spin bowling on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Spin bowling is a
Spin bowling is a
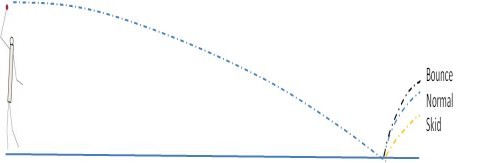


 It is customary among cricket commentators to describe and judge the quality of spin bowling in terms of the characteristics ''flight'', ''turn'', ''bounce'', ''drift'', and ''dip''. All these are arts to deceive the batsman and require much practice. The basic trajectory of spin bowling is two-lines-at-an-angle, but the above characteristics (described below) modify this 'normal' trajectory into more complex shapes.
Turn: How much the ball turns after pitching (e.g. 5 degree deviation after meeting the ground). It depends on the number and direction of revolutions of the ball. The movement and rotation of the ball varies, depending on the position of the wrist and the finger. An occasional unexpected straight ball can usefully be included in an attack, but spin variation is the main technique used to deceive the batsman and take wickets. A high rate of turn is above 33 rev/second, or 2000 rpm. Graeme Swann consistently spun over 2000 rpm, the most amongst English spinners until Liam Dawson topped 35 rev/second, or 2100 rpm. Also, the slower the ball, the more it tends to deviate. For an offspinner, you will have to bowl from wide of off-stump to get the ball to turn into the right-handed batsman and force them to nick off the edge to a fielder or into the top of off stump.
Bounce: Getting the ball to bounce more than normal, so that the ball meets the batsman at a greater height than expected. Sometimes, if the ball spins horizontally (e.g. a slider), the batsman will not be able to make contact with the ball and it may hit the stumps before the second bounce.
Drift: Getting the ball to move sideways while in air. Late drift causes the batsman to cover the wrong line and the ball may catch the edge of the bat.
Dip: Getting the ball to pitch (meet the ground) at a shorter distance than normal. Late dip causes the batsman to misjudge the length of the ball.
Flight: throwing the ball up a bit more than normal, so that its time in the air before pitching is longer. A slow ball with extra flight may deceive the batsman into thinking it is slower than it is and therefore mistiming his shot. This is very effective for offspinners. Usually a spin bowler relies on tricks during flight to produce turn, bounce, drift and dip, or combinations of them.
It is customary among cricket commentators to describe and judge the quality of spin bowling in terms of the characteristics ''flight'', ''turn'', ''bounce'', ''drift'', and ''dip''. All these are arts to deceive the batsman and require much practice. The basic trajectory of spin bowling is two-lines-at-an-angle, but the above characteristics (described below) modify this 'normal' trajectory into more complex shapes.
Turn: How much the ball turns after pitching (e.g. 5 degree deviation after meeting the ground). It depends on the number and direction of revolutions of the ball. The movement and rotation of the ball varies, depending on the position of the wrist and the finger. An occasional unexpected straight ball can usefully be included in an attack, but spin variation is the main technique used to deceive the batsman and take wickets. A high rate of turn is above 33 rev/second, or 2000 rpm. Graeme Swann consistently spun over 2000 rpm, the most amongst English spinners until Liam Dawson topped 35 rev/second, or 2100 rpm. Also, the slower the ball, the more it tends to deviate. For an offspinner, you will have to bowl from wide of off-stump to get the ball to turn into the right-handed batsman and force them to nick off the edge to a fielder or into the top of off stump.
Bounce: Getting the ball to bounce more than normal, so that the ball meets the batsman at a greater height than expected. Sometimes, if the ball spins horizontally (e.g. a slider), the batsman will not be able to make contact with the ball and it may hit the stumps before the second bounce.
Drift: Getting the ball to move sideways while in air. Late drift causes the batsman to cover the wrong line and the ball may catch the edge of the bat.
Dip: Getting the ball to pitch (meet the ground) at a shorter distance than normal. Late dip causes the batsman to misjudge the length of the ball.
Flight: throwing the ball up a bit more than normal, so that its time in the air before pitching is longer. A slow ball with extra flight may deceive the batsman into thinking it is slower than it is and therefore mistiming his shot. This is very effective for offspinners. Usually a spin bowler relies on tricks during flight to produce turn, bounce, drift and dip, or combinations of them.
 Spin bowling is a
Spin bowling is a bowling
Bowling is a Throwing sports#Target sports, target sport and recreational activity in which a player rolls a bowling ball, ball toward Bowling pin, pins (in pin bowling) or another target (in target bowling). Most references to ''bowling'' are ...
technique in cricket
Cricket is a Bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball game played between two Sports team, teams of eleven players on a cricket field, field, at the centre of which is a cricket pitch, pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two Bail (cr ...
, in which the ball is delivered relatively slowly but with rapid rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersect ...
, giving it the potential to deviate sharply after bouncing. A bowler who uses this technique is called a spinner, a spin bowler, or a slow bowler.
It is one of the two main approaches to bowling, the other being fast bowling
Fast bowling (also referred to as pace bowling) is a type of bowling in cricket, in which the ball is delivered at high speed. The fastest bowlers bowl the ball at over . Practitioners of fast bowling are known as fast bowlers or quicks. Also ...
.
A spinner may bowl with their right-arm or left-arm, and with a finger spin or wrist spin action. Therefore, there are four types of spin bowling: off spin
Off spin is a type of spin bowling in cricket. A bowler who uses this technique is called an off spinner. Off spinners bowl with their right-arm and a finger spin action. Their normal delivery is called an off break, which spins from left to r ...
, leg spin
Leg spin is a type of spin bowling in cricket. A bowler who uses this technique is called a leg spinner. Leg spinners bowl with their right-arm and a wrist spin action. The leg spinner's normal delivery is called a leg break, which spins fr ...
, left-arm orthodox spin
Left-arm orthodox spin or left-arm off spin, also known as slow left-arm orthodox spin bowling, is a type of spin bowling in cricket
Cricket is a Bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball game played between two Sports team, teams of eleven ...
and left-arm unorthodox spin
Left-arm unorthodox spin, also known as slow left-arm wrist spin, is a type of spin bowling in the sport of cricket . Left-arm unorthodox spin bowlers use wrist spin to spin the ball, and make it deviate, or 'turn' from left to right after pit ...
.
The bowlers with the highest, second-highest and fourth-highest number of wickets
In the sport of cricket, the term wicket has several meanings:
* It is either of the two sets of three stumps and two bails at each end of the pitch. The fielding team's players can hit the wicket with the ball in a number of ways to get a ...
in the history of Test cricket
Test cricket is a Forms of cricket, format of the sport of cricket, considered the game’s most prestigious and traditional form. Often referred to as the "ultimate test" of a cricketer's skill, endurance, and temperament, it is a format of i ...
, Muttiah Muralitharan
Deshabandu Muttiah Muralitharan (born 1972) is a Sri Lankan cricket coach, businessman and former professional cricketer. Averaging over six wickets per Test match, he is widely regarded as one of the greatest players in the history of the ...
, Shane Warne
Shane Keith Warne (13 September 1969 – 4 March 2022) was an Australian international cricketer whose career ran from 1992 to 2007. Warne played as a right-arm leg spin bowler and a lower-order right-handed batter for Victoria, Hampshire ...
and Anil Kumble, respectively, were spinners.
Purpose
The main aim of spin bowling is to bowl thecricket ball
A cricket ball is a hard, solid ball used to play cricket. A cricket ball consists of a cork (material), cork core wound with String (structure), string then a leather cover stitched on, and manufacture is regulated by cricket law at first-clas ...
with rapid rotation so that when it bounces on the pitch it will deviate from its normal straight path, thus making it difficult for the batsman
In cricket, batting is the act or skill of hitting the cricket ball, ball with a cricket bat, bat to score runs (cricket), runs and prevent the dismissal (cricket), loss of one's wicket. Any player who is currently batting is, since Septembe ...
to hit the ball cleanly.Knight, pp.122–123. The speed the ball travels is not critical, and is significantly slower than that for fast bowling
Fast bowling (also referred to as pace bowling) is a type of bowling in cricket, in which the ball is delivered at high speed. The fastest bowlers bowl the ball at over . Practitioners of fast bowling are known as fast bowlers or quicks. Also ...
. A typical spin delivery has a speed in the range 70–90 km/h (45–55 mph).
Techniques
Spin bowling is divided into four categories, depending on the physical technique used. There is virtually no overlap between the two basic biomechanical techniques of wrist spin and finger spin. Depending on technique, a spin bowler uses either predominant wrist or finger motion to impart spin to the ball around a horizontal axis that is at an oblique angle to the length of the pitch. This sort of spin means it is also possible for theMagnus effect
The Magnus effect is a phenomenon that occurs when a spin (geometry), spinning Object (physics), object is moving through a fluid. A lift (force), lift force acts on the spinning object and its path may be deflected in a manner not present when ...
to cause the ball to deviate sideways through the air, before it bounces. Such deviation is called ''drift''. The combination of drift and spin can make the ball's trajectory complex, with a change of direction at the bounce.
Spin bowlers are generally given the task of bowling with an old, worn cricket ball. A new cricket ball better suits the techniques of fast bowling than spin bowling, while a worn one grips the pitch better and achieves greater spin. Spin bowlers are also more effective later in a game, as the pitch dries up and begins to crack and crumble. This again provides more purchase for the spinning ball and produces greater deviation. Spin bowlers that open the bowling are rare, but became a more viable option with the introduction of Twenty20 cricket
Twenty20 (abbreviated T20) is a shortened format of cricket. At the professional level, it was introduced by the England and Wales Cricket Board (ECB) in 2003 for the county cricket, inter-county competition. In a Twenty20 game, the two t ...
when pitch conditions are in their favour, and the ball also generally drifts more in the air. Spin bowlers can also be used tactically in shorter forms of the game, to 'take the pace off the ball'. This strategy is especially effective to slow down the scoring rates of batsmen who specialise in making use of the pace of faster bowlers to score runs quickly. The lower inherent momentum of a spin bowler necessitates more power exerted by the batsman to achieve the same results.
Equivalences
Both finger spin and wrist spin bowlers use a range of different angles of spin to confuse the batsman and dismiss them. Many of these variations have direct equivalents in the other discipline, but the names used for the various deliveries may be different.Conditions
Spin bowling has become a forte of bowlers from South Asia. The primary reason for this is that pitches in the sub-continent provide more help to spin bowlers. The faster the pitch degenerates, the earlier the spinners come into the picture. Australian and South African pitches are usually very hard and bouncy, helping the fast bowlers more. They do not break up very much during the match. In contrast, pitches in the sub-continent are not that hard. They are not usually held together by the grass as much; hence they break up more quickly and help spin bowlers. In addition to this, spin bowling is considered to be less tiring than pace bowling as it generally does not employ a lengthy run up. Therefore, spin bowling is more prevalent in the hot and humid conditions of the sub-continent as a form of energy conservation, especially in multi-day competitions. In general, leg-spin is considered to be one of the toughest types of bowling in which to keep control of the ball, but it is very effective in picking off wickets.Bob Woolmer "The Art and Science of Cricket"Flight, turn, bounce, drift, dip



 It is customary among cricket commentators to describe and judge the quality of spin bowling in terms of the characteristics ''flight'', ''turn'', ''bounce'', ''drift'', and ''dip''. All these are arts to deceive the batsman and require much practice. The basic trajectory of spin bowling is two-lines-at-an-angle, but the above characteristics (described below) modify this 'normal' trajectory into more complex shapes.
Turn: How much the ball turns after pitching (e.g. 5 degree deviation after meeting the ground). It depends on the number and direction of revolutions of the ball. The movement and rotation of the ball varies, depending on the position of the wrist and the finger. An occasional unexpected straight ball can usefully be included in an attack, but spin variation is the main technique used to deceive the batsman and take wickets. A high rate of turn is above 33 rev/second, or 2000 rpm. Graeme Swann consistently spun over 2000 rpm, the most amongst English spinners until Liam Dawson topped 35 rev/second, or 2100 rpm. Also, the slower the ball, the more it tends to deviate. For an offspinner, you will have to bowl from wide of off-stump to get the ball to turn into the right-handed batsman and force them to nick off the edge to a fielder or into the top of off stump.
Bounce: Getting the ball to bounce more than normal, so that the ball meets the batsman at a greater height than expected. Sometimes, if the ball spins horizontally (e.g. a slider), the batsman will not be able to make contact with the ball and it may hit the stumps before the second bounce.
Drift: Getting the ball to move sideways while in air. Late drift causes the batsman to cover the wrong line and the ball may catch the edge of the bat.
Dip: Getting the ball to pitch (meet the ground) at a shorter distance than normal. Late dip causes the batsman to misjudge the length of the ball.
Flight: throwing the ball up a bit more than normal, so that its time in the air before pitching is longer. A slow ball with extra flight may deceive the batsman into thinking it is slower than it is and therefore mistiming his shot. This is very effective for offspinners. Usually a spin bowler relies on tricks during flight to produce turn, bounce, drift and dip, or combinations of them.
It is customary among cricket commentators to describe and judge the quality of spin bowling in terms of the characteristics ''flight'', ''turn'', ''bounce'', ''drift'', and ''dip''. All these are arts to deceive the batsman and require much practice. The basic trajectory of spin bowling is two-lines-at-an-angle, but the above characteristics (described below) modify this 'normal' trajectory into more complex shapes.
Turn: How much the ball turns after pitching (e.g. 5 degree deviation after meeting the ground). It depends on the number and direction of revolutions of the ball. The movement and rotation of the ball varies, depending on the position of the wrist and the finger. An occasional unexpected straight ball can usefully be included in an attack, but spin variation is the main technique used to deceive the batsman and take wickets. A high rate of turn is above 33 rev/second, or 2000 rpm. Graeme Swann consistently spun over 2000 rpm, the most amongst English spinners until Liam Dawson topped 35 rev/second, or 2100 rpm. Also, the slower the ball, the more it tends to deviate. For an offspinner, you will have to bowl from wide of off-stump to get the ball to turn into the right-handed batsman and force them to nick off the edge to a fielder or into the top of off stump.
Bounce: Getting the ball to bounce more than normal, so that the ball meets the batsman at a greater height than expected. Sometimes, if the ball spins horizontally (e.g. a slider), the batsman will not be able to make contact with the ball and it may hit the stumps before the second bounce.
Drift: Getting the ball to move sideways while in air. Late drift causes the batsman to cover the wrong line and the ball may catch the edge of the bat.
Dip: Getting the ball to pitch (meet the ground) at a shorter distance than normal. Late dip causes the batsman to misjudge the length of the ball.
Flight: throwing the ball up a bit more than normal, so that its time in the air before pitching is longer. A slow ball with extra flight may deceive the batsman into thinking it is slower than it is and therefore mistiming his shot. This is very effective for offspinners. Usually a spin bowler relies on tricks during flight to produce turn, bounce, drift and dip, or combinations of them.
References
Bibliography
* Surya Prakash Chaturvedi,''Bharat Ki Spin Parampara'',Rajkamal Prakashan,2007 (this book available only in Hindi) * ''Barclays World of Cricket'', 3rd edition (ed. E W Swanton), Willow Books, 1986. * Julian Knight, ''Cricket for Dummies'', John Wiley and Sons, 2006 {{Cricket positions Bowling (cricket) Cricket terminology