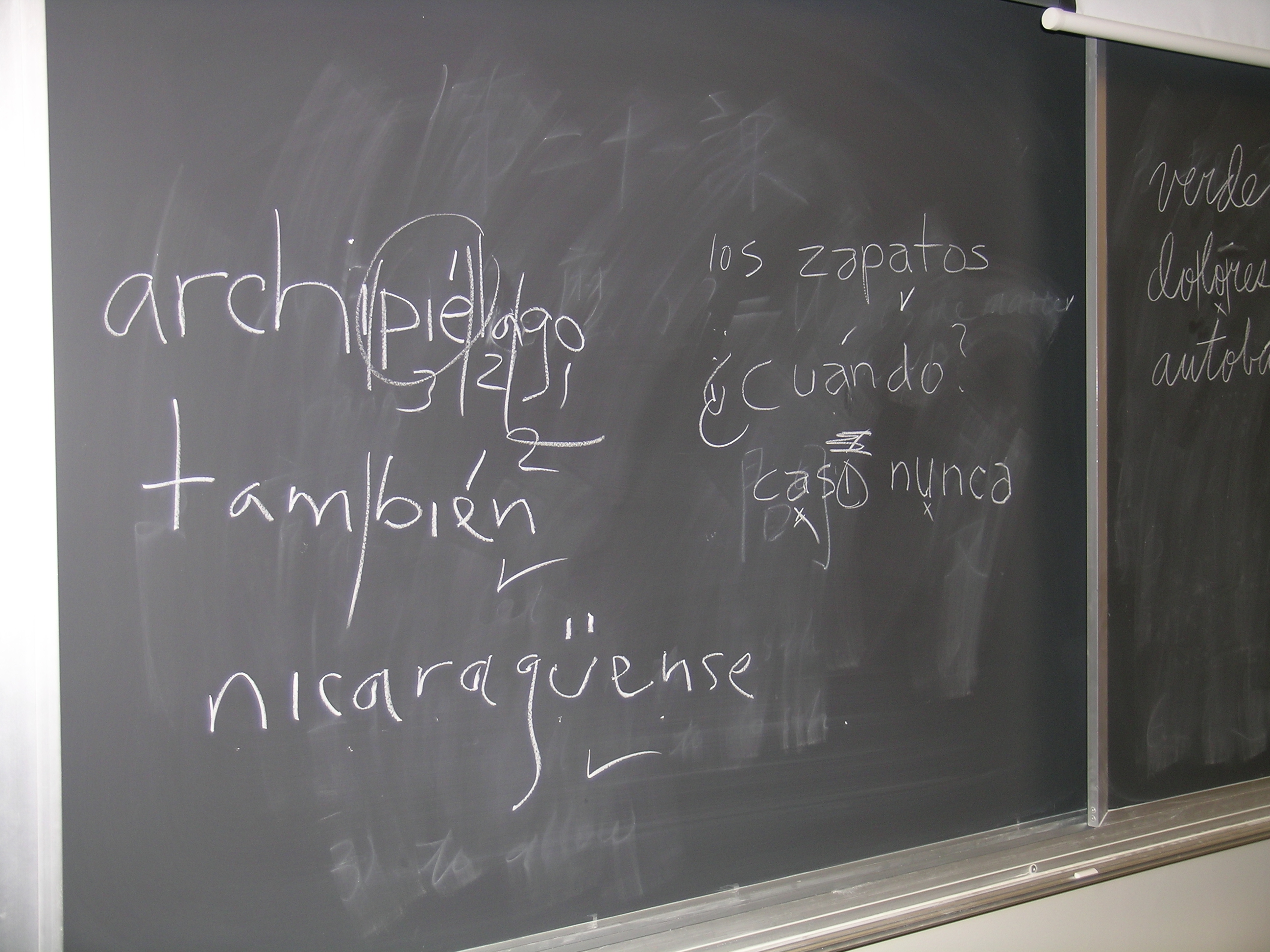|
Nasal Palatal Approximant
The nasal palatal approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some oral languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , that is, a j with a tilde. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is j~, and in the Americanist phonetic notation it is . The nasal palatal approximant is sometimes called a ''nasal yod''; and may be called nasal glides. Features Features of the nasal palatal approximant: * It is a nasal consonant In phonetics, a nasal, also called a nasal occlusive or nasal stop in contrast with an oral stop or nasalized consonant, is an occlusive consonant produced with a lowered velum, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. The vast majo ..., which means air is allowed to escape through the nose, in this case in addition to through the mouth. Occurrence , written , is a common realization of before nasal vowels in many languages of West Africa that do not have a phonemic distinction between voiced nasal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation for the sounds of speech. The IPA is used by linguists, lexicography, lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, speech–language pathology, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators. The IPA is designed to represent those qualities of speech that are part of lexical item, lexical (and, to a limited extent, prosodic) sounds in oral language: phone (phonetics), phones, Intonation (linguistics), intonation and the separation of syllables. To represent additional qualities of speechsuch as tooth wikt:gnash, gnashing, lisping, and sounds made with a cleft lip and cleft palate, cleft palatean extensions to the International Phonetic Alphabet, extended set of symbols may be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polish Language
Polish (, , or simply , ) is a West Slavic languages, West Slavic language of the Lechitic languages, Lechitic subgroup, within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is written in the Latin script. It is primarily spoken in Poland and serves as the official language of the country, as well as the language of the Polish diaspora around the world. In 2024, there were over 39.7 million Polish native speakers. It ranks as the sixth-most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional Dialects of Polish, dialects. It maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, Honorifics (linguistics), honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (, , , , , , , , ) to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet. The traditional set compri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Yakut Language
The Yakut language ( ), also known as the Sakha language ( ) or Yakutian, is a Siberian Turkic language spoken by around 450,000 native speakers—primarily by ethnic Yakuts. It is one of the official languages of the Sakha Republic, a republic in the Russian Federation. The Yakut language has a large number of loanwords of Mongolic origin, a layer of vocabulary of unclear origin, as well as numerous recent borrowings from Russian. Like other Turkic languages, Yakut is an agglutinative language and features vowel harmony. Classification Yakut is a member of the Northeastern Common Turkic family of languages, which also includes Shor, Tuvan and Dolgan. Like most Turkic languages, Yakut has vowel harmony, is agglutinative and has no grammatical gender. Word order is usually subject–object–verb. Yakut has been influenced by Tungusic and Mongolian languages. Historically, Yakut left the community of Common Turkic speakers relatively early. Due to this, it diverge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spanish Orthography
Spanish orthography is the orthography used in the Spanish language. The alphabet uses the Latin script. The spelling is fairly phonemic orthography, phonemic, especially in comparison to more opaque orthographies like English orthography, English, having a relatively consistent mapping of graphemes to phonemes; in other words, the pronunciation of a given Spanish-language word can largely be predicted from its spelling and to a slightly lesser extent vice versa. Spanish punctuation uniquely includes the use of inverted question and exclamation marks: . Spanish uses capital letters much less often than English; they are not used on adjectives derived from proper nouns (e.g. ''francés'', ''español'', ''portugués'' from ''Francia'', ''España'', and ''Portugal'', respectively) and book titles capitalize only the first word (e.g. ''The Revolt of the Masses, La rebelión de las masas''). Spanish uses only the acute accent over any vowel: . This accent is used to mark the tonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sabine River Spanish
Sabine River Spanish is a variety of the Spanish language spoken on both sides of the Sabine River between Texas and Louisiana. It has been spoken by a few communities descended from the 18th-century colonists who established Los Adaes and Nacogdoches. Due to its historical origins, it has a mostly conservative phonology with a vocabulary derived from rural Mexican Spanish. It is facing language death as it has not been passed onto children for several generations. Classification Sabine River Spanish was formed from rural Mexican Spanish, in spite of the common belief in Nacogdoches that the Spanish-speaking group around the Sabine River is of Isleño origin. The Sabine River Spanish-speaking communities have no terms to identify themselves as a group. , in reference to Los Adaes, has been used by Armistead and Dr. Comfort Pratt for the dialect spoken on the Louisiana side of the river. uses "Zwolle-Ebarb Spanish", from the names of two towns in Louisiana where it's sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spanish Language
Spanish () or Castilian () is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a world language, global language with 483 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain, and about 558 million speakers total, including second-language speakers. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries, as well as one of the Official languages of the United Nations, six official languages of the United Nations. Spanish is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Shipibo Language
Shipibo (also Shipibo-Conibo, Shipibo-Konibo) is a Panoan language spoken in Peru and Brazil by approximately 26,000 speakers. Shipibo is a recognized indigenous Languages of Peru, language of Peru. Dialects Shipibo has three attested dialects: * Shipibo and Konibo (Conibo), which have merged * Kapanawa of the Tapiche River, which is obsolescent Extinct Xipináwa (Shipinawa) is thought to have been a dialect as well, but there is no linguistic data. Phonology Vowels * and are lower than their cardinal counterparts (in addition to being more front in the latter case): , , is more front than cardinal : , whereas is more close and more central than cardinal . The first three vowels tend to be somewhat more central in closed syllables, whereas before coronal consonants (especially ) can be as central as . * In connected speech, two adjacent vowels may be realized as a rising diphthong. Nasal * The oral vowels are phonetically nasalized after a nasal consonant, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nasalization
In phonetics, nasalization (or nasalisation in British English) is the production of a sound while the velum is lowered, so that some air escapes through the nose during the production of the sound by the mouth. An archetypal nasal sound is . In the International Phonetic Alphabet, nasalization is indicated by printing a tilde diacritic above the symbol for the sound to be nasalized: is the nasalized equivalent of , and is the nasalized equivalent of . A subscript diacritic , called an or , is sometimes seen, especially when the vowel bears tone marks that would interfere with the superscript tilde. For example, are more legible in most fonts than . Nasal vowels Many languages have nasal vowels to different degrees, but only a minority of world languages around the world have nasal vowels as contrasting phonemes. That is the case, among others, of French, Portuguese, Hindustani, Nepali, Breton, Gheg Albanian, Hmong, Hokkien, Yoruba, and Cherokee. Those nasal vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nasal Vowel
A nasal vowel is a vowel that is produced with a lowering of the soft palate (or velum) so that the air flow escapes through the nose and the mouth simultaneously, as in the French vowel /ɑ̃/ () or Amoy []. By contrast, oral vowels are produced without nasalization. Nasalized vowels are vowels under the influence of neighbouring sounds. For instance, the [] of the word ''hand'' is affected by the following nasal consonant. In most languages, vowels adjacent to nasal consonants are produced partially or fully with a lowered velum in a natural process of assimilation and are therefore technically nasal, but few speakers would notice. That is the case in English: vowels preceding nasal consonants are nasalized, but there is no phonemic distinction between nasal and oral vowels, and all vowels are considered phonemically oral. Some languages contrast oral vowels and nasalized vowels phonemically. Linguists make use of minimal pairs to decide whether or not the nasality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Portuguese Phonology
The phonology of Portuguese varies among dialects, in extreme cases leading to some difficulties in mutual intelligibility. This article on phonology focuses on the pronunciations that are generally regarded as standard. Since Portuguese is a pluricentric language, and differences between European Portuguese (EP), Brazilian Portuguese (BP), and Angolan Portuguese (AP) can be considerable, varieties are distinguished whenever necessary. Consonants The consonant inventory of Portuguese is fairly conservative. The medieval Galician-Portuguese system of seven sibilants (, , , and apicoalveolar ) is still distinguished in spelling (intervocalic ''c/ç z, x g/j, ch, ss -s-'' respectively), but is reduced to the four fricatives by the merger of into and apicoalveolar into either or (depending on dialect and syllable position), except in parts of northern Portugal (most notably in the Trás-os-Montes region). These changes are known as deaffrication. Other than this, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Portuguese Alphabet
Portuguese orthography is based on the Latin alphabet and makes use of the acute accent, the circumflex accent, the grave accent, the tilde, and the cedilla to denote stress, vowel height, nasalization, and other sound changes. The diaeresis (diacritic), diaeresis was abolished by the last Portuguese Language Orthographic Agreement of 1990, Orthography Agreement. Accented letters and digraphs are not counted as separate characters for collation purposes. The spelling of Portuguese language, Portuguese is largely phonemic orthography, phonemic, but some phonemes can be spelled in more than one way. In ambiguous cases, the correct spelling is determined through a combination of etymology with morphology (linguistics), morphology and tradition; so there is not a perfect one-to-one correspondence between sounds and letters or digraphs. Knowing the main inflectional paradigms of Portuguese and being acquainted with the orthography of other Western European languages can be helpful. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brazilian Portuguese
Brazilian Portuguese (; ; also known as pt-BR) is the set of Variety (linguistics), varieties of Portuguese language native to Brazil. It is spoken by almost all of the 203 million inhabitants of Brazil and widely across the Brazilian diaspora, today consisting of about two million Brazilians who have emigrated to other countries. With a population of over 203 million, Brazil is by far the world's largest List of Portuguese speaking countries, Portuguese-speaking nation and the only one in the Americas where Portuguese, of which Brazilian Portuguese is a variety, is the official language under Article 13 of the Constitution. The Academia Brasileira de Letras (ABL) plays a significant cultural role in its development but has no legal regulatory authority over the language, which is shaped primarily by usage and educational norms in Brazil. Brazilian Portuguese differs notably from European Portuguese in phonetics, vocabulary, and grammar, though it remains a variety of Portuguese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |