extras Illegal deliveries These are extras that are awarded because the bowler or fielders have violated certain rules in how they deliver the ball to the batter (i.e. they are not bowling from far away enough, or the ball is out of the batter's reach), or where they are positioned in the field. Most methods of dismissal can not occur on an illegal delivery. Illegal deliveries do not count towards the completion of the over they occur in, and thus in limited overs cricket, il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dismissal (cricket)
In cricket, a dismissal occurs when a batting (cricket), batter's innings is brought to an end by the opposing team. Other terms used are the batter being out, the batting side losing a wicket, and the fielding side (and often the bowler) taking a wicket. The Cricket ball, ball becomes Dead ball#Cricket, dead (meaning that no further runs can be scored off that Delivery (cricket), delivery), and the dismissed batter must leave the Cricket field, field of play for the rest of their team's innings, to be replaced by a team-mate. A team's End of an innings, innings ends if ten of the eleven team members are dismissed. Players bat in Batting pair, pairs so, when only one batter remains who can be not out, it is not possible for the team to bat any longer. This is known as ''dismissing'' or ''bowling out'' the batting team, who are said to be ''All out (cricket), all out''. The most common methods of dismissing a batter are (in descending order of frequency): caught, bowled, leg befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wide (cricket)
In cricket, a wide is a type of Illegal delivery (cricket), illegal delivery to a Batting (cricket), batter (the other type being a no-ball) that is judged by the umpire (cricket), umpire to be too wide or (in international cricket) too high to be hit by the batsman by means of a normal cricket shot. It is also a type of Extra (cricket), extra, being the Run (cricket), run awarded to the batting team as a consequence of such an illegal delivery. Definition Wide balls are covered by Law 22 of the Laws of Cricket. A delivery is a wide if it is not sufficiently within reach for the batter to be able to hit it with the bat by means of a normal cricket stroke from where the batter is standing, and also would not have been sufficiently within reach for the batter to be able to hit it with the bat by means of a normal cricket stroke if the batter were standing in a normal Batting (cricket)#Stance, guard position. Therefore a delivery is not a wide if the ball hits the bat or batsman, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundarm Bowling
In cricket, roundarm bowling is a bowling (cricket), bowling style that was introduced in the first quarter of the 19th century and largely superseded underarm bowling by the 1830s. Using a roundarm action, the bowler (cricket), bowlers extend their arm about 90 degrees from their body at the point where they release the ball. Roundarm fell into decline after 1864 when the current style of overarm bowling was legalised, although W. G. Grace continued to use it to the end of his career. Origin The spread of roundarm in the 1820s was a natural reaction to the growing predominance of batsmen over the age-old underarm style of bowling. Its adherents argued that the legalisation of roundarm was essential to restore the balance between batting and bowling. However, high-scoring matches were still comparatively rare owing to vagaries in pitch conditions. The idea of roundarm is sometimes attributed to Christiana Willes, sister of Kent cricketer John Willes (cricketer), John Willes. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin Bowling
Spin bowling is a bowling (cricket), bowling technique in cricket, in which the ball is Delivery (cricket), delivered relatively slowly but with rapid rotation, giving it the potential to deviate sharply after bouncing. A bowler who uses this technique is called a spinner, a spin bowler, or a slow bowler. It is one of the two main approaches to bowling, the other being fast bowling. A spinner may bowl with their right-arm or left-arm, and with a finger spin or wrist spin action. Therefore, there are four types of spin bowling: off spin, leg spin, left-arm orthodox spin and left-arm unorthodox spin. The bowlers with the highest, second-highest and fourth-highest number of Dismissal (cricket), wickets in the history of Test cricket, Muttiah Muralitharan, Shane Warne and Anil Kumble, respectively, were spinners. Purpose The main aim of spin bowling is to bowl the cricket ball with rapid rotation so that when it bouncing ball, bounces on the cricket pitch, pitch it will deviate f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crease (cricket)
In cricket, a crease is a white line painted or chalked on the field of play, that defines the area within which the Batsman (cricket), batters and bowler (cricket), bowlers operate. The term ''crease'' may also be used to refer to the rectangular area enclosed by the lines. Law 7 of the Laws of Cricket governs the size and position of the crease markings, and defines the actual line as the back edge of the width of the marked line on the soil, i.e., the edge nearest to the wicket at that end. Four creases (one popping crease, one bowling crease, and two return creases) are drawn at each end of the cricket pitch, pitch, around the two sets of stump (cricket), stumps. The bowling creases lie 22 yards (66 feet or 20.12 m) apart, and mark the ends of the pitch. For the fielding side, the crease defines whether there is a no-ball because the wicket-keeper has moved in front of the wicket before he is permitted to do so. In addition, historically part of the bowler (cricket), bowler' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Form Cricket
Short form cricket is a collective term for several modified forms of the sport of cricket, with playing times significantly shorter than more traditional forms of the game. A typical short form cricket match can be completed within two to three hours, compared to 7–8 hours for a one-day cricket match, or five days for a Test match. They generally are limited overs cricket matches, with each team batting for a maximum of 5 to 20 overs (30 to 120 legal balls) depending on the format. These short forms of cricket have been developed locally by various authorities, to fill a perceived marketing vacancy for a form of the sport which can be completed in a few hours, rather than a full day. They tend to emphasise the more "exciting" aspects of cricket as seen by more casual observers of the game, which includes aggressive batting and fast run scoring. In this regard, they are successful, as shortened forms of cricket attract crowds of spectators who might not otherwise attend a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Bowling
Fast bowling (also referred to as pace bowling) is a type of bowling in cricket, in which the ball is delivered at high speed. The fastest bowlers bowl the ball at over . Practitioners of fast bowling are known as fast bowlers or quicks. Also included in this broad category are bowlers who do not achieve the highest speeds, who may instead be known by a range of other terms, such as medium fast bowlers. In addition to delivering the ball at speed, this type of bowler may also use seam bowling or swing bowling techniques, to make it even harder for the batter to play the ball correctly. The mixture of speed, seam and swing that can be achieved depends on several factors, including the individual bowler's skill, the condition of the ball, and the weather. Seam and swing are particularly important for bowlers who do not achieve the highest speeds. Therefore, they might also be referred to as a seam bowler, a swing bowler, or a fast bowler who can swing it, for example, if this i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |