|
Naphtha Launch
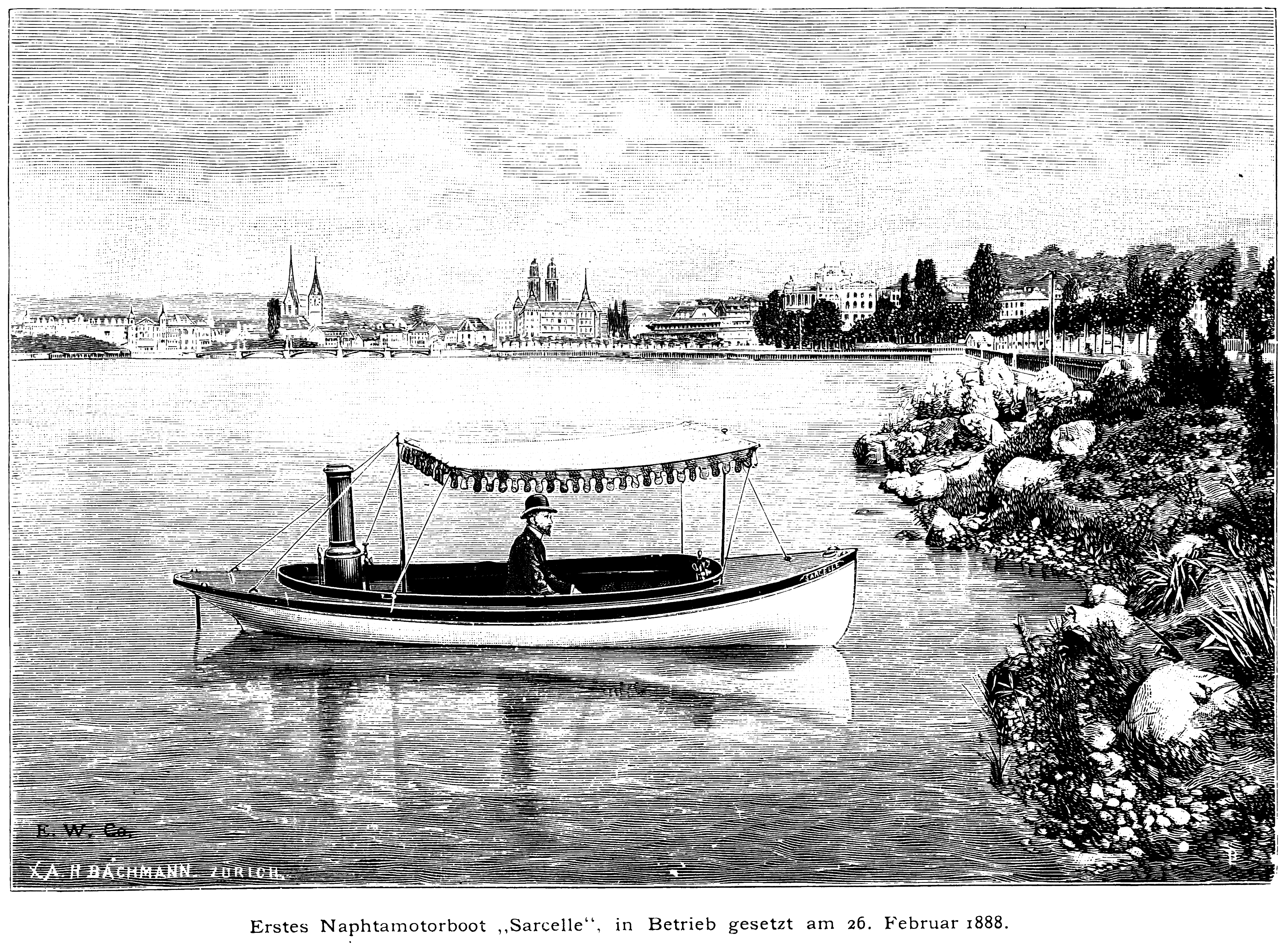
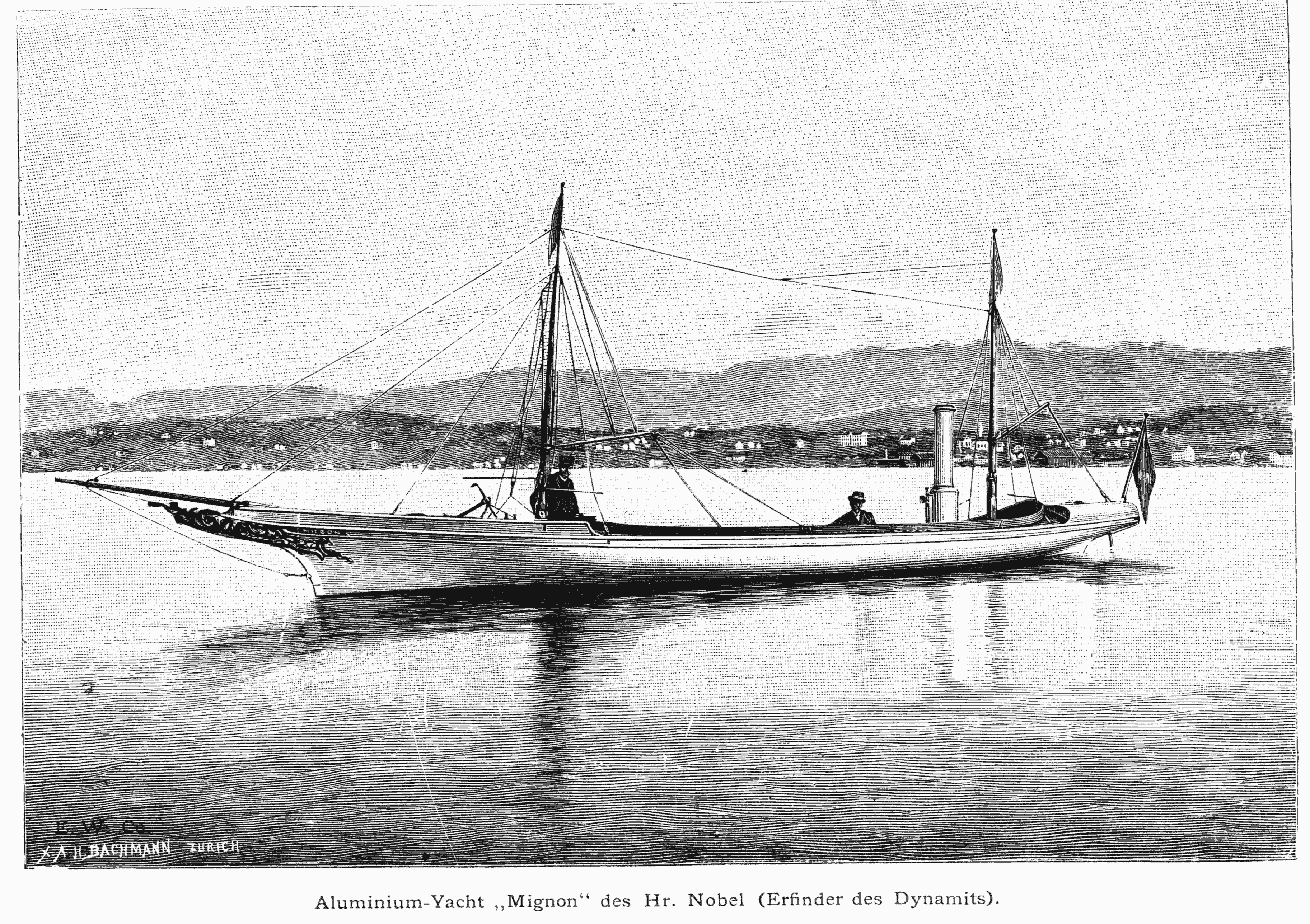
A naphtha launch, sometimes called a "vapor launch", was a small motor launch, powered by a naphtha engine. They were a particularly American design, brought into being by a local law that made it impractical to use a steam launch for private use. Naphtha launches By the 1880s, the small steam engine was well established as a power unit for small steam launches, as well as for large boats. However US law, prompted by some past boiler explosions, required that ''all'' steam boats carry a licensed engineer at all times. Although this was no difficulty for a commercial craft, it prevented small steam launches from being used for personal and recreational purposes. Becoming such an engineer required an apprenticeship of two years beforehand. One of the few amateurs to achieve this and to become their own engineer was Rosamund Burgess, wife of boat designer Starling Burgess. A more popular alternative to the steam launch was the naphtha launch, which used an alternative power s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Yacht Club
A yacht club is a boat club specifically related to yachting. Description Yacht clubs are mostly located by the sea, although there some that have been established at a lake or riverside locations. Yacht or sailing clubs have either a marina or a delimited section of the beach or shoreline with buoys marking the areas off-limits for swimmers as well as safe offshore anchorages. On shore they also include a perimeter reserved for the exclusive use of the members of the club as well as a clubhouse with attached bar, café or restaurant where members socialize in a pleasant and informal setting. Although the terms ''Yacht Club'' and ''Sailing Club'' tend to be synonymous, some general differences regarding the recreational use of boats can be broadly outlined. Historically a ''Yacht Club'' tended to focus on a membership composed of yacht owners, including motorboats. This type of club often was extremely exclusive, attracting the aristocracy or the high class and leavin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Steam Generator (boiler)
A steam generator is a form of low water-content boiler (steam generator), boiler, similar to a flash steam boiler. The usual construction is as a spiral coil of water-tube boiler, water-tube, arranged as a single, or monotube boiler, monotube, coil. Circulation is once-through and pumped under pressure, as a forced-circulation boiler. The narrow-tube construction, without any large-diameter drums or tanks, means that they are safe from the effects of boiler explosion, explosion,This safety from explosion is due to two causes. Firstly, small diameter tubes are inherently stronger than large tubes of the same construction, as was first appreciated by William Fairbairn in the mid-19th century. Secondly, the low water-content means that there is relatively little volume of water per area of heating surface (i.e. boiler power). As the destructive energy of a boiler explosion is largely due to the sudden release of this energy, and proportional to water volume, a low water-content boile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Water-tube Boiler
A high pressure watertube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. In smaller boilers, additional generating tubes are separate in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on the water-filled tubes that make up the walls of the furnace to generate steam. The heated water/steam mixture then rises into the steam drum. Here, saturated steam is drawn off the top of the drum. In some services, the steam passes through tubes in the hot gas path, (a superheater) to become superheated. Superheated steam is a dry gas and therefore is typically used to drive turbines, since water droplets can severely damage turbine blades. Saturated water at the bottom of the steam drum returns to the lower drum via large-bore 'downcomer tubes', where it pre-heats the feedwater supply. (In large utility boilers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monotube Boiler
A monotube steam generator is a type of steam generator consisting of a single tube, usually in a multi-layer spiral, that forms a once-through steam generator (OTSG). The first of these was the Herreshoff steam generator of 1873. Principles For the sake of efficiency, it is desirable to minimise the steam content of the generator. Heat can then be transferred efficiently into liquid water, rather than into low-density steam. Monotube steam generators may either boil gradually along their length, usually pumped circulation systems, but where this boiling does not disrupt the circulation. Otherwise they can use the Benson supercritical system, where the pressure is sufficient to prevent boiling (within the heated volume) altogether. Examples Examples of Monotube steam generators include: * Industrial steam generators * The water-tube boilers of the monotube type used in steam cars, such as: ** AMC ** Clayton Steam Generator ** Doble steam car ** Gardner-Serpollet ** Locomob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Simple Expansion Steam Engine
A compound engine is an engine that has more than one stage for recovering energy from the same working fluid, with the exhaust from the first stage passing through the second stage, and in some cases then on to another subsequent stage or even stages. Originally invented as a means of making steam engines more efficient, the compounding of engines by use of several stages has also been used on internal combustion engines and continues to have niche markets there. The stages of a compound engine may be either of differing or of similar technologies, for example: * In a turbo-compound engine, the exhaust gas from the cylinders passes through a turbine, the two stages being dissimilar. * In a compound steam locomotive, the steam passes from the high-pressure cylinder or cylinders to the low-pressure cylinder or cylinders, the two stages being similar. * In a triple-expansion steam engine, the steam passes through three successive cylinders of increasing size and decreasing press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Steam Car
A steam car is a car (automobile) propelled by a steam engine. A steam engine is an external combustion engine (ECE), whereas the gasoline and diesel engines that eventually became standard are internal combustion engines (ICE). ECEs have a lower thermal efficiency, but carbon monoxide production is more readily regulated. The first experimental steam-powered cars were built in the 18th and 19th centuries, but it was not until after Richard Trevithick had developed the use of high-pressure steam around 1800 that mobile steam engines became a practical proposition. By the 1850s there was a flurry of new steam car manufacturers. Development was hampered by adverse legislation (the UK Locomotive Acts from the 1860s) as well as the rapid development of internal combustion engine technology in the 1900s, leading to the commercial demise of steam-powered vehicles. Relatively few remained in use after the Second World War. Many of these vehicles were acquired by enthusiasts for preser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Naphtha
Naphtha (, recorded as less common or nonstandard in all dictionaries: ) is a flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture. Generally, it is a fraction of crude oil, but it can also be produced from natural-gas condensates, petroleum distillates, and the fractional distillation of coal tar and peat. In some industries and regions, the name ''naphtha'' refers to crude oil or refined petroleum products such as kerosene or diesel fuel. Naphtha is also known as Shellite in Australia. Etymology The word ''naphtha'' comes from Latin through Ancient Greek (), derived from Middle Persian ''naft'' ("wet", "naphtha"), the latter meaning of which was an assimilation from the Akkadian 𒉌𒆳𒊏 (see Semitic relatives such as Arabic petroleum" Syriac ''naftā'', and Hebrew , meaning petroleum). Antiquity The book of II Maccabees (2nd cent. BC) tells how a "thick water" was put on a sacrifice at the time of Nehemiah and when the sun shone it caught fire. It adds that "those aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Working Fluid
For fluid power, a working fluid is a gas or liquid that primarily transfers force, motion, or mechanical energy. In hydraulics, water or hydraulic fluid transfers force between hydraulic components such as hydraulic pumps, hydraulic cylinders, and hydraulic motors that are assembled into hydraulic machinery, hydraulic drive systems, etc. In pneumatics, the working fluid is air or another gas which transfers force between pneumatic components such as compressors, vacuum pumps, pneumatic cylinders, and pneumatic motors. In pneumatic systems, the working gas also energy storage, stores energy because it is compressible. (Gases also heat up as they are compressed and cool as they expand. Some gases also condense into liquids as they are compressed and boil as pressure is reduced.) For passive heat transfer, a working fluid is a gas or liquid, usually called a coolant or heat transfer fluid, that primarily transfers heat into or out of a region of interest by conduction (heat), conduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Steam Engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed by a connecting rod and Crank (mechanism), crank into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is most commonly applied to reciprocating engines as just described, although some authorities have also referred to the steam turbine and devices such as Hero's aeolipile as "steam engines". The essential feature of steam engines is that they are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term ''steam engine'' can refer to either complete steam plants (including Boiler (power generation), boilers etc.), such as railway steam locomot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
External Combustion Engine
An external combustion engine (EC engine) is a Reciprocating engine, reciprocating heat engine where a working fluid, contained internally, is heated by combustion in an external source, through the engine wall or a heat exchanger. The fluid then, by expanding and acting on the mechanism (engineering), mechanism of the engine, produces motion and usable Mechanical work, work. The fluid is then dumped (open cycle), or cooled, compressed and reused (closed cycle). In these types of engines, the combustion is primarily used as a heat source, and the engine can work equally well with other types of heat sources. Combustion "Combustion" refers to burning fuel with an oxidizer, to supply the heat. Engines of similar (or even identical) configuration and operation may use a supply of heat from other sources such as nuclear, solar, geothermal or exothermic reactions not involving combustion; they are not then strictly classed as external combustion engines, but as external thermal eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Naptha Engine
A naphtha launch, sometimes called a "vapor launch", was a small motor Launch (boat), launch, powered by a #Naphtha engine, naphtha engine. They were a particularly American design, brought into being by a local law that made it impractical to use a steam launch for private use. Naphtha launches By the 1880s, the small marine steam engine, steam engine was well established as a power unit for small steam launches, as well as for large boats. However US law, prompted by some past boiler explosions, required that ''all'' steam boats carry a licensed engineer at all times. Although this was no difficulty for a commercial craft, it prevented small steam launches from being used for personal and recreational purposes. Becoming such an engineer required an apprenticeship of two years beforehand. One of the few amateurs to achieve this and to become their own engineer was Rosamund Burgess, wife of boat designer Starling Burgess. A more popular alternative to the steam launch was the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |