|
Monobactam
Monobactams are bacterially-produced monocyclic β-lactam antibiotics. The β-lactam ring is not fused to another ring, in contrast to most other β-lactams. Monobactams are narrow-spectrum antibiotics effective only against (strictly or facultatively) aerobic Gram-negative bacilli, exhibiting a high level of resistance to beta-lactamases of these organisms. Due to their narrow spectrum, monobactams can be used to treat infections by susceptible bacteria without disrupting the patient's microbiota. Monobactams are nevertheless seldom used. Aztreonam is the archetypal monobactam. Other monobactams include tigemonam, nocardicin A, carumonam and tabtoxin. An example of a monobactam that lacks antibiotic activity, but is used clinically for other purposes, is the cholesterol absorption inhibitor ezetimibe which is used to treat hypercholesterolemia. Pharmacology Monobactams exert their antibacterial effects by binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), thereby inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems ( ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties. Beta-lactamases produced by gram-negative bacteria are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment. Structure The structure of a '' Streptomyces'' serine β-lactamase (SBLs) is given by . The alpha-beta fold () resembles that of a DD-transpeptidase, from which the enzyme is thought to have evolved. β-lactam antibio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigemonam
Tigemonam is a monobactam antibiotic An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy .... References Monobactam antibiotics Thiazoles Sulfonic acids {{antibiotic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carumonam
Carumonam (INN) is a monobactam antibiotic. It is very resistant to beta-lactamase Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems ( ertapenem), although carbapene ...s, which means that it is more difficult for bacteria to break down using β-lactamase enzymes. References Monobactam antibiotics Thiazoles Carbamates Sulfamates {{antibiotic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan gram-negative cell wall, cell wall sandwiched between an inner (Cytoplasm, cytoplasmic) Cell membrane, membrane and an Bacterial outer membrane, outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth. Within this category, notable species include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', along with various pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They pose significant challenges in the medical field due to their outer membrane, which acts as a protective barrier against numerous Antibiotic, antibiotics (including penicillin), Detergent, detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztreonam
Aztreonam, sold under the brand name Azactam among others, is an antibiotic used primarily to treat infections caused by gram-negative bacteria such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''. This may include bone infections, endometritis, intra abdominal infections, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis. It is given by intravenous or intramuscular injection or by inhalation. Common side effects when given by injection include pain at the site of injection, vomiting, and rash. Common side effects when inhaled include wheezing, cough, and vomiting. Serious side effects include ''Clostridioides difficile'' infection and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. Those who are allergic to other β-lactam have a low rate of allergy to aztreonam. Use in pregnancy appears to be safe. It is in the monobactam family of medications. Aztreonam inhibits cell wall synthesis by blocking peptidoglycan crosslinking to cause bacterial death. Aztreonam was approved for medical use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceftazidime
Ceftazidime, sold under the brand name Fortaz among others, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. Specifically it is used for joint infections, meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, urinary tract infections, malignant otitis externa, ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' infection, and vibrio infection. It is given by injection into a vein, muscle, or eye. Common side effects include nausea, allergic reactions, and pain at the site of injection. Other side effects may include ''Clostridioides difficile'' diarrhea. It is not recommended in people who have had previous anaphylaxis to a penicillin. Its use is relatively safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is in the third-generation cephalosporin family of medications and works by interfering with the bacteria's cell wall. Ceftazidime was patented in 1978 and came into commercial use in 1984. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabtoxin
Tabtoxin, also known as wildfire toxin, is a simple monobactam phytotoxin produced by ''Pseudomonas syringae''. It is the precursor to the antibiotic tabtoxinine β-lactam (TBL). It is produced by: * Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci, the causal agent of the wildfire of tobacco. * P. syringae pv. coronafaciens * P. syringae pv. garcae * P. syringae BR2, causes a disease of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) similar to tobacco wildfire. This organism is closely related to P. syringae pv. tabaci but cannot be classified in the pathovar tabaci because it is not pathogenic on tobacco. Tabtoxin is a dipeptide precursor to the biologically active form of TBL, differing by having an extra threonine attached by a peptide bond to the C terminus. Tabtoxin is required by BR2(R) for both chlorosis and lesion formation on bean. All mutations that affected tabtoxin production, whether spontaneous deletion or transposon induced, also affected lesion formation, and in all cases, restoration of tabtoxin prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
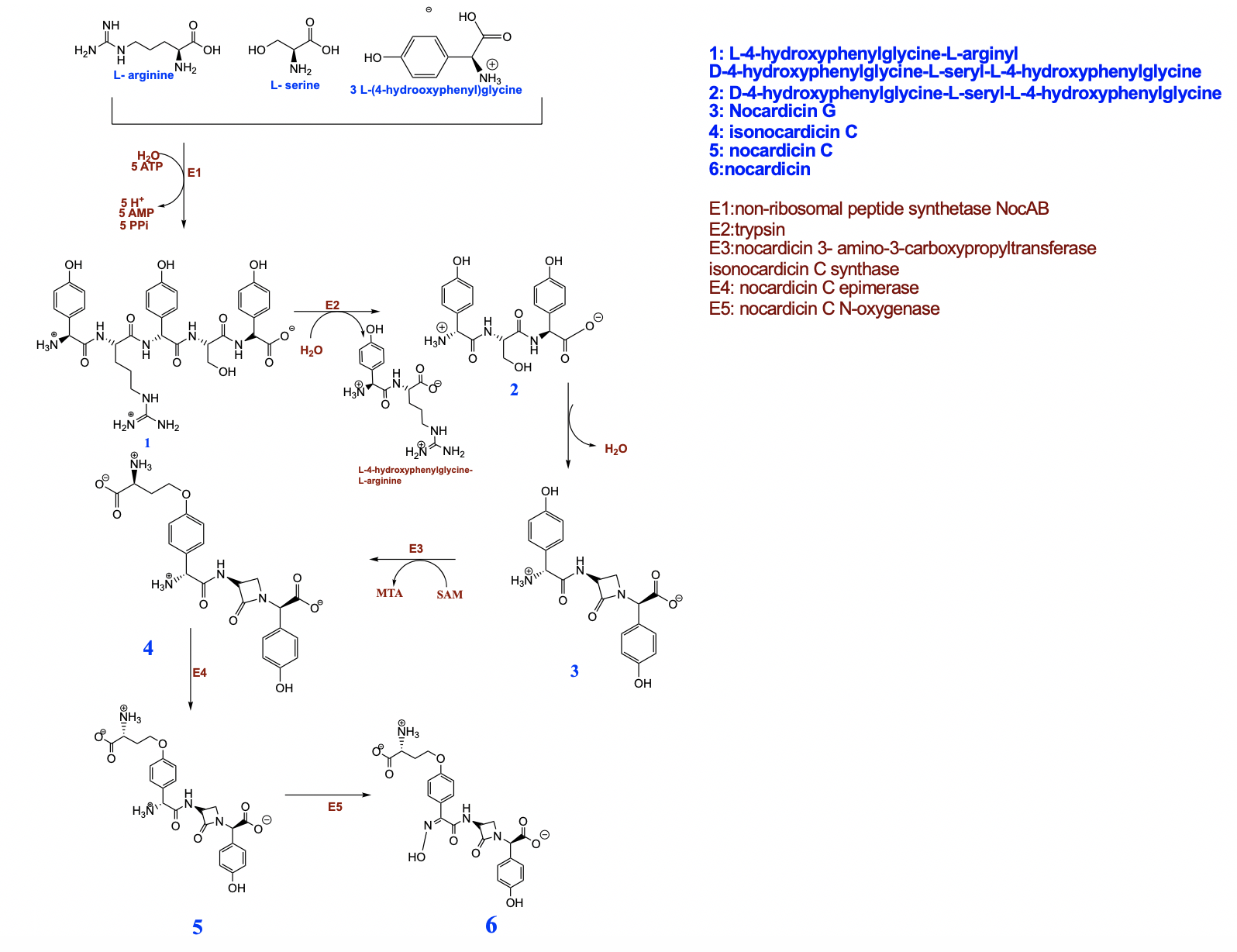
Nocardicin A
Nocardicin A is a monocyclic β-lactam antibiotic included in the monobactam subclass. It is obtained from the fermentation broth of a strain of actinomycetes ''Nocardia uniformis'' subsp. ''tsuyamenensis'' as a metabolic product catalyzed by the enzyme nocardicin-A epimerase. It is stereochemically and biologically related to penicillin and cephalosporins The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus ''Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''. Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotic .... References {{CephalosporinAntiBiotics Monobactam antibiotics Alpha-Amino acids Amino acid derivatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacilli
Bacilli is a Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic Class (biology), class of bacteria that includes two orders, Bacillales and Lactobacillales, which contain several well-known pathogens such as ''Bacillus anthracis'' (the cause of anthrax). ''Bacilli'' are almost exclusively gram-positive bacteria. The name ''Bacillus'', capitalized and Italics, italicized, refers to a specific genus of bacteria. The name Bacilli, capitalized but not italicized, can also refer to a less specific taxonomic group of bacteria that includes two orders, one of which contains the genus ''Bacillus''. When the word is formatted with lowercase and not italicized, 'bacillus', it will most likely be referring to shape and not to the genus at all. Ambiguity Several related concepts make use of similar words, and the ambiguity can create considerable confusion. The term "''Bacillus''" (capitalized and italicized) is also the name of a genus (''Bacillus anthracis'') that, among many other genera, falls within the cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
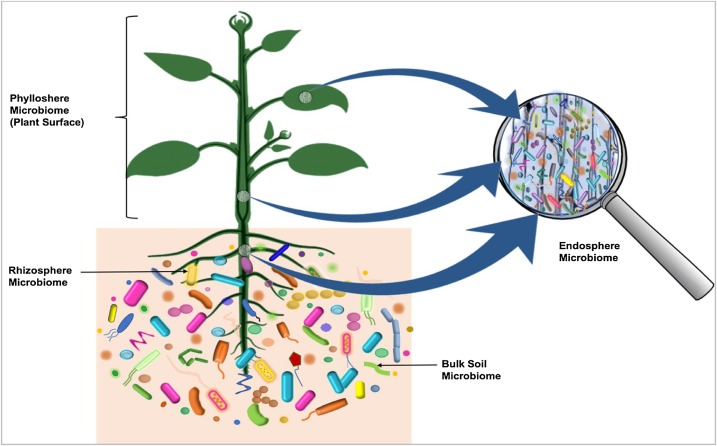
Microbiota
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, mutualistic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. The term ''microbiome'' describes either the collective genomes of the microbes that reside in an ecological niche or else the microbes themselves. The microbiome and host emerged during evolution as a synergistic unit from epigenetics and genetic characteristics, sometimes collectively referred to as a holobiont. The presence of microbiota in human and other metazoan guts has been critical for understanding the co-evolution between metazoans and bacteria. Microbiota play key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses via their fermentation product ( short-chain fatty acid), acetate. Introduction All plants and animals, from simple life fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrow-spectrum Antibiotic
A narrow-spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that is only able to kill or inhibit limited species of bacteria. Examples of narrow-spectrum antibiotics include fidaxomicin and sarecycline Sarecycline, sold under the brand name Seysara, is a narrow-spectrum tetracycline-derived antibiotic medication. It is specifically designed for the treatment of acne, and was approved by the FDA in October 2018 for the treatment of inflammat .... Advantages * Narrow-spectrum antibiotic allow to kill or inhibit only those bacteria species that are unwanted (i.e. causing disease). As such, it leaves most of the beneficial bacteria unaffected, hence minimizing the collateral damage on the microbiota. * Low propensity for bacterial resistance development. Disadvantages Often, the exact species of bacteria causing the illness is unknown, in which case narrow-spectrum antibiotics can't be used, and broad-spectrum antibiotics are used instead. To know the exact species of bacteria causing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |