|
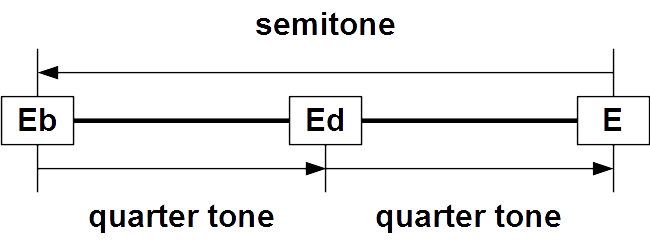
Neutral Interval
In music theory, a neutral interval is an interval (music), interval that is neither a major and minor, major nor minor, but instead in between. For example, in Equal temperament#Twelve-tone equal temperament, equal temperament, a major third is 400 cent (music), cents, a minor third is 300 cents, and a neutral third is 350 cents. A neutral interval Inversion (interval), inverts to a neutral interval. For example, the inverse of a neutral third is a neutral sixth. Roughly, neutral intervals are a quarter tone sharp from minor intervals and a quarter tone flat from major intervals. In just intonation, as well as in tunings such as 31 equal temperament, 31-ET, 41 equal temperament, 41-ET, or 72 equal temperament, 72-ET, which more closely approximate just intonation, the intervals are closer together. *#Neutral second, Neutral second *Neutral third *Neutral sixth *#Neutral seventh, Neutral seventh Second A neutral second or medium second is an interval wider than a minor seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral Seventh
In music theory, a neutral interval is an interval that is neither a major nor minor, but instead in between. For example, in equal temperament, a major third is 400 cents, a minor third is 300 cents, and a neutral third is 350 cents. A neutral interval inverts to a neutral interval. For example, the inverse of a neutral third is a neutral sixth. Roughly, neutral intervals are a quarter tone sharp from minor intervals and a quarter tone flat from major intervals. In just intonation, as well as in tunings such as 31-ET, 41-ET, or 72-ET, which more closely approximate just intonation, the intervals are closer together. * Neutral second *Neutral third *Neutral sixth * Neutral seventh Second A neutral second or medium second is an interval wider than a minor second and narrower than a major second. Three distinct intervals may be termed neutral seconds: * The intermediate neutral second, called the lesser undecimal neutral second , has a ratio between the higher-freque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
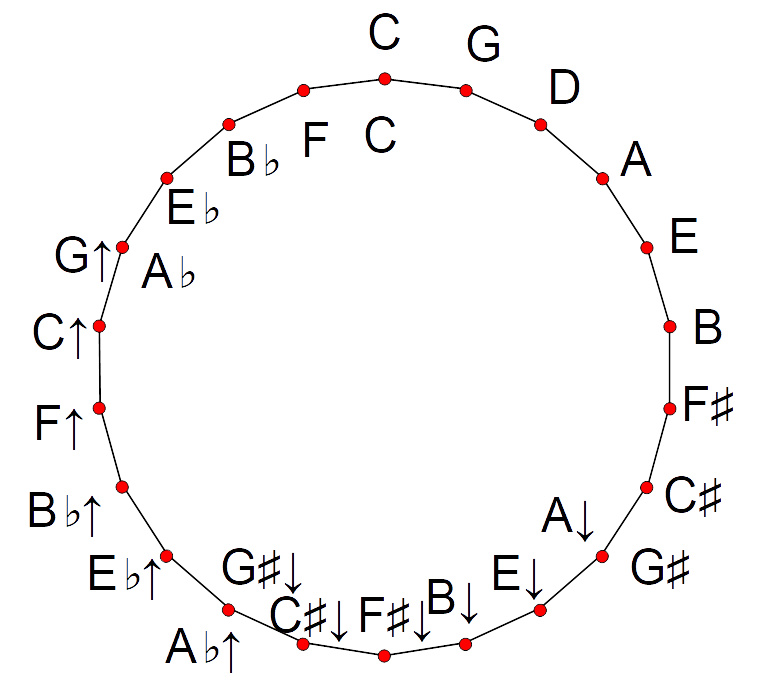
22 Equal Temperament
In music, 22 equal temperament, called 22-TET, 22- EDO, or 22-ET, is the tempered scale derived by dividing the octave into 22 equal steps (equal frequency ratios). Each step represents a frequency ratio of , or 54.55 cents (). When composing with 22-ET, one needs to take into account a variety of considerations. Considering the 5-limit, there is a difference between 3 fifths and the sum of 1 fourth and 1 major third. It means that, starting from C, there are two A's—one 16 steps and one 17 steps away. There is also a difference between a major tone and a minor tone. In C major, the second note (D) will be 4 steps away. However, in A minor, where A is 6 steps below C, the fourth note (D) will be 9 steps above A, so 3 steps above C. So when switching from C major to A minor, one needs to slightly change the D note. These discrepancies arise because, unlike 12-ET, 22-ET does not temper out the syntonic comma of 81/80, but instead exaggerates its size by mapping it to one ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarter Tone Scale
A quarter tone is a pitch halfway between the usual notes of a chromatic scale or an interval about half as wide (orally, or logarithmically) as a semitone, which itself is half a whole tone. Quarter tones divide the octave by 50 cents each, and have 24 different pitches. Quarter tones have their roots in the music of the Middle East and more specifically in Persian traditional music. However, the first evidenced proposal of the equally-tempered quarter tone scale, or 24 equal temperament, was made by 19th-century music theorists Heinrich Richter in 1823Julian Rushton, "Quarter-Tone", ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', second edition, edited by Stanley Sadie and John Tyrrell (London: Macmillan, 2001). and Mikhail Mishaqa about 1840. Composers who have written music using this scale include: Pierre Boulez, Julián Carrillo, Mildred Couper, George Enescu, Alberto Ginastera, Gérard Grisey, Alois Hába, Ljubica Marić, Charles Ives, Tristan Murail, Krzysztof P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Tone System
The modern Arab tone system, or system of musical tuning, is based upon the theoretical division of the octave into twenty-four equal divisions or 24-tone equal temperament, the distance between each successive note being a quarter tone (50 cents). Each tone has its own name not repeated in different octaves, unlike systems featuring octave equivalency. The lowest tone is named ''yakah'' and is determined by the lowest pitch in the range of the singer. The next higher octave is ''nawa'' and the second ''tuti''. However, from these twenty-four tones, seven are selected to produce a scale and thus the interval of a quarter tone is never used and the three-quarter tone or neutral second should be considered the characteristic interval. By contrast, in the European equally tempered scale the octave is divided into twelve equal divisions, or exactly half as many as the Arab system. Thus, when Arabic music is written in European musical notation, a slashed or reversed flat sign is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Music
Arabic music () is the music of the Arab world with all its diverse List of music styles, music styles and genres. Arabic countries have many rich and varied styles of music and also many linguistic Varieties of Arabic, dialects, with each country and region having their own Folk music, traditional music. Arabic music has a long history of interaction with many other regional Music genre, musical styles and genres. It represents the music of all the Member states of the Arab League, peoples that make up the Arab world today. History Pre-Islamic period Pre-Islamic Arabia was the cradle of many intellectual achievements, including music, Music theory, musical theory and the development of musical instruments. In Yemen, the main center of pre-Islamic Arab sciences, literature and arts, musicians benefited from the patronage of the Kings of Sabaeans, Sabaʾ who encouraged the development of music. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cent (music)
The cent is a logarithmic unit of measure used for musical intervals. Twelve-tone equal temperament divides the octave into 12 semitones of 100 cents each. Typically, cents are used to express small intervals, to check intonation, or to compare the sizes of comparable intervals in different tuning systems. For humans, a single cent is too small to be perceived between successive notes. Cents, as described by Alexander John Ellis, follow a tradition of measuring intervals by logarithms that began with Juan Caramuel y Lobkowitz in the 17th century. Ellis chose to base his measures on the hundredth part of a semitone, \sqrt 200/math>, at Robert Holford Macdowell Bosanquet's suggestion. Making extensive measurements of musical instruments from around the world, Ellis used cents to report and compare the scales employed, and further described and utilized the system in his 1875 edition of Hermann von Helmholtz's ''On the Sensations of Tone''. It has become the standard me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or Musical tuning#Tuning systems, tuning system that approximates Just intonation, just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into steps such that the ratio of the frequency, frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same. This system yields Pitch (music), pitch steps perceived as equal in size, due to the logarithmic changes in pitch frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been 12 equal temperament (also known as ''12 tone equal temperament'', ' or ', informally abbreviated as ''12 equal''), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the twelfth root of two, 12th root of 2, (\sqrt[12] ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western world, Western countries the term ''equal temperamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleventh Harmonic
In music theory, the tritone is defined as a musical interval spanning three adjacent whole tones (six semitones). For instance, the interval from F up to the B above it (in short, F–B) is a tritone as it can be decomposed into the three adjacent whole tones F–G, G–A, and A–B. Narrowly defined, each of these whole tones must be a step in the scale, so by this definition, within a diatonic scale there is only one tritone for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned interval F–B is the only tritone formed from the notes of the C major scale. More broadly, a tritone is also commonly defined as any interval with a width of three whole tones (spanning six semitones in the chromatic scale), regardless of scale degrees. According to this definition, a diatonic scale contains two tritones for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned C major scale contains the tritones F–B (from F to the B above it, also called augmented fourth) and B–F (from B to the F above i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Series (music)
The harmonic series (also overtone series) is the sequence of harmonics, musical tones, or pure tones whose frequency is an integer multiple of a ''fundamental frequency''. Definite pitch, Pitched musical instruments are often based on an Acoustics, acoustic resonator such as a String (music), string or a column of air, which Oscillation, oscillates at numerous Normal mode, modes simultaneously. As waves travel in both directions along the string or air column, they reinforce and cancel one another to form standing waves. Interaction with the surrounding air produces audible sound waves, which travel away from the instrument. These frequencies are generally integer multiples, or harmonics, of the Fundamental frequency, fundamental and such multiples form the Harmonic series (mathematics), harmonic series. The fundamental, which is usually perceived as the lowest #Partial, partial present, is generally perceived as the Pitch (music), pitch of a musical tone. The musical timbre of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. The interval of time between events is called the period. It is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times per minute (2 hertz), its period is one half of a second. Special definitions of frequency are used in certain contexts, such as the angular frequency in rotational or cyclical properties, when the rate of angular progress is measured. Spatial frequency is defined for properties that vary or cccur repeatedly in geometry or space. The unit of measurement of frequency in the International System of Units (SI) is the hertz, having the symbol Hz. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |